Health
A look at COVID-19 vaccinations in Canada on Saturday, March 27th, 2021 – Thompson Citizen


A look at COVID-19 vaccinations in Canada.
The latest numbers on COVID-19 vaccinations in Canada as of 4:00 a.m. ET on Saturday, March 27, 2021.
Trending Stories
In Canada, the provinces are reporting 217,025 new vaccinations administered for a total of 4,800,753 doses given. Nationwide, 657,212 people or 1.7 per cent of the population has been fully vaccinated. The provinces have administered doses at a rate of 12,667.136 per 100,000.
There were 25,400 new vaccines delivered to the provinces and territories for a total of 6,199,808 doses delivered so far. The provinces and territories have used 77.43 per cent of their available vaccine supply.
Please note that Newfoundland, P.E.I., Nova Scotia, New Brunswick and the territories typically do not report on a daily basis.
Newfoundland is reporting 9,178 new vaccinations administered over the past seven days for a total of 55,231 doses given. The province has administered doses at a rate of 105.477 per 1,000. In the province, 1.82 per cent (9,527) of the population has been fully vaccinated. There were zero new vaccines delivered to Newfoundland for a total of 84,280 doses delivered so far. The province has received enough of the vaccine to give 16 per cent of its population a single dose. The province has used 65.53 per cent of its available vaccine supply.
P.E.I. is reporting 3,479 new vaccinations administered over the past seven days for a total of 20,258 doses given. The province has administered doses at a rate of 127.707 per 1,000. In the province, 3.87 per cent (6,139) of the population has been fully vaccinated. There were zero new vaccines delivered to P.E.I. for a total of 27,205 doses delivered so far. The province has received enough of the vaccine to give 17 per cent of its population a single dose. The province has used 74.46 per cent of its available vaccine supply.
Nova Scotia is reporting 25,112 new vaccinations administered over the past seven days for a total of 83,148 doses given. The province has administered doses at a rate of 85.202 per 1,000. In the province, 2.42 per cent (23,662) of the population has been fully vaccinated. There were zero new vaccines delivered to Nova Scotia for a total of 154,630 doses delivered so far. The province has received enough of the vaccine to give 16 per cent of its population a single dose. The province has used 53.77 per cent of its available vaccine supply.
New Brunswick is reporting 20,294 new vaccinations administered over the past seven days for a total of 75,962 doses given. The province has administered doses at a rate of 97.382 per 1,000. In the province, 1.57 per cent (12,211) of the population has been fully vaccinated. There were zero new vaccines delivered to New Brunswick for a total of 123,115 doses delivered so far. The province has received enough of the vaccine to give 16 per cent of its population a single dose. The province has used 61.7 per cent of its available vaccine supply.
Quebec is reporting 56,135 new vaccinations administered for a total of 1,121,958 doses given. The province has administered doses at a rate of 131.121 per 1,000. There were zero new vaccines delivered to Quebec for a total of 1,372,573 doses delivered so far. The province has received enough of the vaccine to give 16 per cent of its population a single dose. The province has used 81.74 per cent of its available vaccine supply.
Ontario is reporting 82,996 new vaccinations administered for a total of 1,838,592 doses given. The province has administered doses at a rate of 125.167 per 1,000. In the province, 2.09 per cent (306,373) of the population has been fully vaccinated. There were zero new vaccines delivered to Ontario for a total of 2,353,665 doses delivered so far. The province has received enough of the vaccine to give 16 per cent of its population a single dose. The province has used 78.12 per cent of its available vaccine supply.
Manitoba is reporting 5,060 new vaccinations administered for a total of 157,399 doses given. The province has administered doses at a rate of 114.305 per 1,000. In the province, 3.72 per cent (51,268) of the population has been fully vaccinated. There were 7,800 new vaccines delivered to Manitoba for a total of 248,180 doses delivered so far. The province has received enough of the vaccine to give 18 per cent of its population a single dose. The province has used 63.42 per cent of its available vaccine supply.
Saskatchewan is reporting 6,941 new vaccinations administered for a total of 162,695 doses given. The province has administered doses at a rate of 137.976 per 1,000. In the province, 2.97 per cent (34,993) of the population has been fully vaccinated. There were zero new vaccines delivered to Saskatchewan for a total of 188,025 doses delivered so far. The province has received enough of the vaccine to give 16 per cent of its population a single dose. The province has used 86.53 per cent of its available vaccine supply.
Alberta is reporting 26,592 new vaccinations administered for a total of 558,763 doses given. The province has administered doses at a rate of 126.933 per 1,000. In the province, 2.16 per cent (94,947) of the population has been fully vaccinated. There were zero new vaccines delivered to Alberta for a total of 697,415 doses delivered so far. The province has received enough of the vaccine to give 16 per cent of its population a single dose. The province has used 80.12 per cent of its available vaccine supply.
British Columbia is reporting 27,185 new vaccinations administered for a total of 637,856 doses given. The province has administered doses at a rate of 124.30 per 1,000. In the province, 1.70 per cent (87,233) of the population has been fully vaccinated. There were 17,600 new vaccines delivered to British Columbia for a total of 810,220 doses delivered so far. The province has received enough of the vaccine to give 16 per cent of its population a single dose. The province has used 78.73 per cent of its available vaccine supply.
Yukon is reporting 222 new vaccinations administered for a total of 33,825 doses given. The territory has administered doses at a rate of 810.549 per 1,000. In the territory, 25.86 per cent (10,791) of the population has been fully vaccinated. There were zero new vaccines delivered to Yukon for a total of 51,400 doses delivered so far. The territory has received enough of the vaccine to give 120 per cent of its population a single dose. The territory has used 65.81 per cent of its available vaccine supply.
The Northwest Territories are reporting zero new vaccinations administered for a total of 35,397 doses given. The territory has administered doses at a rate of 784.525 per 1,000. In the territory, 29.44 per cent (13,283) of the population has been fully vaccinated. There were zero new vaccines delivered to the Northwest Territories for a total of 51,600 doses delivered so far. The territory has received enough of the vaccine to give 110 per cent of its population a single dose. The territory has used 68.6 per cent of its available vaccine supply.
