Art
Fort McKay artist's council art reflects reconciliation and healing hopes, but demands injustices be confronted – Fort McMurray Today
Article content
The artwork in the new council chambers at the Jubilee Centre reflects the hopes and beliefs that local First Nation and Métis peoples have for reconciliation.
Article content
But Frederick McDonald, an artist from the Fort McKay First Nation commissioned for the paintings, made sure people at an April 25 unveiling ceremony didn’t forget why the artwork was made in the first place.
In a nine-minute poem, McDonald made people at the ceremony confront the legacies of the residential school system, 60s scoop and colonialism have on Indigenous peoples.
He talked about the high rates of homelessness, drug and alcohol addictions, unemployment, food insecurity and suicide found today in Indigenous communities across Canada.
His poem discussed the racism and discrimination inflicted upon Indigenous peoples by some leaders in politics, policing, health care, education, religion and business. He blasted the RCMP’s role in enforcing these policies throughout the years.
Politicians from all levels and parties were skewered. Even racist depictions of Indigenous people in movies and TV shows weren’t spared in his poem. If people listening to his poetry felt uncomfortable, that was his point.
“Have you heard enough? Have you had enough? Do you want to do something? Really, you still want to talk about truth and reconciliation?” he said.
“If you do, let’s talk about healing. Let’s talk about all our pains: there’s, your’s and mine. Let’s talk about the drum’s. Let’s talk about the dance. Let’s talk about celebrations and ceremony, about differences of culture, about understanding and working together. So much to do. So much to do. So let’s begin.”
Article content
McDonald’s poem captured the rage felt by so many First Nation, Métis and Inuit people, but his three paintings in the council chambers reflects his optimism in the future. He wanted his art to acknowledge the past but not dwell on pain or anger. This was also insisted upon by an elders council.
“As Aboriginal people, we want to be able to tell our own stories, so that’s what these paintings are all about,” said McDonald. “It’s about us sharing our stories, sharing them in a positive manner, working towards the future together—not side-by-side, not separate—but together going forward.”
A fourth piece is a talking stick, which was created by Elder Shurley Arthurs of the Fort McMurray First Nation 468. It sits at the desk where guest speakers address council. All the pieces were bound by teachings of honesty, love, truth, humility, wisdom, courage and respect.
“We hope relations between all people will continue to flourish. That is my big wish. I pray for that everyday. Because with the world as it is, who knows how much short time we have?” said Arthurs. “Love the people around you. It’s very important.”
Council decided in 2019 that the artwork for the new chambers would be completed by Indigenous artists, following a motion made by Councillor Keith McGrath. A committee was formed that included elders, knowledge keepers and creatives from Indigenous communities in the region.
Mayor Sandy Bowman said the art will remind council of the Indigenous history of this region, which serves “as a constant reminder to unite, and foster change and understanding.”









vmcdermott@postmedia.com
Art
The Venice Biennale and the Art of Turning Backward – The New York Times


There is a sour tendency in cultural politics today — a growing gap between speaking about the world and acting in it.
In the domain of rhetoric, everyone has grown gifted at pulling back the curtain. An elegant museum gallery is actually a record of imperial violence; a symphony orchestra is a site of elitism and exploitation: these critiques we can now deliver without trying. But when it comes to making anything new, we are gripped by near-total inertia. We are losing faith with so many institutions of culture and society — the museum, the market, and, especially this week, the university — but cannot imagine an exit from them. We throw bricks with abandon, we lay them with difficulty, if at all. We engage in perpetual protest, but seem unable to channel it into anything concrete.
So we spin around. We circle. And, maybe, we start going backward.
I’ve just spent a week tramping across Venice, a city of more than 250 churches, and where did I encounter the most doctrinaire catechism? It was in the galleries of the 2024 Venice Biennale, still the world’s principal appointment to discover new art, whose current edition is at best a missed opportunity, and at worst something like a tragedy.
It’s often preachy, but that’s not its biggest problem. The real problem is how it tokenizes, essentializes, minimizes and pigeonholes talented artists — and there are many here, among more than 300 participants — who have had their work sanded down to slogans and lessons so clear they could fit in a curator’s screenshot. This is a Biennale that speaks the language of assurance, but is actually soaked in anxiety, and too often resorts, as the Nigerian author Wole Soyinka deplored in a poem, to “cast the sanctimonious stone / And leave frail beauty shredded in the square / Of public shame.”
