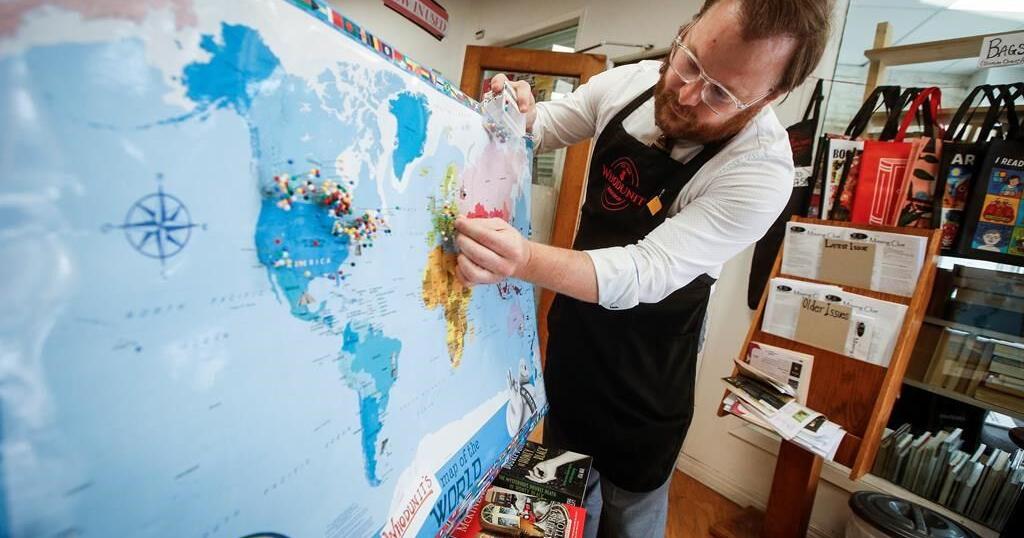
WINNIPEG – Some 250 coloured tacks pepper a large-scale world map among bookshelves at Whodunit Mystery Bookstore.
Estonia, Finland, Japan and even Fenwick, Ont., have pins representing places outside Winnipeg where someone has ordered a page-turner from the independent bookstore that specializes in mystery and crime fiction novels.
For 30 years, the store has been offering fans of Agatha Christie’s Hercule Poirot or Arthur Conan Doyle’s Sherlock Holmes a place to get lost in whodunits both old and new.
Jack and Wendy Bumsted bought the shop in the Crescentwood neighbourhood in 2007 from another pair of mystery lovers.
The married couple had been longtime customers of the store. Wendy Bumsted grew up reading Perry Mason novels while her husband was a historian with vast knowledge of the crime fiction genre.
At the time, Jack Bumsted was retiring from teaching at the University of Manitoba when he was looking for his next venture.
“The bookstore came up and we bought it, I think, within a week,” Wendy Bumsted said in an interview.
“It never didn’t seem like a good idea.”
In the years since the Bumsteds took ownership, the family has witnessed the decline in mail-order books, the introduction of online retailers, a relocation to a new space next to the original, a pandemic and the death of beloved co-owner Jack Bumsted in 2020.
But with all the changes that come with owning a small business, customers continue to trust their next mystery fix will come from one of the shelves at Whodunit.
Many still request to be called about books from specific authors, or want to be notified if a new book follows their favourite format. Some arrive at the shop like clockwork each week hoping to get suggestions from Wendy Bumsted or her son on the next big hit.
“She has really excellent instincts on what we should be getting and what we should be promoting,” Micheal Bumsted said of his mother.
Wendy Bumsted suggested the store stock “Thursday Murder Club,” the debut novel from British television host Richard Osman, before it became a bestseller. They ordered more copies than other bookstores in Canada knowing it had the potential to be a hit, said Michael Bumsted.
The store houses more than 18,000 new and used novels. That’s not including the boxes of books that sit in Wendy Bumsted’s tiny office, or the packages that take up space on some of the only available seating there, waiting to be added to the inventory.
Just as the genre has evolved, so has the Bumsteds’ willingness to welcome other subjects on their shelves — despite some pushback from loyal customers and initially the Bumsted patriarch.
For years, Jack Bumsted refused to sell anything outside the crime fiction genre, including his own published books. Instead, he would send potential buyers to another store, but would offer to sign the books if they came back with them.
Wendy Bumsted said that eventually changed in his later years.
Now, about 15 per cent of the store’s stock is of other genres, such as romance or children’s books.
The COVID-19 pandemic forced them to look at expanding their selection, as some customers turned to buying books through the store’s website, which is set up to allow purchasers to get anything from the publishers the Bumsteds have contracts with.
In 2019, the store sold fewer than 100 books online. That number jumped to more than 3,000 in 2020, as retailers had to deal with pandemic lockdowns.
After years of running a successful mail-order business, the store was able to quickly adapt when it had to temporarily shut its doors, said Michael Bumsted.
“We were not a store…that had to figure out how to get books to people when they weren’t here.”
He added being a community bookstore with a niche has helped the family stay in business when other retailers have struggled. Part of that has included building lasting relationships.
“Some people have put it in their wills that their books will come to us,” said Wendy Bumsted.
Some of those collections have included tips on traveling through Asia in the early 2000s or the history of Australian cricket.
Micheal Bumsted said they’ve had to learn to be patient with selling some of these more obscure titles, but eventually the time comes for them to find a new home.
“One of the great things about physical books is that they can be there for you when you are ready for them.”
This report by The Canadian Press was first published on Sept. 15, 2024.