Science
A super-rare meteor storm may light up the sky Monday night – The Weather Network
While it is possible that we may see nothing at all extraordinary on Monday night, there’s the chance we may see hundreds, if not thousands, of meteors streaking through the sky.
Roughly 27 years ago, in 1995, astronomers watched as a comet began to shatter. Although comet 73P/Schwassman-Wachmann 3 had been discovered some 65 years before, it had been a fairly unremarkable object for all that time. Even the meteor shower associated with it, the tau Herculids which peak at the end of May each year, barely produces any meteors at all. Since 1995, though, the comet brightened significantly as it broke into multiple fragments. This breakup also ejected a fair amount of dust and debris out around the comet.
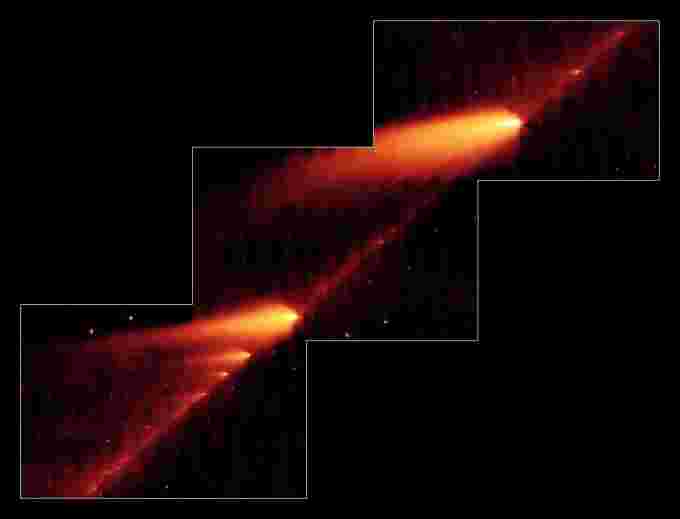
This image from NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope shows an infrared view of the shattered remnants of Comet 73P/Schwassman-Wachmann 3, strung out in a trail of beads along its orbit. The larger fragments can be seen to emit plumes of ice, dust and gas, which are pushed away by radiation pressure due to sunlight. (Credit: NASA)
Since then the tau Herculids have remained a fairly unimpressive meteor shower. Each year, it occurs between late May and mid-June, and peaks at the end of May. However, it usually produces so few meteors that it hasn’t been worth mentioning in any seasonal night sky observing guides.
This year is different, though.
On the night of May 30-31, 2022, astronomers believe there is a chance that Earth could pass through a concentrated cluster of debris from 73P/Schwassman-Wachmann 3. If that chance pays out, it will likely produce an outburst that rivals the major annual meteor showers, such as the Perseids or the Geminids. However, there’s also the potential that we could see thousands of bright streaks in the sky as it delivers a meteor storm!
The time to watch for this depends on where you live. Researchers with the Institute for Celestial Mechanics and Computation of Ephemerides at the Paris Observatory have shown that if an outburst occurs, it will be centred over California’s Baja Peninsula at around 10 p.m. PDT on May 30. Most of North America will be able to see it, with the exception of the Arctic and the Pacific Northwest.
For Canada, this means that the eastern half of the country has the best chance to see any outburst that may occur. The chances become more slim the farther west an observer is, due to the effects of twilight.
Meteor activity is expected to last for only a few hours, peaking around 1 a.m. EDT on Tuesday — 2:30 a.m. NDT, 2 a.m. ADT, 12 a.m. CDT, 11 p.m. CST/MDT, and 10 p.m. PDT.


ON THE OTHER HAND
Although we may see something truly awe-inspiring on Monday night, we shouldn’t get our hopes up too much.
“This is going to be an all or nothing event,” said Bill Cooke, of NASA’s Meteoroid Environment Office.
Meteor showers are the result of Earth passing through streams of debris left behind by comets and some asteroids as they orbit the Sun. The key word in all of that, for this story, is behind. The tiny meteoroids in the debris stream are nearly always blown off the comet or asteroid to follow along in the wake of their parent object.