Nunavut is reporting 175 new vaccinations administered for a total of 19,669 doses given. The territory has administered doses at a rate of 507.902 per 1,000. In the territory, 17.52 per cent (6,785) of the population has been fully vaccinated. There were zero new vaccines delivered to Nunavut for a total of 37,500 doses delivered so far. The territory has received enough of the vaccine to give 97 per cent of its population a single dose. The territory has used 52.45 per cent of its available vaccine supply.
*Notes on data: The figures are compiled by the COVID-19 Open Data Working Group based on the latest publicly available data and are subject to change. Note that some provinces report weekly, while others report same-day or figures from the previous day. Vaccine doses administered is not equivalent to the number of people inoculated as the approved vaccines require two doses per person. The vaccines are currently not being administered to children under 18 and those with certain health conditions. In some cases the number of doses administered may appear to exceed the number of doses distributed as some provinces have been drawing extra doses per vial.
This report was automatically generated by The Canadian Press Digital Data Desk and was first published March 27, 2021.
Health
Toronto reports 2 more measles cases. Use our tool to check the spread in Canada – Toronto Star
/* OOVVUU Targeting */
const path = ‘/news/canada’;
const siteName = ‘thestar.com’;
let domain = ‘thestar.com’;
if (siteName === ‘thestar.com’)
domain = ‘thestar.com’;
else if (siteName === ‘niagarafallsreview.ca’)
domain = ‘niagara_falls_review’;
else if (siteName === ‘stcatharinesstandard.ca’)
domain = ‘st_catharines_standard’;
else if (siteName === ‘thepeterboroughexaminer.com’)
domain = ‘the_peterborough_examiner’;
else if (siteName === ‘therecord.com’)
domain = ‘the_record’;
else if (siteName === ‘thespec.com’)
domain = ‘the_spec’;
else if (siteName === ‘wellandtribune.ca’)
domain = ‘welland_tribune’;
else if (siteName === ‘bramptonguardian.com’)
domain = ‘brampton_guardian’;
else if (siteName === ‘caledonenterprise.com’)
domain = ‘caledon_enterprise’;
else if (siteName === ‘cambridgetimes.ca’)
domain = ‘cambridge_times’;
else if (siteName === ‘durhamregion.com’)
domain = ‘durham_region’;
else if (siteName === ‘guelphmercury.com’)
domain = ‘guelph_mercury’;
else if (siteName === ‘insidehalton.com’)
domain = ‘inside_halton’;
else if (siteName === ‘insideottawavalley.com’)
domain = ‘inside_ottawa_valley’;
else if (siteName === ‘mississauga.com’)
domain = ‘mississauga’;
else if (siteName === ‘muskokaregion.com’)
domain = ‘muskoka_region’;
else if (siteName === ‘newhamburgindependent.ca’)
domain = ‘new_hamburg_independent’;
else if (siteName === ‘niagarathisweek.com’)
domain = ‘niagara_this_week’;
else if (siteName === ‘northbaynipissing.com’)
domain = ‘north_bay_nipissing’;
else if (siteName === ‘northumberlandnews.com’)
domain = ‘northumberland_news’;
else if (siteName === ‘orangeville.com’)
domain = ‘orangeville’;
else if (siteName === ‘ourwindsor.ca’)
domain = ‘our_windsor’;
else if (siteName === ‘parrysound.com’)
domain = ‘parrysound’;
else if (siteName === ‘simcoe.com’)
domain = ‘simcoe’;
else if (siteName === ‘theifp.ca’)
domain = ‘the_ifp’;
else if (siteName === ‘waterloochronicle.ca’)
domain = ‘waterloo_chronicle’;
else if (siteName === ‘yorkregion.com’)
domain = ‘york_region’;
let sectionTag = ”;
try
if (domain === ‘thestar.com’ && path.indexOf(‘wires/’) = 0)
sectionTag = ‘/business’;
else if (path.indexOf(‘/autos’) >= 0)
sectionTag = ‘/autos’;
else if (path.indexOf(‘/entertainment’) >= 0)
sectionTag = ‘/entertainment’;
else if (path.indexOf(‘/life’) >= 0)
sectionTag = ‘/life’;
else if (path.indexOf(‘/news’) >= 0)
sectionTag = ‘/news’;
else if (path.indexOf(‘/politics’) >= 0)
sectionTag = ‘/politics’;
else if (path.indexOf(‘/sports’) >= 0)
sectionTag = ‘/sports’;
else if (path.indexOf(‘/opinion’) >= 0)
sectionTag = ‘/opinion’;
} catch (ex)
const descriptionUrl = ‘window.location.href’;
const vid = ‘mediainfo.reference_id’;
const cmsId = ‘2665777’;
let url = `https://pubads.g.doubleclick.net/gampad/ads?iu=/58580620/$domain/video/oovvuu$sectionTag&description_url=$descriptionUrl&vid=$vid&cmsid=$cmsId&tfcd=0&npa=0&sz=640×480&ad_rule=0&gdfp_req=1&output=vast&unviewed_position_start=1&env=vp&impl=s&correlator=`;
url = url.split(‘ ‘).join(”);
window.oovvuuReplacementAdServerURL = url;
Canada has seen a concerning rise in measles cases in the first months of 2024.
By the third week of March, the country had already recorded more than three times the number of cases as all of last year. Canada had just 12 cases of measles in 2023, up from three in 2022.
function buildUserSwitchAccountsForm()
var form = document.getElementById(‘user-local-logout-form-switch-accounts’);
if (form) return;
// build form with javascript since having a form element here breaks the payment modal.
var switchForm = document.createElement(‘form’);
switchForm.setAttribute(‘id’,’user-local-logout-form-switch-accounts’);
switchForm.setAttribute(‘method’,’post’);
switchForm.setAttribute(‘action’,’https://www.thestar.com/tncms/auth/logout/?return=https://www.thestar.com/users/login/?referer_url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.thestar.com%2Fnews%2Fcanada%2Ftoronto-reports-2-more-measles-cases-use-our-tool-to-check-the-spread-in-canada%2Farticle_20aa7df4-e88f-11ee-8fad-8f8368d7ff53.html’);
switchForm.setAttribute(‘style’,’display:none;’);
var refUrl = document.createElement(‘input’); //input element, text
refUrl.setAttribute(‘type’,’hidden’);
refUrl.setAttribute(‘name’,’referer_url’);
refUrl.setAttribute(‘value’,’https://www.thestar.com/news/canada/toronto-reports-2-more-measles-cases-use-our-tool-to-check-the-spread-in-canada/article_20aa7df4-e88f-11ee-8fad-8f8368d7ff53.html’);
var submit = document.createElement(‘input’);
submit.setAttribute(‘type’,’submit’);
submit.setAttribute(‘name’,’logout’);
submit.setAttribute(‘value’,’Logout’);
switchForm.appendChild(refUrl);
switchForm.appendChild(submit);
document.getElementsByTagName(‘body’)[0].appendChild(switchForm);
function handleUserSwitchAccounts()
window.sessionStorage.removeItem(‘bd-viafoura-oidc’); // clear viafoura JWT token
// logout user before sending them to login page via return url
document.getElementById(‘user-local-logout-form-switch-accounts’).submit();
return false;
buildUserSwitchAccountsForm();
#ont-map-iframepadding:0;width:100%;border:0;overflow:hidden;
#ontario-cases-iframepadding:0;width:100%;border:0;overflow:hidden;
#province-table-iframepadding:0;width:100%;border:0;overflow:hidden;
console.log(‘=====> bRemoveLastParagraph: ‘,0);
Health
Cancer Awareness Month – Métis Nation of Alberta


