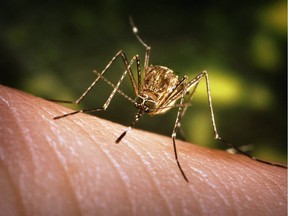
Contractors working for Lambton Public Health began applying larvicide June 26 in roadway catch basins around Sarnia and the rest of Lambton County to help control the local mosquito population and reduce the risk of the spread of the West Nile virus.
Health
Efforts begin to reduce spread of West Nile virus in Sarnia area
Passenger vehicles with a flashing beacon and the Pestalto insignia may also be used, the county said.
It’s the first of three rounds of larvicide treatments to local road catch basins, said Lori Lucas, a supervisor in health protection with Lambton Public Health. The second round is scheduled to begin July 17 and the third Aug. 14.
Each round takes about two weeks to complete, she said.
The St. Clair Region Conservation Authority had the larvicide contract with the county for “years and years” but decided not to do the work this year and Pestalto received the $93,000 contact, Lucas said.
“When there’s larvae in the catch basins, the larvicide prevents those larvae from turning into adult mosquitoes,” Lucas said.
West Nile virus is most commonly spread to humans by the bite of an infected mosquito.
The first human case of West Nile virus infection in Canada was reported in Ontario in 2002, according to Health Canada.
Lucas said local residents also are being urged to take steps to reduce the risk of the spread of West Nile virus, including emptying any standing water in their yards, including in toys and containers, as well as keeping eaves clear of debris.
“We know mosquitoes like to breed in those small pockets of shallow water where the water is stagnant,” she said.
Taking other steps to reduce the chance of mosquito bites is also encouraged.
That includes using insect repellent with DEET, particularly during peak mosquito hours at dawn and dusk.
Lambton Public Health says there were no reported local human cases of West Nile virus in 2022 or 2021, and one case in 2020. A total of seven local human cases have been recorded since 2012.
There were 23 human cases in Ontario last year.
“Most people that experience West Nile don’t get sick,” Lucas said. “They just experience very mild flu-like symptoms.”
Those cases generally wouldn’t lead to testing, she said.
Because of that, the virus could be present even if test-confirmed human cases aren’t showing up in the statistics.
“It probably is one of those illnesses that is under-reported just because most people don’t get severely ill,” Lucas said.
“But we still like to raise awareness and do what we can to help reduce cases.”
Local surveillance and testing of mosquito traps is set to begin locally in early July, the agency said.
Collecting and testing dead birds is no longer part of the agency’s West Nile virus surveillance program. Anyone who finds a dead bird should use gloves or a bag to put it out for garbage collection, Lambton Public Health said.
Information about West Nile virus is available from Lambton Public Health by calling 519-383-3824, and toll-free at 1-800-667-1839, ext. 3824, as well as online at lambtonpublichealth.ca.
Health
Canada to donate up to 200,000 vaccine doses to combat mpox outbreaks in Africa
The Canadian government says it will donate up to 200,000 vaccine doses to fight the mpox outbreak in Congo and other African countries.
It says the donated doses of Imvamune will come from Canada’s existing supply and will not affect the country’s preparedness for mpox cases in this country.
Minister of Health Mark Holland says the donation “will help to protect those in the most affected regions of Africa and will help prevent further spread of the virus.”
Dr. Madhukar Pai, Canada research chair in epidemiology and global health, says although the donation is welcome, it is a very small portion of the estimated 10 million vaccine doses needed to control the outbreak.
Vaccine donations from wealthier countries have only recently started arriving in Africa, almost a month after the World Health Organization declared the mpox outbreak a public health emergency of international concern.
A few days after the declaration in August, Global Affairs Canada announced a contribution of $1 million for mpox surveillance, diagnostic tools, research and community awareness in Africa.
On Thursday, the Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention said mpox is still on the rise and that testing rates are “insufficient” across the continent.
Jason Kindrachuk, Canada research chair in emerging viruses at the University of Manitoba, said donating vaccines, in addition to supporting surveillance and diagnostic tests, is “massively important.”
But Kindrachuk, who has worked on the ground in Congo during the epidemic, also said that the international response to the mpox outbreak is “better late than never (but) better never late.”
“It would have been fantastic for us globally to not be in this position by having provided doses a much, much longer time prior than when we are,” he said, noting that the outbreak of clade I mpox in Congo started in early 2023.
Clade II mpox, endemic in regions of West Africa, came to the world’s attention even earlier — in 2022 — as that strain of virus spread to other countries, including Canada.
Two doses are recommended for mpox vaccination, so the donation may only benefit 100,000 people, Pai said.
Pai questioned whether Canada is contributing enough, as the federal government hasn’t said what percentage of its mpox vaccine stockpile it is donating.
“Small donations are simply not going to help end this crisis. We need to show greater solidarity and support,” he said in an email.