In the case of this potential outburst of the tau Herculids, it all depends on debris from 73P/Schwassman-Wachmann 3 being ejected with enough force during the breakup to shoot it ahead of the comet.
The reason for this is due to the timing and relative positions of Earth, the comet’s orbit and debris stream, and the main fragments of the comet.
Normally, we see next to nothing at this time of year from the comet’s very diffuse debris stream. After the comet shattered, though, there was a lot more dust and debris located near the remaining fragments. If we could encounter some of that more concentrated debris, it would produce the outburst we’re looking for. However, the timing is off.


At the moment, those larger fragments of the comet are nowhere near us. They’re due to pass through our current location in space over the next few months. By then, though, Earth will be millions of kilometres away from where we are now, as the planet continues along its orbit around the Sun. So, for this outburst to happen, we need some of the debris to have shot so far ahead of the fragments that it is in our path on Monday night.
According to NASA, observations with the Spitzer Space Telescope did show that some of the debris was ejected with enough force that we should encounter it.
“This is one reason why astronomers are excited,” Lee Mohon wrote on NASA’s Watch the Skies blog.
PROMISING SIGNS
There’s no indication yet if the outburst is actually occurring, and we’ve certainly been disappointed by previous outburst predictions. However, we are seeing some promising signs.
The Spanish Meteor Network managed to capture a tau Herculid fireball on Friday night.
¡PRIMER BÓLIDO TAU HERCÚLIDA #SPMN270522H! Registrado ayer viernes sobre #Aragón por Antonio Lasala @AntonioLG1 a las 23h57m46s TUC. Ojalá sea el anuncio de muchos más fragmentos del cometa #73P #SW3 en las próximas noches. ¿Preparados para la campaña? 🤩https://t.co/TcmTt2hGHM pic.twitter.com/cm0gPwbCvA
¡PRIMER BÓLIDO TAU HERCÚLIDA Red de Investigación Bólidos y Meteoritos (SPMN) on Twitter: “¡PRIMER BÓLIDO TAU HERCÚLIDA #SPMN270522H! Registrado ayer viernes sobre #Aragón por Antonio Lasala @AntonioLG1 a las 23h57m46s TUC. Ojalá sea el anuncio de muchos más fragmentos del cometa #73P #SW3 en las próximas noches. ¿Preparados para la campaña? 🤩https://t.co/TcmTt2hGHM pic.twitter.com/cm0gPwbCvA / Twitter”! Registrado ayer viernes sobre Red de Investigación Bólidos y Meteoritos (SPMN) on Twitter: “¡PRIMER BÓLIDO TAU HERCÚLIDA #SPMN270522H! Registrado ayer viernes sobre #Aragón por Antonio Lasala @AntonioLG1 a las 23h57m46s TUC. Ojalá sea el anuncio de muchos más fragmentos del cometa #73P #SW3 en las próximas noches. ¿Preparados para la campaña? 🤩https://t.co/TcmTt2hGHM pic.twitter.com/cm0gPwbCvA / Twitter” por Antonio Lasala Red de Investigación Bólidos y Meteoritos (SPMN) on Twitter: “¡PRIMER BÓLIDO TAU HERCÚLIDA #SPMN270522H! Registrado ayer viernes sobre #Aragón por Antonio Lasala @AntonioLG1 a las 23h57m46s TUC. Ojalá sea el anuncio de muchos más fragmentos del cometa #73P #SW3 en las próximas noches. ¿Preparados para la campaña? 