Science
5 things scientists learned in 2020 from research conducted in space – CTV News

TORONTO —
With dozens of experiments being conducted at any given time on the International Space Station (ISS), much was learned high above a planet in the grips of a pandemic.
NASA reports that between Oct. 1, 2019 and Oct. 1, 2020, research performed on the ISS appeared in more than 300 scientific publications.
Here are some of the results of research conducted by astronauts and published in 2020.
Canadian contributions to anemia research
The Canadian Space Agency’s research on the ISS studied the effects of space anemia, a condition astronauts often develop, on the human body.
Called the MARROW investigation, researchers looked at microgravity and its effects on bone marrow. Research shows that microgravity has similar effects on the body as long-term bed rest on Earth, with nearly half of astronauts (48 per cent) developing anemia after long-duration missions.
Blood-producing cells and fat cells share space within the bone marrow. When fat cells grow, it reduces the amount of space left for blood-producing cells, a process seen in both astronauts and bed-ridden patients.
The study suggests recovery can take between one and three months depending on the length of the space mission.
A better understanding of the effects of microgravity and space travel on the body is needed, researchers write, for “space travel to other planets, space tourism and for the care of bedridden patients who present similar changes as astronauts.”
Possible treatment for bone density problems
An Italian Space Agency study found that a specific kind of nanoparticle could be used as a countermeasure to the osteoporosis problems astronauts often face after prolonged periods in space.
Five years after Italian scientists sent the experiment to an all-woman team to perform, their results have been published in the research journal Scientific Reports.
The study suggests that nanoparticles made of similar minerals to those found in bones and teeth can promote stem cells to become osteoblasts, or cells that form new bone.
According to the Canadian Space Agency, because of the microgravity environment of space, astronauts lose on average 1 to 2 per cent of their bone mineral density each month, making this research promising for preventing bone health problems in astronauts on longer space missions, as well as for use in osteoporosis treatments here on Earth.
Joystick feedback works in video games and space
Video game enthusiasts may be familiar with the sensation of force feedback on joysticks, but a new study shows that similar haptic technology is beneficial in space.
For the uninitiated, some joysticks and other video game devices vibrate or jolt when certain actions are performed, and the feedback brings in yet another one of the five senses into the gameplay.
Researchers on the ISS tested similar force feedback on the mechanisms that astronauts use to control teleoperated robots. Because research shows that microgravity has an effect on motion control after six weeks, haptic feedback can be helpful for those on teleoperated missions to feel more in tune with the robot or rover they are trying to operate.
Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s research may be easier in microgravity
Amyloid beta fibrils, protein aggregations found in the brains of people with some neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, were studied under conditions on Earth and in space by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency.
The fibrils grown on Earth and in space were “practically indistinguishable” from each other, but the fibrils in space grew much slower, making them much easier to use for detailed investigations.
This development could aid in future studies of treatments for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
How microbes spread, even in space
While not all microbes are bad – some are even beneficial for human health – it is important to keep track of how they spread.
Bacteria and fungi from Earth hitchhike to the ISS on the astronauts headed there, and results published from the NASA Microbial Tracking-2 study found that microbes are even left behind in the fingerprints found around the station.
Not only that, but the microorganisms living in the fingerprints on the station’s surfaces could be traced back to an individual astronaut’s skin and used to determine when they arrived.
This research can not only be used to protect the health of astronauts as they work and live in an enclosed space, but also to help workers at hospital and other health-care settings here on Earth understand the presence of microbes in their environments.
Science
"Hi, It's Me": NASA's Voyager 1 Phones Home From 15 Billion Miles Away – NDTV


