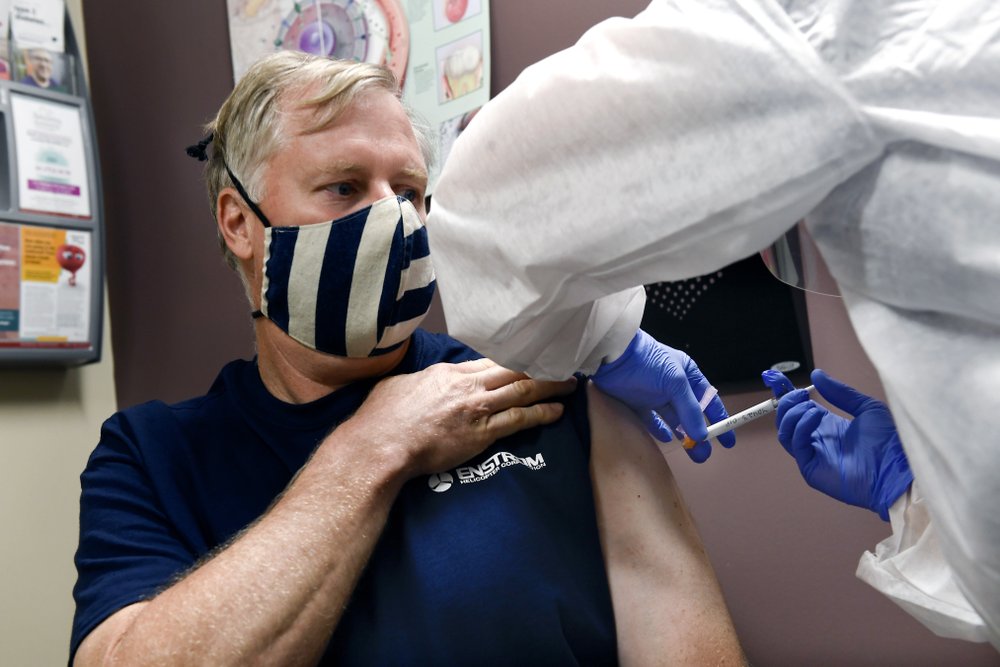
The biggest test yet of an experimental COVID-19 vaccine got underway Monday with the first of some 30,000 Americans rolling up their sleeves to receive shots created by the US government as part of the all-out global race to stop the pandemic.
The glimmer of hope came even as Google, in one of the gloomiest assessments of the coronavirus’s staying power from a major employer, decreed that most of its 200,000 employees and contractors should work from home through next June — a decision that could influence other big companies.
Final-stage testing of the vaccine, developed by the National Institutes of Health and Moderna Inc., began with volunteers at numerous sites around the US given either a real dose or a dummy without being told which.
“I’m excited to be part of something like this. This is huge,” said Melissa Harting, a 36-year-old nurse who received an injection in Binghamton, New York. Especially with family members in front-line jobs that could expose them to the virus, she added, “doing our part to eradicate it is very important to me.”
Another company, Pfizer Inc., announced late Monday that it had started its own study of its vaccine candidate in the US and elsewhere. That study also aimed to recruit 30,000 people.
It will be months before results trickle in, and there is no guarantee the vaccines will ultimately work against the scourge that has killed over 650,000 people around the world, including almost 150,000 in the US.
“We’ve been sitting on the sidelines passively attempting to wear our masks and social distance and not go out when it’s not necessary. This is the first step of becoming active against this,” said Dr. Frank Eder of Meridian Clinical Research, the company that runs the Binghamton trial site. “There’s really no other way to get past this.”
As if to underline how high the stakes are, there were more setbacks in efforts to contain the coronavirus.
In Washington, the Trump administration disclosed that national security adviser Robert O’Brien has the virus — the highest-ranking US official to test positive so far. The White House said he has mild symptoms and “has been self-isolating and working from a secure location off site.”