“That is the biggest lesson from the COVID-19 pandemic — our collective safety is tied with that of other nations.”
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Sept. 13, 2024.
Canadian Press health coverage receives support through a partnership with the Canadian Medical Association. CP is solely responsible for this content.
The Canadian Press. All rights reserved.
Health
How many Nova Scotians are on the doctor wait-list? Number hit 160,000 in June
HALIFAX – The Nova Scotia government says it could be months before it reveals how many people are on the wait-list for a family doctor.
The head of the province’s health authority told reporters Wednesday that the government won’t release updated data until the 160,000 people who were on the wait-list in June are contacted to verify whether they still need primary care.
Karen Oldfield said Nova Scotia Health is working on validating the primary care wait-list data before posting new numbers, and that work may take a matter of months. The most recent public wait-list figures are from June 1, when 160,234 people, or about 16 per cent of the population, were on it.
“It’s going to take time to make 160,000 calls,” Oldfield said. “We are not talking weeks, we are talking months.”
The interim CEO and president of Nova Scotia Health said people on the list are being asked where they live, whether they still need a family doctor, and to give an update on their health.
A spokesperson with the province’s Health Department says the government and its health authority are “working hard” to turn the wait-list registry into a useful tool, adding that the data will be shared once it is validated.
Nova Scotia’s NDP are calling on Premier Tim Houston to immediately release statistics on how many people are looking for a family doctor. On Tuesday, the NDP introduced a bill that would require the health minister to make the number public every month.
“It is unacceptable for the list to be more than three months out of date,” NDP Leader Claudia Chender said Tuesday.
Chender said releasing this data regularly is vital so Nova Scotians can track the government’s progress on its main 2021 campaign promise: fixing health care.
The number of people in need of a family doctor has more than doubled between the 2021 summer election campaign and June 2024. Since September 2021 about 300 doctors have been added to the provincial health system, the Health Department said.
“We’ll know if Tim Houston is keeping his 2021 election promise to fix health care when Nova Scotians are attached to primary care,” Chender said.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Sept. 11, 2024.
The Canadian Press. All rights reserved.
Health
Newfoundland and Labrador monitoring rise in whooping cough cases: medical officer
ST. JOHN’S, N.L. – Newfoundland and Labrador‘s chief medical officer is monitoring the rise of whooping cough infections across the province as cases of the highly contagious disease continue to grow across Canada.
Dr. Janice Fitzgerald says that so far this year, the province has recorded 230 confirmed cases of the vaccine-preventable respiratory tract infection, also known as pertussis.
Late last month, Quebec reported more than 11,000 cases during the same time period, while Ontario counted 470 cases, well above the five-year average of 98. In Quebec, the majority of patients are between the ages of 10 and 14.
Meanwhile, New Brunswick has declared a whooping cough outbreak across the province. A total of 141 cases were reported by last month, exceeding the five-year average of 34.
The disease can lead to severe complications among vulnerable populations including infants, who are at the highest risk of suffering from complications like pneumonia and seizures. Symptoms may start with a runny nose, mild fever and cough, then progress to severe coughing accompanied by a distinctive “whooping” sound during inhalation.
“The public, especially pregnant people and those in close contact with infants, are encouraged to be aware of symptoms related to pertussis and to ensure vaccinations are up to date,” Newfoundland and Labrador’s Health Department said in a statement.
Whooping cough can be treated with antibiotics, but vaccination is the most effective way to control the spread of the disease. As a result, the province has expanded immunization efforts this school year. While booster doses are already offered in Grade 9, the vaccine is now being offered to Grade 8 students as well.
Public health officials say whooping cough is a cyclical disease that increases every two to five or six years.
Meanwhile, New Brunswick’s acting chief medical officer of health expects the current case count to get worse before tapering off.
A rise in whooping cough cases has also been reported in the United States and elsewhere. The Pan American Health Organization issued an alert in July encouraging countries to ramp up their surveillance and vaccination coverage.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Sept. 10, 2024.
The Canadian Press. All rights reserved.
-
Sports20 hours ago
Lawyer says Chinese doping case handled ‘reasonably’ but calls WADA’s lack of action “curious”
-
News20 hours ago
RCMP say 3 dead, suspects at large in targeted attack at home in Lloydminster, Sask.
-
News19 hours ago
B.C. to scrap consumer carbon tax if federal government drops legal requirement: Eby
-
Sports5 hours ago
Dolphins will bring in another quarterback, while Tagovailoa deals with concussion
-
Sports6 hours ago
David Beckham among soccer dignitaries attending ex-England coach Sven-Goran Eriksson’s funeral
-
News20 hours ago
Ceiling high for Vancouver Whitecaps midfielder Ahmed: Canada coach
-
News19 hours ago
A linebacker at West Virginia State is fatally shot on the eve of a game against his old school
-
News20 hours ago
Ottawa loses bid to quash Israel advocates’ lawsuit calling for halt to UNRWA funding