<!–
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 was mankind’s first spacecraft to enter the interstellar medium
Washington, United States:
NASA’s Voyager 1 probe — the most distant man-made object in the universe — is returning usable information to ground control following months of spouting gibberish, the US space agency announced Monday.
The spaceship stopped sending readable data back to Earth on November 14, 2023, even though controllers could tell it was still receiving their commands.
In March, teams working at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory discovered that a single malfunctioning chip was to blame, and devised a clever coding fix that worked within the tight memory constraints of its 46-year-old computer system.
window._rrCode = window._rrCode || [];_rrCode.push(function() (function(v,d,o,ai)ai=d.createElement(“script”);ai.defer=true;ai.async=true;ai.src=v.location.protocol+o;d.head.appendChild(ai);)(window, document, “//a.vdo.ai/core/v-ndtv/vdo.ai.js”); );
“Voyager 1 spacecraft is returning usable data about the health and status of its onboard engineering systems,” the agency said.
Hi, it’s me. – V1 https://t.co/jgGFBfxIOe
— NASA Voyager (@NASAVoyager) April 22, 2024
“The next step is to enable the spacecraft to begin returning science data again.”
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 was mankind’s first spacecraft to enter the interstellar medium, in 2012, and is currently more than 15 billion miles from Earth. Messages sent from Earth take about 22.5 hours to reach the spacecraft.
Its twin, Voyager 2, also left the solar system in 2018.
Both Voyager spacecraft carry “Golden Records” — 12-inch, gold-plated copper disks intended to convey the story of our world to extraterrestrials.
These include a map of our solar system, a piece of uranium that serves as a radioactive clock allowing recipients to date the spaceship’s launch, and symbolic instructions that convey how to play the record.
The contents of the record, selected for NASA by a committee chaired by legendary astronomer Carl Sagan, include encoded images of life on Earth, as well as music and sounds that can be played using an included stylus.
window._rrCode = window._rrCode || [];_rrCode.push(function(){ (function(d,t) var s=d.createElement(t); var s1=d.createElement(t); if (d.getElementById(‘jsw-init’)) return; s.setAttribute(‘id’,’jsw-init’); s.setAttribute(‘src’,’https://www.jiosaavn.com/embed/_s/embed.js?ver=’+Date.now()); s.onload=function()document.getElementById(‘jads’).style.display=’block’;s1.appendChild(d.createTextNode(‘JioSaavnEmbedWidget.init(a:”1″, q:”1″, embed_src:”https://www.jiosaavn.com/embed/playlist/85481065″,”dfp_medium” : “1”,partner_id: “ndtv”);’));d.body.appendChild(s1);; if (document.readyState === ‘complete’) d.body.appendChild(s); else if (document.readyState === ‘loading’) var interval = setInterval(function() if(document.readyState === ‘complete’) d.body.appendChild(s); clearInterval(interval); , 100); else window.onload = function() d.body.appendChild(s); ; )(document,’script’); });
Their power banks are expected to be depleted sometime after 2025. They will then continue to wander the Milky Way, potentially for eternity, in silence.
(Except for the headline, this story has not been edited by NDTV staff and is published from a syndicated feed.)
Science
West Antarctica's ice sheet was smaller thousands of years ago – here's why this matters today – The Conversation
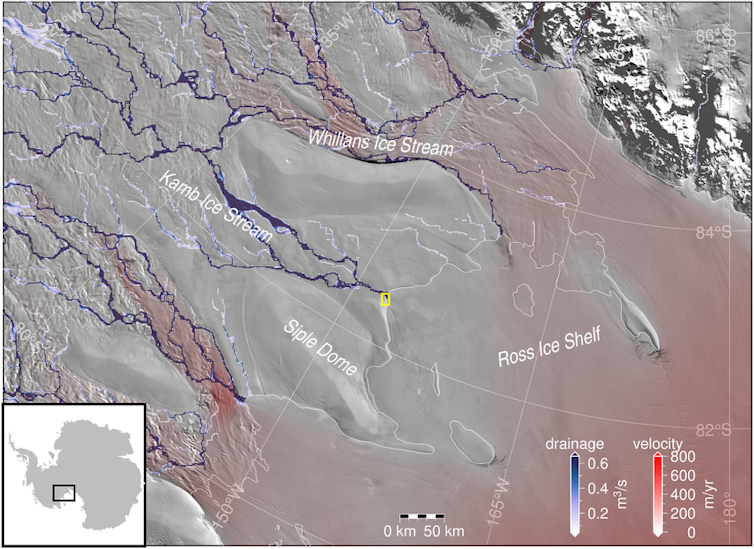