This year’s Biennale opened last week under an ominous star. The Venetian megashow consists of a central exhibition, spanning two locations, as well as around 90 independent pavilions organized by individual nations. One of these nations is Israel, and in the weeks before the vernissage an activist group calling itself the “Art Not Genocide Alliance” had petitioned the show’s organizers to exclude Israel from participating. The Biennale refused; a smaller appeal against the pavilion of Iran also went nowhere. (As for Russia, it remains nation non grata for the second Biennale in a row.) With disagreements over the war in Gaza spilling into cultural institutions across the continent — they’d already sunk Documenta, the German exhibition that is Venice’s only rival for attendance and prestige — the promise of a major controversy seemed to hang over the Giardini della Biennale.
As it happened, the artist and curator of Israel’s pavilion surprised the preview audience by closing their own show, and posted a sign at the entrance declaring it would stay shut until “a cease-fire and hostage release agreement is reached.” A small protest took place anyway (“No Death in Venice” was one slogan), but the controversy had only a tiny impact on the Prosecco-soaked Venetian carnival that is opening week. Right next door, at the U.S. Pavilion, twice as many visitors were waiting to get inside as were protesting.
One could strain to read the Israeli withdrawal productively, as part of a century-long tradition of empty, vacated or closed exhibitions by artists such as Rirkrit Tiravanija, Graciela Carnevale, and all the way back to Marcel Duchamp. Probably it was the only possible response to an untenable situation. Either way, the Israel pavilion encapsulated in miniature a larger dilemma and deficiency, in Venice and in culture more broadly: a thoroughgoing inability — even Foucault did not go this far! — to think about art, or indeed life, as anything other than a reflection of political, social or economic power.
That is certainly the agenda of the central exhibition, organized by the Brazilian museum director Adriano Pedrosa. I’d cheered when he was appointed curator of this year’s edition. At the São Paulo Museum of Art, one of Latin America’s boldest cultural institutions, Pedrosa had masterminded a cycle of centuries-spanning exhibitions that reframed Brazilian art as a crucible of African, Indigenous, European and pan-American history. His nomination came a few weeks after Giorgia Meloni became Italy’s first far-right prime minister since World War II. And Pedrosa — who had successfully steered his museum through Brazil’s own far-right presidency of 2018-22 — promised a show of cosmopolitanism and variety, as expressed in a title, “Foreigners Everywhere,” that seemed like a moderate anti-Meloni dig.
But what Pedrosa has actually brought to Venice is a closed, controlled, and at times belittling showcase, which smooths out all the distinctions and contradictions of a global commons. The show is remarkably placid, especially in the Giardini. There are large doses of figurative painting and (as customary these days) weaving and tapestry arranged in polite, symmetrical arrays. There is art of great beauty and power, such as three cosmological panoramas by the self-taught Amazonian painter Santiago Yahuarcani, and also far less sophisticated work celebrated by the curator in the exact same way.
In the brutal rounding-down arithmetic of the 2024 Venice Biennale, to be a straniero — a “foreigner” or “stranger,” applied equally to graduates of the world’s most prestigious M.F.A. programs and the mentally ill — implies moral credibility, and moral credibility equals artistic importance. Hence Pedrosa’s inclusion of L.G.B.T.Q. people as “foreigners,” as if gender or sexuality were proof of progressive bona fides. (Gay men have led far-right parties in the Netherlands and Austria; over at Venice’s Peggy Guggenheim Collection is a wonderfully pervy show of the polymathic Frenchman Jean Cocteau, who praised Nazis while drawing sailors without their bell-bottoms.)
Even more bizarre is the designation of the Indigenous peoples of Brazil and Mexico, of Australia and New Zealand, as “foreigners”; surely they should be the one class of people exempt from such estrangement. In some galleries, categories and classifications take precedence over formal sophistication to a derogatory degree. The Pakistan-born artist Salman Toor, who paints ambiguous scenes of queer New York with real acuity and invention, is shown alongside simplistic queer-and-trans-friendly street art from an Indian NGO “spreading positivity and hope to their communities.”
Over and over, the human complexity of artists gets upstaged by their designation as group members, and art itself gets reduced to a symptom or a triviality. I felt that particularly in three large, shocking galleries in the central pavilion of the Giardini, packed tight with more than 100 paintings and sculptures made in Asia, Africa, Latin America and the Middle East between 1915 and 1990. These constitute the bulk of what Pedrosa calls the show’s nucleo storico, its historical core, and this was the part of the Biennale I’d looked forward to most. It had promised to demonstrate that the world outside the North Atlantic has a history of modern art far richer than our leading museums have shown us.