Cancer Awareness Month
Posted on: Apr 18, 2024
April is Cancer Awareness Month
As we recognize Cancer Awareness Month, we stand together to raise awareness, support those affected, advocate for prevention, early detection, and continued research towards a cure. Cancer is the leading cause of death for Métis women and the second leading cause of death for Métis men. The Otipemisiwak Métis Government of the Métis Nation Within Alberta is working hard to ensure that available supports for Métis Citizens battling cancer are culturally appropriate, comprehensive, and accessible by Métis Albertans at all stages of their cancer journey.
Receiving a cancer diagnosis, whether for yourself or a loved one, can feel overwhelming, leaving you unsure of where to turn for support. In June, our government will be launching the Cancer Supports and Navigation Program which will further support Métis Albertans and their families experiencing cancer by connecting them to OMG-specific cancer resources, external resources, and providing navigation support through the health care system. This program will also include Métis-specific peer support groups for those affected by cancer.
With funding from the Canadian Partnership Against Cancer (CPAC) we have also developed the Métis Cancer Care Course to ensure that Métis Albertans have access to culturally safe and appropriate cancer services. This course is available to cancer care professionals across the country and provides an overview of who Métis people are, our culture, our approaches to health and wellbeing, our experiences with cancer care, and our cancer journey.
Together, we can make a difference in the fight against cancer and ensure equitable access to culturally safe and appropriate care for all Métis Albertans. Please click on the links below to learn more about the supports available for Métis Albertans, including our Compassionate Care: Cancer Transportation program.
I wish you all good health and happiness!
Bobbi Paul-Alook
Secretary of Health & Seniors
Health
Type 2 diabetes is not one-size-fits-all: Subtypes affect complications and treatment options – The Conversation