The move to restart the national pastime ran into trouble just five days into the long-delayed season: Two major league baseball games scheduled for Monday night were called off as the Miami Marlins coped with an outbreak — the Marlins’ home opener against the Baltimore Orioles, and the New York Yankees’ game in Philadelphia, where the Marlins used the clubhouse over the weekend.
As for relief from the economic damage done by the virus, Republicans on Capitol Hill rolled out a $1 trillion package that includes another round of $1,200 direct payments but reduces the extra $600 a week in federal unemployment benefits that expire for millions of Americans on Friday. Republicans proposed $200 a week, saying the generous bump discourages people from returning to work. Democrats call the added benefits a lifeline for those who have lost their jobs.
Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin and White House chief of staff Mark Meadows worked through the weekend on the GOP proposal and have agreed to negotiate with House Speaker Nancy Pelosi and Democratic Senate leader Chuck Schumer. House Democrats passed a $3 trillion relief package a couple of months ago.
In Europe, rising infections in Spain and other countries caused alarm only weeks after nations reopened their borders in hopes of reviving tourism. Over the weekend, Britain imposed a 14-day quarantine on travelers arriving from Spain, Norway ordered a 10-day quarantine for people returning from the entire Iberian peninsula, and France urged its citizens not to visit Spain’s Catalonia region.
Scientists set speed records getting vaccines into massive testing just months after the coronavirus emerged. But they stressed that the public shouldn’t fear that anyone is cutting corners.
“This is a significant milestone,” NIH Director Francis Collins said after the first test injection of Moderna’s vaccine was given, at 6:45 a.m. in Savannah, Georgia. “Yes, we’re going fast, but no, we are not going to compromise” on proving whether the vaccine is safe and effective.
“We are focusing on speed because every day matters,” added Stephane Bancel, CEO of Massachusetts-based Moderna.
After volunteers get two doses a month apart, scientists will closely track which group experiences more infections as they go about their daily routines, especially in areas where the virus is spreading unchecked.
The answer probably won’t come until November or December, cautioned Dr. Anthony Fauci, NIH’s infectious-diseases chief.
Among many questions the study may answer: How much protection does just one dose offer compared with the two scientists think are needed? If it works, will it protect against severe disease or block infection entirely?
Don’t expect a vaccine as strong as the measles vaccine, which prevents about 97% of measles infections, Fauci said, adding he would be happy with a COVID-19 vaccine that’s 60% effective.
Several other vaccines made by China and by Britain’s Oxford University began smaller final-stage tests in Brazil and other hard-hit countries earlier this month. But the U.S. requires its own tests of any vaccine that might be used in the country.
Full Coverage: Virus Outbreak
Every month through the fall, the government-funded COVID-19 Prevention Network will roll out a new study of a leading candidate, each with 30,000 volunteers.
The final US study of the Oxford shot is set to begin in August, followed by a candidate from Johnson & Johnson in September and one from Novavax in October.
That’s a stunning number of people needed to roll up their sleeves for science. In recent weeks, more than 150,000 Americans filled out an online registry signaling interest, Collins said. But many more are needed.
NIH is working to make sure that the study isn’t just filled with healthy, younger volunteers but includes populations hit hardest by COVID-19, including older adults, those in poor health and African-Americans and Latinos.
“We really are going to depend upon that sense of volunteerism for individuals from every different corner of society if we’re going to really find out how this vaccine, and its potential to end this terrible pandemic, is go to work in each of those groups,” Collins said.
___
By LAURAN NEERGAARD, MICHAEL HILL and JOCELYN NOVECK
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Department of Science Education. The AP is solely responsible for all content.
Image: Nurse Carolyn Grausgruber gives volunteer Ithaca firefighter Wade Bardo, of Erin, N.Y., an injection as the world’s biggest study of a possible COVID-19 vaccine, developed by the National Institutes of Health and Moderna Inc., gets underway Monday, July 27, 2020, in Binghamton, N.Y. (AP Photo/Hans Pennink)