As the climate warms and Antarctica’s glaciers and ice sheets melt, the resulting rise in sea level has the potential to displace hundreds of millions of people around the world by the end of this century.
A key uncertainty in how much and how fast the seas will rise lies in whether currently “stable” parts of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet can become “unstable”.
One such region is West Antarctica’s Siple Coast, where rivers of ice flow off the continent and drain into the ocean.
Journal of Geophysical Research, CC BY-SA
This ice flow is slowed down by the Ross Ice Shelf, a floating mass of ice nearly the size of Spain, which holds back the land-based ice. Compared to other ice shelves in West Antarctica, the Ross Ice Shelf has little melting at its base because the ocean below it is very cold.
Although this region has been stable during the past few decades, recent research suggest this was not always the case. Radiocarbon dating of sediments from beneath the ice sheet tells us that it retreated hundreds of kilometres some 7,000 years ago, and then advanced again to its present position within the last 2,000 years.
Figuring out why this happened can help us better predict how the ice sheet will change in the future. In our new research, we test two main hypotheses.
Read more:
What an ocean hidden under Antarctic ice reveals about our planet’s future climate
Testing scenarios
Scientists have considered two possible explanations for this past ice sheet retreat and advance. The first is related to Earth’s crust below the ice sheet.
As an ice sheet shrinks, the change in ice mass causes the Earth’s crust to slowly uplift in response. At the same time, and counterintuitively, the sea level drops near the ice because of a weakening of the gravitational attraction between the ice sheet and the ocean water.
As the ice sheet thinned and retreated since the last ice age, crustal uplift and the fall in sea level in the region may have re-grounded floating ice, causing ice sheet advance.
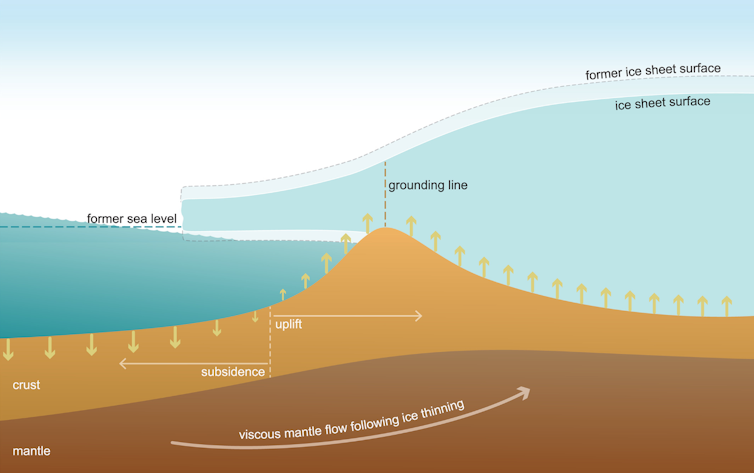
AGU, CC BY-SA
The other hypothesis is that the ice sheet behaviour may be due to changes in the ocean. When the surface of the ocean freezes, forming sea ice, it expels salt into the water layers below. This cold briny water is heavier and mixes deep into the ocean, including under the Ross Ice Shelf. This blocks warm ocean currents from melting the ice.
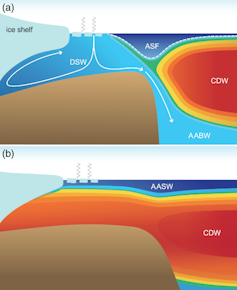
AGU, CC BY-SA
Seafloor sediments and ice cores tell us that this deep mixing was weaker in the past when the ice sheet was retreating. This means that warm ocean currents may have flowed underneath the ice shelf and melted the ice. Mixing increased when the ice sheet was advancing.
We test these two ideas with computer model simulations of ice sheet flow and Earth’s crustal and sea surface responses to changes in the ice sheet with varying ocean temperature.
Because the rate of crustal uplift depends on the viscosity (stickiness) of the underlying mantle, we ran simulations within ranges estimated for West Antarctica. A stickier mantle means slower crustal uplift as the ice sheet thins.
The simulations that best matched geological records had a stickier mantle and a warmer ocean as the ice sheet retreated. In these simulations, the ice sheet retreats more quickly as the ocean warms.
When the ocean cools, the simulated ice sheet readvances to its present-day position. This means that changes in ocean temperature best explain the past ice sheet behaviour, but the rate of crustal uplift also affects how sensitive the ice sheet is to the ocean.