🤩https://t.co/TcmTt2hGHM pic.twitter.com/cm0gPwbCvA / Twitter” a las 23h57m46s TUC. Ojalá sea el anuncio de muchos más fragmentos del cometa Red de Investigación Bólidos y Meteoritos (SPMN) on Twitter: “¡PRIMER BÓLIDO TAU HERCÚLIDA #SPMN270522H! Registrado ayer viernes sobre #Aragón por Antonio Lasala @AntonioLG1 a las 23h57m46s TUC. Ojalá sea el anuncio de muchos más fragmentos del cometa #73P #SW3 en las próximas noches. ¿Preparados para la campaña? 🤩https://t.co/TcmTt2hGHM pic.twitter.com/cm0gPwbCvA / Twitter” Red de Investigación Bólidos y Meteoritos (SPMN) on Twitter: “¡PRIMER BÓLIDO TAU HERCÚLIDA #SPMN270522H! Registrado ayer viernes sobre #Aragón por Antonio Lasala @AntonioLG1 a las 23h57m46s TUC. Ojalá sea el anuncio de muchos más fragmentos del cometa #73P #SW3 en las próximas noches. ¿Preparados para la campaña? 🤩https://t.co/TcmTt2hGHM pic.twitter.com/cm0gPwbCvA / Twitter” en las próximas noches. ¿Preparados para la campaña? 🤩Red de Investigación Bólidos y Meteoritos (SPMN) on Twitter: “¡PRIMER BÓLIDO TAU HERCÚLIDA #SPMN270522H! Registrado ayer viernes sobre #Aragón por Antonio Lasala @AntonioLG1 a las 23h57m46s TUC. Ojalá sea el anuncio de muchos más fragmentos del cometa #73P #SW3 en las próximas noches. ¿Preparados para la campaña? 🤩https://t.co/TcmTt2hGHM pic.twitter.com/cm0gPwbCvA / Twitter” Red de Investigación Bólidos y Meteoritos (SPMN) on Twitter: “¡PRIMER BÓLIDO TAU HERCÚLIDA #SPMN270522H! Registrado ayer viernes sobre #Aragón por Antonio Lasala @AntonioLG1 a las 23h57m46s TUC. Ojalá sea el anuncio de muchos más fragmentos del cometa #73P #SW3 en las próximas noches. ¿Preparados para la campaña? 🤩https://t.co/TcmTt2hGHM pic.twitter.com/cm0gPwbCvA / Twitter”
— Red de Investigación Bólidos y Meteoritos (SPMN) (@RedSpmn) Red de Investigación Bólidos y Meteoritos (SPMN) on Twitter: “¡PRIMER BÓLIDO TAU HERCÚLIDA #SPMN270522H! Registrado ayer viernes sobre #Aragón por Antonio Lasala @AntonioLG1 a las 23h57m46s TUC. Ojalá sea el anuncio de muchos más fragmentos del cometa #73P #SW3 en las próximas noches. ¿Preparados para la campaña? 🤩https://t.co/TcmTt2hGHM pic.twitter.com/cm0gPwbCvA / Twitter”
Additionally, the Global Meteor Network detected its first tau Herculids, too.
First tau Herculids were detected last night by the #globalmeteornetwork. The geocentric radiant was R.A. = 203.2°, Dec = 17.7 deg based on 17 orbits. The activity seems to be only starting – first detected on May 28, 19h UT with a ZHR ~ 0.3 and not dropping. pic.twitter.com/MoU8CXVRIf
First tau Herculids were detected last night by the Denis Vida on Twitter: “First tau Herculids were detected last night by the #globalmeteornetwork. The geocentric radiant was R.A. = 203.2°, Dec = 17.7 deg based on 17 orbits. The activity seems to be only starting – first detected on May 28, 19h UT with a ZHR ~ 0.3 and not dropping. pic.twitter.com/MoU8CXVRIf / Twitter”. The geocentric radiant was R.A. = 203.2°, Dec = 17.7 deg based on 17 orbits. The activity seems to be only starting – first detected on May 28, 19h UT with a ZHR ~ 0.3 and not dropping. Denis Vida on Twitter: “First tau Herculids were detected last night by the #globalmeteornetwork. The geocentric radiant was R.A. = 203.2°, Dec = 17.7 deg based on 17 orbits. The activity seems to be only starting – first detected on May 28, 19h UT with a ZHR ~ 0.3 and not dropping. pic.twitter.com/MoU8CXVRIf / Twitter”
The questions that remain are 1) how much debris is in our path for Monday night, and 2) exactly how fast will it be travelling when it gets swept up by Earth’s atmosphere.
