Article content
B.C.’s economy is not as healthy as it might appear, since it relies too much on housing and newcomers to keep it above water, say prominent economists and analysts.
Analysis: B.C. has an unusual economy because it hinges so heavily on “outside money,” say economists. How long can it go on?

B.C.’s economy is not as healthy as it might appear, since it relies too much on housing and newcomers to keep it above water, say prominent economists and analysts.
The real estate sector makes up a much larger section of the B.C. economy than in the rest of the country. The B.C. economy is heavily reliant on large-scale flows of people arriving each year from other provinces and countries, say the specialists.
They maintain B.C. has not been effective at developing its resources, businesses and industrial capacity in a way that increases wages and improves productivity. This B.C. phenomenon, going on for two decades, puts demand pressure on housing prices.
Don Wright, former head of B.C.’s civil service, says there is a general feeling among British Columbians that the economy is healthy because unemployment is relatively low and government revenues stable.
But there is a distinct possibility the economy is not sustainable, Wright says.
B.C.’s trade deficit has been growing steadily since 2005. The province, he said, is “spending about $28 billion more per year than we are earning.”
Both Wright and David Williams, senior policy analyst for the Business Council of B.C., say the provincial economy is too dependent on large-scale in-migration to bring in capital, which fuels the housing sector and props up spending on goods and services.
Last year, according to the B.C. government, the province welcomed a record 100,000 new people. About 33,000 came from other provinces, which is the highest amount in three decades. The other 67 per cent arrived from other countries, a lower proportion than normal, and most chose Metro Vancouver.
B.C. has an unusual economy because it hinges so heavily on “outside money;” on new arrivals coming in to “buy real estate and support consumption with income earned elsewhere,” says Wright, an economist who gives presentations on the issue to Ottawa politicians and business organizations.
“In essence we are ‘exporting’ the right to reside in B.C.,” Wright says.
“This has become our largest ‘export industry.’ It accounts for more than twice the annual level of forest industry exports. In the short run, this injection of dollars does create the impression of a healthy economy, but how long can this go on?”

The business council’s Williams generally agrees. A tremendous amount of B.C. money is going into “housing-related consumption,” he says.
But investment dollars are not flowing strongly enough into such things as new machinery and equipment and intellectual property rights, said the business economist. Those sectors can much more add to the “economy’s future productive capacity” and potentially increase stagnant wages.
In-migration should not be seen as a cure-all for the economic woes of Canada or B.C., says Williams.
He questions the way Canada, particularly B.C., depends on “record immigration levels to turbocharge population growth and housing demand.” Canadian economists believe immigration numbers have an overall neutral effect on real wages and gross domestic product per capita.
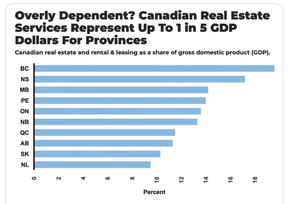
According to Stephen Punwasi, of Better Dwelling, B.C.’s economy is almost twice as reliant as neighbouring Alberta on real estate, which accounts for 20 per cent of B.C.’s GDP.
That compares to an average of 13.5 per cent across the country, a proportion that is still much higher than in the United States. If B.C.’s construction industry is included, it adds up to almost one third of B.C.’s GDP coming from real-estate related services.
Canada, and especially B.C., are “addicted” to real estate-driven growth, says Punwasi, who maintains it’s an unhealthy dependence that won’t be easy to break.
Wright, who was NDP Premier John Horgan’s deputy minister until stepping down in 2020, cites the danger of over-relying on new arrivals.
When 100,000 people move into B.C. and buy houses and services “it creates the illusion that the economy is strong. But for me the question is, ‘Is it sustainable?,’” Wright says.
“Let’s say somebody from outside B.C. retires to Comox and buys a place. And they’ve accumulated a lot of net wealth over their life. Whenever they spend money, it’s money that’s not being earned in B.C. In the short term it’s not bad for the economy, because it creates employment when somebody goes out and eats at a restaurant.”
But Wright doesn’t think relying on imported wealth is sustainable — for two reasons.
The first is that “you only get to sell off a piece of real estate to somebody outside the province once,” he said.
“And another reason is it’s not socially sustainable: Young people cannot afford a house anymore.” And too many new real-estate units are not suitable for families.
“A whole generation is going to be frozen out of the housing market, unless they have a well-capitalized, generous bank of mom and dad.”
What might happen to B.C. “when the party stops?” Wright asks, referring to a time when newcomers stop bringing in tens of billions of dollars each year from beyond provincial borders?
B.C., he said, will need to restructure by strengthening sectors such as forestry and mining, manufacturing and high tech — all of which are capable of producing superior middle-class wages.
“We better know,” Wright says, “how to rebuild the standard of living of the next generation.”





