Economy
Fast Internet Everywhere Could Add $160 Billion to US Economy – BNN

(Bloomberg) — The U.S. economy stands to gain $160 billion a year in extra output from a successful national high-speed internet plan that would boost labor productivity and allow more people to work from home, according to new research.
The study, which is based on survey data, attempts to put precise numbers on one of the bigger unknowns in President Joe Biden’s infrastructure plan: how much is universal broadband really worth?
“Moving to high-quality, fully reliable home internet service for all Americans would raise earnings-weighted labor productivity by an estimated 1.1% in the coming years,” economists Jose Maria Barrero, Nicholas Bloom and Steven Davis wrote in a paper released July 27. “The implied output gains are $160 billion per year,” equivalent to about 0.7% of gross domestic product.The study’s authors describe an “abrupt, enormous” shift to remote work as a result of the pandemic, which they expect to settle with about 20% of the U.S. labor force persistently working from home. The share could be higher for so-called knowledge workers whose jobs are mostly done on computer networks anyway.
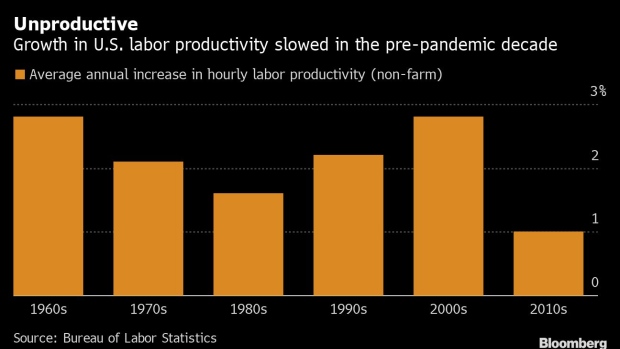
Slow productivity growth has been a major concern about the U.S. economy in recent years. Overall labor productivity was increasing at an average pace of around 1% in the decade before the pandemic, a historically low figure.
Davis, an economist at University of Chicago’s Booth School, said the biggest beneficiaries of the broadband plan are likely to be middle-income workers. Those on lower wages are often in jobs that require on-site labor, while high earners already have fast and reliable internet.
Middle Class
The research finds “few effects at the top end and fewer effects at the bottom end,” Davis said in an interview. “Evening out the earnings distribution in the short run is not one of our arguments.”
Biden’s plan aims to spread high-speed internet into corners of the country that don’t have a reliable service now. Senate negotiators are currently discussing a $65 billion investment in broadband investment, including the extension of monthly subsidies for low-income Americans, as part of a broader infrastructure bill.
More than 80% of respondents in the survey conducted by Davis and his colleagues said they had reliable internet quality, while around 16% reported moderate-to-poor or no connectivity. One of the big differences with high-speed broadband is the ability to move beyond text and messaging to video conferencing.
“Our data also suggest that better home internet access increases the propensity to work from home,” the economists wrote. “Universal access would, according to our estimate, raise the extent of WFH in the post-pandemic economy by about 0.7 of a percentage point,” they wrote, referring to work-from-home.
©2021 Bloomberg L.P.
Economy
Biden's Hot Economy Stokes Currency Fears for the Rest of World – Bloomberg