If there is only a small amount of relatively slow-moving meteoroids, we likely won’t see anything. The meteor shower may still occur, but as the researchers point out, it may only be picked up by Canadian Meteor Radar.
If there’s a lot of fast-moving debris, though, with plenty of ‘sand’ and ‘gravel’ mixed in with the dust, we could see a spectacular display light up the sky.
TIPS FOR WATCHING A METEOR SHOWER
Meteor showers are events that nearly everyone can watch. No special equipment is required. In fact, binoculars and telescopes make it harder to see meteor showers, by restricting your field of view. However, there are a few things to keep in mind so you don’t miss out on these amazing events.
The three best practices for observing the night sky are:
- Check the weather,
- Get away from light pollution, and
- Be patient.
Clear skies are essential. Even a few hours of cloudy skies can ruin your chances of watching an event such as a meteor shower. So, be sure to check The Weather Network on TV, on our website, or from our app, and look for my articles on our Space News page, just to be sure that you have the most up-to-date sky forecast.
Next, you need to get away from city light pollution. If you look up into the sky from home, what do you see? The Moon, a planet or two, perhaps a few bright stars such as Vega, Betelgeuse and Procyon, as well as some passing airliners? If so, there’s too much light pollution in your area to get the most out of a meteor shower. You might catch an exceptionally bright fireball if one happens to fly past overhead, but that’s likely all you’ll see. So, to get the most out of your stargazing and meteor watching, get out of the city. The farther away you can get, the better.
Watch: What light pollution is doing to city views of the Milky Way
For most regions of Canada, getting out from under light pollution is simply a matter of driving outside of your city, town or village until a multitude of stars is visible above your head.
In some areas, especially in southern Ontario and along the St. Lawrence River, the concentration of light pollution is too high. Getting far enough outside of one city to escape its light pollution tends to put you under the light pollution dome of the next city over. The best options for getting away from light depend on your location. In southwestern Ontario and the Niagara Peninsula, the shores of Lake Erie can offer some excellent views. In the GTA and farther east, drive north and seek out the various Ontario provincial parks or Quebec provincial parks. Even if you’re confined to the parking lot after hours, these are usually excellent locations from which to watch (and you don’t run the risk of trespassing on someone’s property).
If you can’t get away, the suburbs can offer at least a slightly better view of the night sky. Here, the key is to limit the amount of direct light in your field of view. Dark backyards, sheltered from street lights by surrounding houses and trees, are your best haven. The video above provides a good example of viewing based on the concentration of light pollution in the sky. Also, check for dark sky preserves in your area.
When viewing a meteor shower, be mindful of the phase of the Moon. Meteor showers are typically at their best when viewed during the New Moon or Crescent Moon. However, a Gibbous or Full Moon can be bright enough to wash out all but the brightest meteors. Since we can’t get away from the Moon, the best option is just to time your outing right, so the Moon has already set or is low in the sky. Also, you can angle your field of view to keep the Moon out of your direct line of sight. This will reduce its impact on your night vision and allow you to spot more meteors.
Once you’ve verified you have clear skies and you’ve limited your exposure to light pollution, this is where being patient comes in.
For best viewing, your eyes need some time to adapt to the dark. Give yourself at least 20 minutes, but 30-45 minutes is best for your eyes to adjust from being exposed to bright light.
Note that this, likely more than anything else, is the one thing that causes the most disappointment when it comes to watching a meteor shower.
If you step out into your backyard from a brightly lit home and looking up for a few minutes, you might be lucky enough to catch a rare bright fireball meteor. However, it’s far more likely that you won’t see anything at all. Meteors may be streaking overhead, but it takes time for our eyes to adjust, so that we can actually pick out those brief flashes of light. Waiting for at least twenty minutes, while avoiding sources of light during that time (streetlights, car headlights and interior lights, and smartphone and tablet screens) dramatically improves your chances of avoiding disappointment.