As Joe Biden this week hailed America’s booming economy as the strongest in the world during a reelection campaign tour of battleground-state Pennsylvania, global finance chiefs convening in Washington had a different message: cool it.
The push-back from central bank governors and finance ministers gathering for the International Monetary Fund-World Bank spring meetings highlight how the sting from a surging US economy — manifested through high interest rates and a strong dollar — is ricocheting around the world by forcing other currencies lower and complicating plans to bring down borrowing costs.
Canada’s Prime Minister Justin Trudeau and Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland hold the 2024-25 budget, on Parliament Hill in Ottawa, on April 16.Patrick Doyle/Reuters
Alex Whalen and Jake Fuss are analysts at the Fraser Institute.
Amid a federal budget riddled with red ink and tax hikes, the Trudeau government has increased capital gains taxes. The move will be disastrous for Canada’s growth prospects and its already-lagging investment climate, and to make matters worse, research suggests it won’t work as planned.
Currently, individuals and businesses who sell a capital asset in Canada incur capital gains taxes at a 50-per-cent inclusion rate, which means that 50 per cent of the gain in the asset’s value is subject to taxation at the individual or business’s marginal tax rate. The Trudeau government is raising this inclusion rate to 66.6 per cent for all businesses, trusts and individuals with capital gains over $250,000.
The problems with hiking capital gains taxes are numerous.
First, capital gains are taxed on a “realization” basis, which means the investor does not incur capital gains taxes until the asset is sold. According to empirical evidence, this creates a “lock-in” effect where investors have an incentive to keep their capital invested in a particular asset when they might otherwise sell.
For example, investors may delay selling capital assets because they anticipate a change in government and a reversal back to the previous inclusion rate. This means the Trudeau government is likely overestimating the potential revenue gains from its capital gains tax hike, given that individual investors will adjust the timing of their asset sales in response to the tax hike.
Second, the lock-in effect creates a drag on economic growth as it incentivizes investors to hold off selling their assets when they otherwise might, preventing capital from being deployed to its most productive use and therefore reducing growth.
Budget’s capital gains tax changes divide the small business community
And Canada’s growth prospects and investment climate have both been in decline. Canada currently faces the lowest growth prospects among all OECD countries in terms of GDP per person. Further, between 2014 and 2021, business investment (adjusted for inflation) in Canada declined by $43.7-billion. Hiking taxes on capital will make both pressing issues worse.
Contrary to the government’s framing – that this move only affects the wealthy – lagging business investment and slow growth affect all Canadians through lower incomes and living standards. Capital taxes are among the most economically damaging forms of taxation precisely because they reduce the incentive to innovate and invest. And while taxes on capital gains do raise revenue, the economic costs exceed the amount of tax collected.
Previous governments in Canada understood these facts. In the 2000 federal budget, then-finance minister Paul Martin said a “key factor contributing to the difficulty of raising capital by new startups is the fact that individuals who sell existing investments and reinvest in others must pay tax on any realized capital gains,” an explicit acknowledgment of the lock-in effect and costs of capital gains taxes. Further, that Liberal government reduced the capital gains inclusion rate, acknowledging the importance of a strong investment climate.
At a time when Canada badly needs to improve the incentives to invest, the Trudeau government’s 2024 budget has introduced a damaging tax hike. In delivering the budget, Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland said “Canada, a growing country, needs to make investments in our country and in Canadians right now.” Individuals and businesses across the country likely agree on the importance of investment. Hiking capital gains taxes will achieve the exact opposite effect.


Nigeria’s economy, which ranked as Africa’s largest in 2022, is set to slip to fourth place this year and Egypt, which held the top position in 2023, is projected to fall to second behind South Africa after a series of currency devaluations, International Monetary Fund forecasts show.
The IMF’s World Economic Outlook estimates Nigeria’s gross domestic product at $253 billion based on current prices this year, lagging energy-rich Algeria at $267 billion, Egypt at $348 billion and South Africa at $373 billion.
DJT Stock Rises. Trump Media CEO Alleges Potential Market Manipulation. – Barron's
Trump Media alerts Nasdaq to potential market manipulation from 'naked' short selling of DJT stock – CNBC
Private equity gears up for potential National Football League investments – Financial Times
DJT Stock Jumps. The Truth Social Owner Is Showing Stockholders How to Block Short Sellers. – Barron's




Type 2 diabetes is not one-size-fits-all: Subtypes affect complications and treatment options – The Conversation
Tofino, Pemberton among communities opting in to B.C.'s new short-term rental restrictions – Vancouver Sun
A sunken boat dream has left a bad taste in this Tim Hortons customer's mouth – CBC.ca
Best in Canada: Jets Beat Canucks to Finish Season as Top Canadian Club – The Hockey News