As Joe Biden this week hailed America’s booming economy as the strongest in the world during a reelection campaign tour of battleground-state Pennsylvania, global finance chiefs convening in Washington had a different message: cool it.
The push-back from central bank governors and finance ministers gathering for the International Monetary Fund-World Bank spring meetings highlight how the sting from a surging US economy — manifested through high interest rates and a strong dollar — is ricocheting around the world by forcing other currencies lower and complicating plans to bring down borrowing costs.
Economy
Opinion: Higher capital gains taxes won't work as claimed, but will harm the economy – The Globe and Mail
Canada’s Prime Minister Justin Trudeau and Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland hold the 2024-25 budget, on Parliament Hill in Ottawa, on April 16.Patrick Doyle/Reuters
Alex Whalen and Jake Fuss are analysts at the Fraser Institute.
Amid a federal budget riddled with red ink and tax hikes, the Trudeau government has increased capital gains taxes. The move will be disastrous for Canada’s growth prospects and its already-lagging investment climate, and to make matters worse, research suggests it won’t work as planned.
Currently, individuals and businesses who sell a capital asset in Canada incur capital gains taxes at a 50-per-cent inclusion rate, which means that 50 per cent of the gain in the asset’s value is subject to taxation at the individual or business’s marginal tax rate. The Trudeau government is raising this inclusion rate to 66.6 per cent for all businesses, trusts and individuals with capital gains over $250,000.
The problems with hiking capital gains taxes are numerous.
First, capital gains are taxed on a “realization” basis, which means the investor does not incur capital gains taxes until the asset is sold. According to empirical evidence, this creates a “lock-in” effect where investors have an incentive to keep their capital invested in a particular asset when they might otherwise sell.
For example, investors may delay selling capital assets because they anticipate a change in government and a reversal back to the previous inclusion rate. This means the Trudeau government is likely overestimating the potential revenue gains from its capital gains tax hike, given that individual investors will adjust the timing of their asset sales in response to the tax hike.
Second, the lock-in effect creates a drag on economic growth as it incentivizes investors to hold off selling their assets when they otherwise might, preventing capital from being deployed to its most productive use and therefore reducing growth.
Budget’s capital gains tax changes divide the small business community
And Canada’s growth prospects and investment climate have both been in decline. Canada currently faces the lowest growth prospects among all OECD countries in terms of GDP per person. Further, between 2014 and 2021, business investment (adjusted for inflation) in Canada declined by $43.7-billion. Hiking taxes on capital will make both pressing issues worse.
Contrary to the government’s framing – that this move only affects the wealthy – lagging business investment and slow growth affect all Canadians through lower incomes and living standards. Capital taxes are among the most economically damaging forms of taxation precisely because they reduce the incentive to innovate and invest. And while taxes on capital gains do raise revenue, the economic costs exceed the amount of tax collected.
Previous governments in Canada understood these facts. In the 2000 federal budget, then-finance minister Paul Martin said a “key factor contributing to the difficulty of raising capital by new startups is the fact that individuals who sell existing investments and reinvest in others must pay tax on any realized capital gains,” an explicit acknowledgment of the lock-in effect and costs of capital gains taxes. Further, that Liberal government reduced the capital gains inclusion rate, acknowledging the importance of a strong investment climate.
At a time when Canada badly needs to improve the incentives to invest, the Trudeau government’s 2024 budget has introduced a damaging tax hike. In delivering the budget, Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland said “Canada, a growing country, needs to make investments in our country and in Canadians right now.” Individuals and businesses across the country likely agree on the importance of investment. Hiking capital gains taxes will achieve the exact opposite effect.
Economy
Nigeria's Economy, Once Africa's Biggest, Slips to Fourth Place – Bloomberg


Nigeria’s economy, which ranked as Africa’s largest in 2022, is set to slip to fourth place this year and Egypt, which held the top position in 2023, is projected to fall to second behind South Africa after a series of currency devaluations, International Monetary Fund forecasts show.
The IMF’s World Economic Outlook estimates Nigeria’s gross domestic product at $253 billion based on current prices this year, lagging energy-rich Algeria at $267 billion, Egypt at $348 billion and South Africa at $373 billion.
-
Media6 hours ago
DJT Stock Rises. Trump Media CEO Alleges Potential Market Manipulation. – Barron's
-
Media8 hours ago
Trump Media alerts Nasdaq to potential market manipulation from 'naked' short selling of DJT stock – CNBC
-
Art24 hours ago
Collection of First Nations art stolen from Gordon Head home – Times Colonist
-
Investment7 hours ago
Private equity gears up for potential National Football League investments – Financial Times
-



 Health21 hours ago
Health21 hours agoType 2 diabetes is not one-size-fits-all: Subtypes affect complications and treatment options – The Conversation
-
Media20 hours ago
DJT Stock Jumps. The Truth Social Owner Is Showing Stockholders How to Block Short Sellers. – Barron's
-
Art24 hours ago
Crafting the Painterly Art Style in Eternal Strands – IGN First – IGN
-



 Sports22 hours ago
Sports22 hours agoHow the NHL moved the Arizona Coyotes to Salt Lake City – Sportsnet.ca