You may have heard of Ozempic, the “miracle drug” for weight loss, but did you know that it was actually designed as a new treatment to manage diabetes? In Canada, diabetes affects approximately 10 per cent of the general population. Of those cases, 90 per cent have Type 2 diabetes.
This metabolic disorder is characterized by persistent high blood sugar levels, which can be accompanied by secondary health challenges, including a higher risk of stroke and kidney disease.
Locks and keys
In Type 2 diabetes, the body struggles to maintain blood sugar levels in an acceptable range. Every cell in the body needs sugar as an energy source, but too much sugar can be toxic to cells. This equilibrium needs to be tightly controlled and is regulated by a lock and key system.
In the body’s attempt to manage blood sugar levels and ensure that cells receive the right amount of energy, the pancreatic hormone, insulin, functions like a key. Cells cover themselves with locks that respond perfectly to insulin keys to facilitate the entry of sugar into cells.
Unfortunately, this lock and key system doesn’t always perform as expected. The body can encounter difficulties producing an adequate number of insulin keys, and/or the locks can become stubborn and unresponsive to insulin.
All forms of diabetes share the challenge of high blood sugar levels; however, diabetes is not a singular condition; it exists as a spectrum. Although diabetes is broadly categorized into two main types, Type 1 and Type 2, each presents a diversity of subtypes, especially Type 2 diabetes.
These subtypes carry their own characteristics and risks, and do not respond uniformly to the same treatments.
To better serve people living with Type 2 diabetes, and to move away from a “one size fits all” approach, it is beneficial to understand which subtype of Type 2 diabetes a person lives with. When someone needs a blood transfusion, the medical team needs to know the patient’s blood type. It should be the same for diabetes so a tailored and effective game plan can be implemented.
This article explores four unique subtypes of Type 2 diabetes, shedding light on their causes, complications and some of their specific treatment avenues.
Severe insulin-deficient diabetes: We’re missing keys!
(Lili Grieco-St-Pierre, Jennifer Bruin/Created with BioRender.com)
Insulin is produced by beta cells, which are found in the pancreas. In the severe insulin-deficient diabetes (SIDD) subtype, the key factories — the beta cells — are on strike. Ultimately, there are fewer keys in the body to unlock the cells and allow entry of sugar from the blood.
SIDD primarily affects younger, leaner individuals, and unfortunately, increases the risk of eye disease and blindness, among other complications. Why the beta cells go on strike remains largely unknown, but since there is an insulin deficiency, treatment often involves insulin injections.
Severe insulin-resistant diabetes: But it’s always locked!

(Lili Grieco-St-Pierre, Jennifer Bruin/Created with BioRender.com)
In the severe insulin-resistant diabetes (SIRD) subtype, the locks are overstimulated and start ignoring the keys. As a result, the beta cells produce even more keys to compensate. This can be measured as high levels of insulin in the blood, also known as hyperinsulinemia.
This resistance to insulin is particularly prominent in individuals with higher body weight. Patients with SIRD have an increased risk of complications such as fatty liver disease. There are many treatment avenues for these patients but no consensus about the optimal approach; patients often require high doses of insulin.
Mild obesity-related diabetes: The locks are sticky!