Veronika Meduna, CC BY-SA
What this means for climate policy today
Much attention has been paid to recent studies that show glacial melting may be irreversible in some parts of West Antarctica, such as the Amundsen Sea embayment.
In the context of such studies, policy debates hinge on whether we should focus on adapting to rising seas rather than cutting greenhouse gas emissions. If the ice sheet is already melting, are we too late for mitigation?
Our study suggests it is premature to give up on mitigation.
Global climate models run under high-emissions scenarios show less sea ice formation and deep ocean mixing. This could lead to the same cold-to-warm ocean switch that caused extensive ice sheet retreat thousands of years ago.
For West Antarctica’s Siple Coast, it is better if we prevent this ocean warming from occurring in the first place, which is still possible if we choose a low-emissions future.
Science
NASA's Voyager 1 resumes sending engineering updates to Earth – Phys.org


For the first time since November, NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft is returning usable data about the health and status of its onboard engineering systems. The next step is to enable the spacecraft to begin returning science data again. The probe and its twin, Voyager 2, are the only spacecraft to ever fly in interstellar space (the space between stars).
Voyager 1 stopped sending readable science and engineering data back to Earth on Nov. 14, 2023, even though mission controllers could tell the spacecraft was still receiving their commands and otherwise operating normally. In March, the Voyager engineering team at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California confirmed that the issue was tied to one of the spacecraft’s three onboard computers, called the flight data subsystem (FDS). The FDS is responsible for packaging the science and engineering data before it’s sent to Earth.
The team discovered that a single chip responsible for storing a portion of the FDS memory—including some of the FDS computer’s software code—isn’t working. The loss of that code rendered the science and engineering data unusable. Unable to repair the chip, the team decided to place the affected code elsewhere in the FDS memory. But no single location is large enough to hold the section of code in its entirety.
So they devised a plan to divide affected the code into sections and store those sections in different places in the FDS. To make this plan work, they also needed to adjust those code sections to ensure, for example, that they all still function as a whole. Any references to the location of that code in other parts of the FDS memory needed to be updated as well.


The team started by singling out the code responsible for packaging the spacecraft’s engineering data. They sent it to its new location in the FDS memory on April 18. A radio signal takes about 22.5 hours to reach Voyager 1, which is over 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, and another 22.5 hours for a signal to come back to Earth. When the mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on April 20, they saw that the modification had worked: For the first time in five months, they have been able to check the health and status of the spacecraft.
During the coming weeks, the team will relocate and adjust the other affected portions of the FDS software. These include the portions that will start returning science data.
Voyager 2 continues to operate normally. Launched over 46 years ago, the twin Voyager spacecraft are the longest-running and most distant spacecraft in history. Before the start of their interstellar exploration, both probes flew by Saturn and Jupiter, and Voyager 2 flew by Uranus and Neptune.
Provided by
NASA
Citation:
NASA’s Voyager 1 resumes sending engineering updates to Earth (2024, April 22)
retrieved 22 April 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-04-nasa-voyager-resumes-earth.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
-
Business19 hours ago
Honda to build electric vehicles and battery plant in Ontario, sources say – Global News
-



 Science20 hours ago
Science20 hours agoWill We Know if TRAPPIST-1e has Life? – Universe Today
-
Investment23 hours ago
Down 80%, Is Carnival Stock a Once-in-a-Generation Investment Opportunity?
-



 Health16 hours ago
Health16 hours agoSee how chicken farmers are trying to stop the spread of bird flu – Fox 46 Charlotte
-



 Health19 hours ago
Health19 hours agoSimcoe-Muskoka health unit urges residents to get immunized
-



 Investment18 hours ago
Investment18 hours agoOwn a cottage or investment property? Here's how to navigate the new capital gains tax changes – The Globe and Mail
-
News23 hours ago
Can Canada have an effective climate action policy without a carbon tax?
-



 Tech23 hours ago
Tech23 hours agoIndigenous Craft and Vendors Market a success in Halifax