Sometimes, avoiding your smartphone or tablet isn’t an option. In this case, set the display to reduce the amount of blue light it gives off and reduce the screen’s brightness. That way, it will have less of an impact on your night vision.
You can certainly gaze into the starry sky while you are letting your eyes adjust. You may even see a few of the brighter meteors as your eyes become accustomed to the dark.
Once you’re all set, just look straight up and enjoy the view!
Science
Voyager 1 transmitting data again after Nasa remotely fixes 46-year-old probe – The Guardian


Earth’s most distant spacecraft, Voyager 1, has started communicating properly again with Nasa after engineers worked for months to remotely fix the 46-year-old probe.
Nasa’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), which makes and operates the agency’s robotic spacecraft, said in December that the probe – more than 15bn miles (24bn kilometres) away – was sending gibberish code back to Earth.
In an update released on Monday, JPL announced the mission team had managed “after some inventive sleuthing” to receive usable data about the health and status of Voyager 1’s engineering systems. “The next step is to enable the spacecraft to begin returning science data again,” JPL said. Despite the fault, Voyager 1 had operated normally throughout, it added.
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 was designed with the primary goal of conducting close-up studies of Jupiter and Saturn in a five-year mission. However, its journey continued and the spacecraft is now approaching a half-century in operation.
Voyager 1 crossed into interstellar space in August 2012, making it the first human-made object to venture out of the solar system. It is currently travelling at 37,800mph (60,821km/h).
The recent problem was related to one of the spacecraft’s three onboard computers, which are responsible for packaging the science and engineering data before it is sent to Earth. Unable to repair a broken chip, the JPL team decided to move the corrupted code elsewhere, a tricky job considering the old technology.
The computers on Voyager 1 and its sister probe, Voyager 2, have less than 70 kilobytes of memory in total – the equivalent of a low-resolution computer image. They use old-fashioned digital tape to record data.
The fix was transmitted from Earth on 18 April but it took two days to assess if it had been successful as a radio signal takes about 22 and a half hours to reach Voyager 1 and another 22 and a half hours for a response to come back to Earth. “When the mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on 20 April, they saw that the modification worked,” JPL said.
Alongside its announcement, JPL posted a photo of members of the Voyager flight team cheering and clapping in a conference room after receiving usable data again, with laptops, notebooks and doughnuts on the table in front of them.
The Retired Canadian astronaut Chris Hadfield, who flew two space shuttle missions and acted as commander of the International Space Station, compared the JPL mission to long-distance maintenance on a vintage car.
“Imagine a computer chip fails in your 1977 vehicle. Now imagine it’s in interstellar space, 15bn miles away,” Hadfield wrote on X. “Nasa’s Voyager probe just got fixed by this team of brilliant software mechanics.
Voyager 1 and 2 have made numerous scientific discoveries, including taking detailed recordings of Saturn and revealing that Jupiter also has rings, as well as active volcanism on one of its moons, Io. The probes later discovered 23 new moons around the outer planets.
As their trajectory takes them so far from the sun, the Voyager probes are unable to use solar panels, instead converting the heat produced from the natural radioactive decay of plutonium into electricity to power the spacecraft’s systems.
Nasa hopes to continue to collect data from the two Voyager spacecraft for several more years but engineers expect the probes will be too far out of range to communicate in about a decade, depending on how much power they can generate. Voyager 2 is slightly behind its twin and is moving slightly slower.
In roughly 40,000 years, the probes will pass relatively close, in astronomical terms, to two stars. Voyager 1 will come within 1.7 light years of a star in the constellation Ursa Minor, while Voyager 2 will come within a similar distance of a star called Ross 248 in the constellation of Andromeda.