(Lili Grieco-St-Pierre, Jennifer Bruin/Created with BioRender.com)
Mild obesity-related (MOD) diabetes represents a nuanced aspect of Type 2 diabetes, often observed in individuals with higher body weight. Unlike more severe subtypes, MOD is characterized by a more measured response to insulin. The locks are “sticky,” so it is challenging for the key to click in place and open the lock. While MOD is connected to body weight, the comparatively less severe nature of MOD distinguishes it from other diabetes subtypes.
To minimize complications, treatment should include maintaining a healthy diet, managing body weight, and incorporating as much aerobic exercise as possible. This is where drugs like Ozempic can be prescribed to control the evolution of the disease, in part by managing body weight.
Mild age-related diabetes: I’m tired of controlling blood sugar!
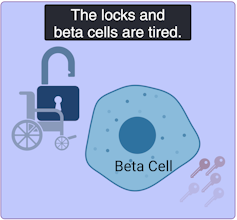
(Lili Grieco-St-Pierre, Jennifer Bruin/Created with BioRender.com)
Mild age-related diabetes (MARD) happens more often in older people and typically starts later in life. With time, the key factory is not as productive, and the locks become stubborn. People with MARD find it tricky to manage their blood sugar, but it usually doesn’t lead to severe complications.
Among the different subtypes of diabetes, MARD is the most common.
Unique locks, varied keys
While efforts have been made to classify diabetes subtypes, new subtypes are still being identified, making proper clinical assessment and treatment plans challenging.
In Canada, unique cases of Type 2 diabetes were identified in Indigenous children from Northern Manitoba and Northwestern Ontario by Dr. Heather Dean and colleagues in the 1980s and 90s. Despite initial skepticism from the scientific community, which typically associated Type 2 diabetes with adults rather than children, clinical teams persisted in identifying this as a distinct subtype of Type 2 diabetes, called childhood-onset Type 2 diabetes.
Read more:
Indigenous community research partnerships can help address health inequities
Childhood-onset Type 2 diabetes is on the rise across Canada, but disproportionately affects Indigenous youth. It is undoubtedly linked to the intergenerational trauma associated with colonization in these communities. While many factors are likely involved, recent studies have discovered that exposure of a fetus to Type 2 diabetes during pregnancy increases the risk that the baby will develop diabetes later in life.
Acknowledging this distinct subtype of Type 2 diabetes in First Nations communities has led to the implementation of a community-based health action plan aimed at addressing the unique challenges faced by Indigenous Peoples. It is hoped that partnered research between communities and researchers will continue to help us understand childhood-onset Type 2 diabetes and how to effectively prevent and treat it.
A mosaic of conditions

(Lili Grieco-St-Pierre, Jennifer Bruin/Created with BioRender.com)
Type 2 diabetes is not uniform; it’s a mosaic of conditions, each with its own characteristics. Since diabetes presents so uniquely in every patient, even categorizing into subtypes does not guarantee how the disease will evolve. However, understanding these subtypes is a good starting point to help doctors create personalized plans for people living with the condition.
While Indigenous communities, lower-income households and individuals living with obesity already face a higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes than the general population, tailored solutions may offer hope for better management. This emphasizes the urgent need for more precise assessments of diabetes subtypes to help customize therapeutic strategies and management strategies. This will improve care for all patients, including those from vulnerable and understudied populations.
-



 Investment12 hours ago
Investment12 hours agoUK Mulls New Curbs on Outbound Investment Over Security Risks – BNN Bloomberg
-



 Tech12 hours ago
Tech12 hours agoSave $700 Off This 4K Projector at Amazon While You Still Can – CNET
-



 Tech11 hours ago
Tech11 hours ago'Kingdom Come: Deliverance II' Revealed In Epic New Trailer And It Looks Incredible – Forbes
-



 Sports10 hours ago
Sports10 hours agoAuston Matthews denied 70th goal as depleted Leafs lose last regular-season game – Toronto Sun
-



 Science12 hours ago
Science12 hours agoJeremy Hansen – The Canadian Encyclopedia
-
Business9 hours ago
BC short-term rental rules take effect May 1 – CityNews Vancouver
-



 Investment9 hours ago
Investment9 hours agoBenjamin Bergen: Why would anyone invest in Canada now? – National Post
-
Art9 hours ago
Collection of First Nations art stolen from Gordon Head home – Times Colonist