Science
iN PHOTOS: Nature lovers celebrate flora, fauna for Earth Day in Kamloops, Okanagan | iNFOnews | Thompson-Okanagan's News Source – iNFOnews
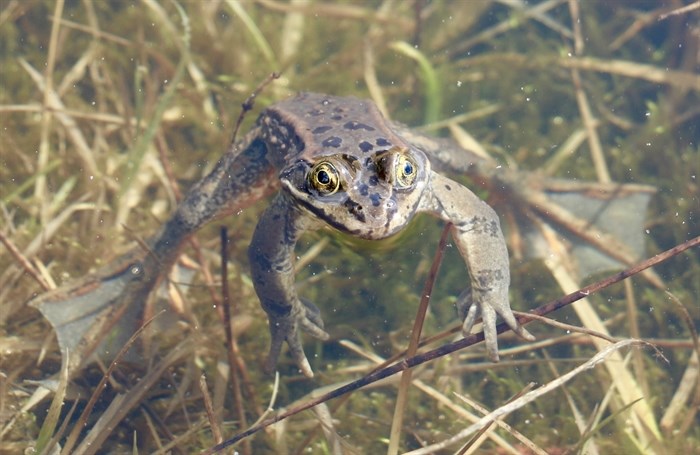


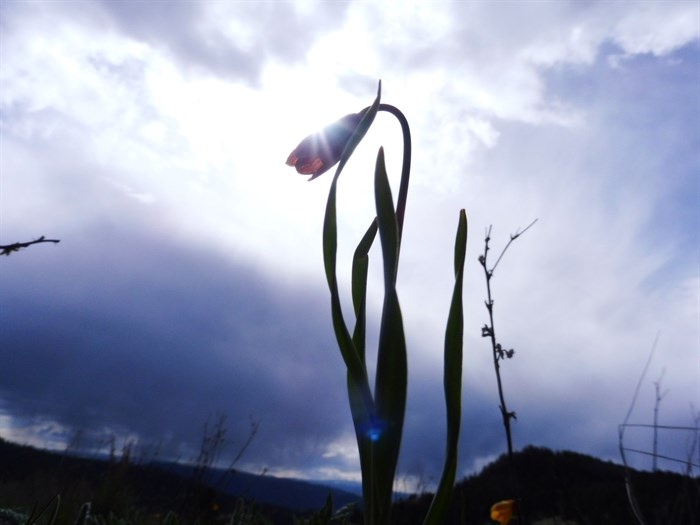
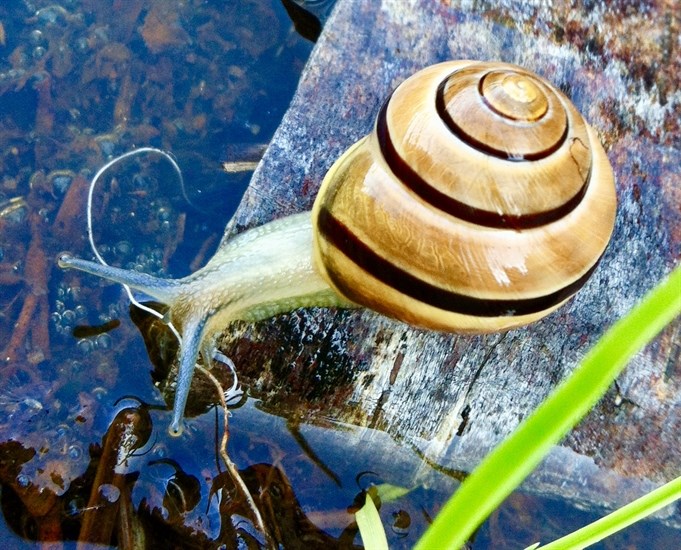
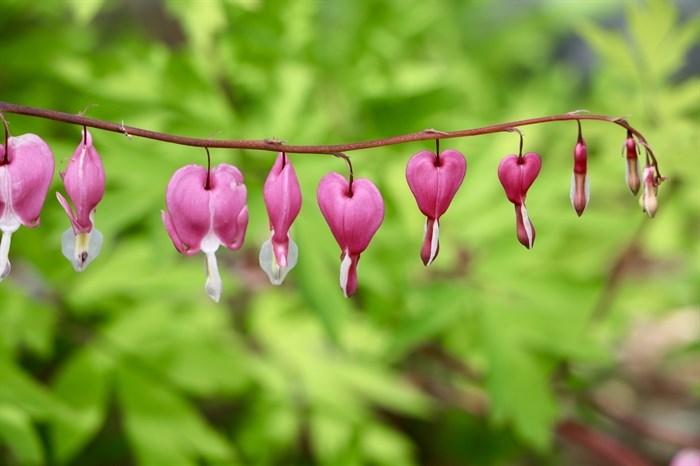
Photographers are sharing their favourite photos of flora and fauna captured in Kamloops and the Okanagan in celebration of Earth Day.
First started in the United States in the 70s, the special day on April 22 continues to be acknowledged around the globe. It’s a day to celebrate the planet and a reminder of the need for environmental conservation and sustainability, according to EarthDay.org.
These stunning nature photos show life in ponds and forests, in skies and on mountains, capturing the beauty and wonder of our local natural environments.
Area photographers shared some of their favourite finds and artistic captures. From frogs to flowers, the great outdoors is teeming with life.
If you have nature photos you want to share, send them to news@infonews.ca.








To contact a reporter for this story, email Shannon Ainslie or call 250-819-6089 or email the editor. You can also submit photos, videos or news tips to the newsroom and be entered to win a monthly prize draw.
We welcome your comments and opinions on our stories but play nice. We won’t censor or delete comments unless they contain off-topic statements or links, unnecessary vulgarity, false facts, spam or obviously fake profiles. If you have any concerns about what you see in comments, email the editor in the link above. SUBSCRIBE to our awesome newsletter here.


Science
An extra moon may be orbiting Earth — and scientists think they know exactly where it came from – Livescience.com


A fast-spinning asteroid that orbits in time with Earth may be a wayward chunk of the moon. Now, scientists think they know exactly which lunar crater it came from.
A new study, published April 19 in the journal Nature Astronomy, finds that the near-Earth asteroid 469219 Kamo’oalewa may have been flung into space when a mile-wide (1.6 kilometers) space rock hit the moon, creating the Giordano Bruno crater.
Kamo’oalewa’s light reflectance matches that of weathered lunar rock, and its size, age and spin all match up with the 13.6-mile-wide (22 km) crater, which sits on the far side of the moon, the study researchers reported.
China plans to launch a sample-return mission to the asteroid in 2025. Called Tianwen-2, the mission will return pieces of Kamo’oalewa about 2.5 years later, according to Live Science’s sister site Space.com.
“The possibility of a lunar-derived origin adds unexpected intrigue to the [Tianwen-2] mission and presents additional technical challenges for the sample return,” Bin Cheng, a planetary scientist at Tsinghua University and a co-author of the new study, told Science.
Related: How many moons does Earth have?
Kamo’oalewa was discovered in 2016 by researchers at Haleakala Observatory in Hawaii. It has a diameter of about 100 to 200 feet (approximately 30 to 60 meters, or about the size of a large Ferris wheel) and spins at a rapid clip of one rotation every 28 minutes. The asteroid orbits the sun in a similar path to Earth, sometimes approaching within 10 million miles (16 million km).
window.sliceComponents = window.sliceComponents || ;
externalsScriptLoaded.then(() => {
window.reliablePageLoad.then(() => {
var componentContainer = document.querySelector(“#slice-container-newsletterForm-articleInbodyContent-UG4KJ7zrhxAytcHZQxVzXK”);
if (componentContainer)
var data = “layout”:”inbodyContent”,”header”:”Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now”,”tagline”:”Get the worldu2019s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.”,”formFooterText”:”By submitting your information you agree to the Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy and are aged 16 or over.”,”successMessage”:”body”:”Thank you for signing up. You will receive a confirmation email shortly.”,”failureMessage”:”There was a problem. Please refresh the page and try again.”,”method”:”POST”,”inputs”:[“type”:”hidden”,”name”:”NAME”,”type”:”email”,”name”:”MAIL”,”placeholder”:”Your Email Address”,”required”:true,”type”:”hidden”,”name”:”NEWSLETTER_CODE”,”value”:”XLS-D”,”type”:”hidden”,”name”:”LANG”,”value”:”EN”,”type”:”hidden”,”name”:”SOURCE”,”value”:”60″,”type”:”hidden”,”name”:”COUNTRY”,”type”:”checkbox”,”name”:”CONTACT_OTHER_BRANDS”,”label”:”text”:”Contact me with news and offers from other Future brands”,”type”:”checkbox”,”name”:”CONTACT_PARTNERS”,”label”:”text”:”Receive email from us on behalf of our trusted partners or sponsors”,”type”:”submit”,”value”:”Sign me up”,”required”:true],”endpoint”:”https://newsletter-subscribe.futureplc.com/v2/submission/submit”,”analytics”:[“analyticsType”:”widgetViewed”],”ariaLabels”:;
var triggerHydrate = function()
window.sliceComponents.newsletterForm.hydrate(data, componentContainer);
if (window.lazyObserveElement)
window.lazyObserveElement(componentContainer, triggerHydrate);
else
triggerHydrate();
}).catch(err => console.log(‘Hydration Script has failed for newsletterForm-articleInbodyContent-UG4KJ7zrhxAytcHZQxVzXK Slice’, err));
}).catch(err => console.log(‘Externals script failed to load’, err));
Follow-up studies suggested that the light spectra reflected by Kamo’oalewa was very similar to the spectra reflected by samples brought back to Earth by lunar missions, as well as to meteorites known to come from the moon.
Cheng and his colleagues first calculated what size object and what speed of impact would be necessary to eject a fragment like Kamo’oalewa from the lunar surface, as well as what size crater would be left behind. They figured out that the asteroid could have resulted from a 45-degree impact at about 420,000 mph (18 kilometers per second) and would have left a 6-to-12-mile-wide (10 to 20 km) crater.
There are tens of thousands of craters that size on the moon, but most are ancient, the researchers wrote in their paper. Near-Earth asteroids usually last only about 10 million years, or at most up to 100 million years before they crash into the sun or a planet or get flung out of the solar system entirely. By looking at young craters, the team narrowed down the contenders to a few dozen options.
The researchers focused on Giordano Bruno, which matched the requirements for both size and age. They found that the impact that formed Giordano Bruno could have created as many as three still-extant Kamo’oalewa-like objects. This makes Giordano Bruno crater the most likely source of the asteroid, the researchers concluded.
“It’s like finding out which tree a fallen leaf on the ground came from in a vast forest,” Cheng wrote on X, formerly known as Twitter.
Confirmation will come after the Tianwen-2 mission brings a piece of Kamo’oalewa back to Earth. Scientists already have a sample of what is believed to be ejecta from Giordano Bruno crater in the Luna 24 sample, a bit of moon rock brought back to Earth in a 1976 NASA mission. By comparing the two, researchers could verify Kamo’oalewa’s origin.
Editor’s note: This article’s headline was updated on April 23 at 10 a.m. ET.
-



 Health23 hours ago
Health23 hours agoSee how chicken farmers are trying to stop the spread of bird flu – Fox 46 Charlotte
-



 Science21 hours ago
Science21 hours agoOsoyoos commuters invited to celebrate Earth Day with the Leg Day challenge – Oliver/Osoyoos News – Castanet.net
-
News21 hours ago
Freeland defends budget measures, as premiers push back on federal involvement – CBC News
-



 Politics21 hours ago
Politics21 hours agoHaberman on why David Pecker testifying is ‘fundamentally different’ – CNN
-
Economy21 hours ago
The Fed's Forecasting Method Looks Increasingly Outdated as Bernanke Pitches an Alternative – Bloomberg
-
Business20 hours ago
Gildan replacing five directors ahead of AGM, will back two Browning West nominees – Yahoo Canada Finance
-



 Health20 hours ago
Health20 hours agoIt's possible to rely on plant proteins without sacrificing training gains, new studies say – The Globe and Mail
-



 Tech20 hours ago
Tech20 hours agoMeta Expands VR Operating System to Third-Party Hardware Makers – MacRumors