Indeed it does. But you won’t learn that here, where paintings of wildly different importance and quality have been shoved together with almost no historical documentation, cultural context, or even visual delight. It flushes away distinctions between free and unfree regimes or between capitalist and socialist societies, or between those who joined an international avant-garde and those who saw art as a nationalist calling. True pioneers, such as the immense Brazilian innovator Tarsila do Amaral, are equated with orthodox or traditionalist portraitists. More ambitious exhibitions — notably the giant “Postwar,” staged in Munich in 2016-17 — used critical juxtaposition and historical documentation to show how and why an Asian modernism, or an African modernism, looked the way it did. Here in Venice, Pedrosa treats paintings from all over as just so many postage stamps, pasted down with little visual acuity, celebrated merely for their rarity to an implied “Western” viewer.
You thought we were all equals? Here you have the logic of the old-style ethnological museum, transposed from the colonial exposition to the Google Images results page. S.H. Raza of India, Saloua Raouda Choucair of Lebanon, the Cuban American Carmen Herrera, and also painters who were new to me, got reduced to so much Global South wallpaper, and were photographed by visitors accordingly. All of which shows that it’s far too easy to speak art’s exculpatory language, to invoke “opacity” or “fugitivity” or whatever today’s decolonial shibboleth may be. But by othering some 95 percent of humanity — by designating just about everyone on earth as “foreigners,” and affixing categories onto them with sticky-backed labels — what you really do is exactly what those dreadful Europeans did before you: you exoticize.
And yet, for all that, there is so much I liked in this year’s Biennale! From the central exhibition I am still thinking about a monumental installation of unfired coils of clay by Anna Maria Maiolino, a winner of the Golden Lion for Lifetime Achievement, that recasts serial production as something intimate, irregular, even anatomical. Karimah Ashadu, who won the Silver Lion for her high-speed film of young men bombing across Lagos on banned motorbikes, gave the economic intensity of megacity life a vigorous visual language. There are the stark, speechless paintings from the 1970s of Romany Eveleigh, whose thousands of scratched little O’s turn writing into an unsemantic howl. There are Yuko Mohri’s mischievously articulated assemblages of found objects, plastic sheeting and fresh fruit, in the Japanese Pavilion, and Precious Okoyomon’s Gesamtkunstwerk of soil, speakers and motion sensors, in the Nigerian Pavilion.
Beyond the Biennale, Christoph Büchel’s frenzied exhibition at the Fondazione Prada assembles mountains of junk and jewels into an impertinent exposé of wealth and debt, colonialism and collecting. In the Palazzo Contarini Polignac, a hazily elegant video by the Odesa-born artist Nikolay Karabinovych reinscribes the Ukrainian landscape as a crossroads of languages, religions and histories. Above all there is Pierre Huyghe, at the Punta della Dogana, who fuses human intelligence and artificial intelligence into the rarest thing of all: an image we have never seen before.
What all these artists have in common is some creative surplus that cannot be exploited — not for a nation’s image, not for a curator’s thesis, not for a collector’s vanity. Rather than the sudsy “politics” of advocacy, they profess that art’s true political value lies in how it exceeds rhetorical function or financial value, and thereby points to human freedom. They are the ones who offered me at least a glimpse of what an equitable global cultural assembly could be: an “anti-museum,” in the phrase of the Cameroonian philosopher Achille Mbembe, where “the exhibiting of subjugated or humiliated humanities” at last becomes a venue where everyone gets to be more than a representative.
I still, unfashionably, keep faith with Mbembe’s dream institution, and the artists here who would have their place in it. But we won’t build it with buzzwords alone, and if anyone had actually been paying attention to the political discourse in this part of the world in a time of war, they would have realized that two can play this game. “An essentially emancipatory, anticolonial movement against unipolar hegemony is taking shape in the most diverse countries and societies” — did someone in the 2024 Venice Biennale say that? No, it was Vladimir Putin.
Art
Turner Prize shortlist includes art showcasing Scottish Sikh community
|
|
A Scottish artist who uses cars, worship bells and Irn-Bru in her work is among the nominees for this year’s Turner Prize.
Glasgow-born Jasleen Kaur’s work reflects her life growing up in the city’s Sikh community.
She is up for the prestigious art award, now in its 40th year, alongside Pio Abad, Claudette Johnson and Delaine Le Bas.
Turner Prize jury chairman Alex Farquharson described it as a “fantastic shortlist of artists”
Works by the nominated artists will go on show at London’s Tate Britain gallery from 25 September.
They will receive £10,000 each, while the winner, to be announced on 3 December, will get £25,000.
In a statement, Farquharson said: “All four make work that is full of life.
“They show how contemporary art can fascinate, surprise and move us, and how it can speak powerfully of complex identities and memories, often through the subtlest of details.
“In the Turner Prize’s 40th year, this shortlist proves that British artistic talent is as rich and vibrant as ever.”
The shortlisted artists are:
Pio Abad
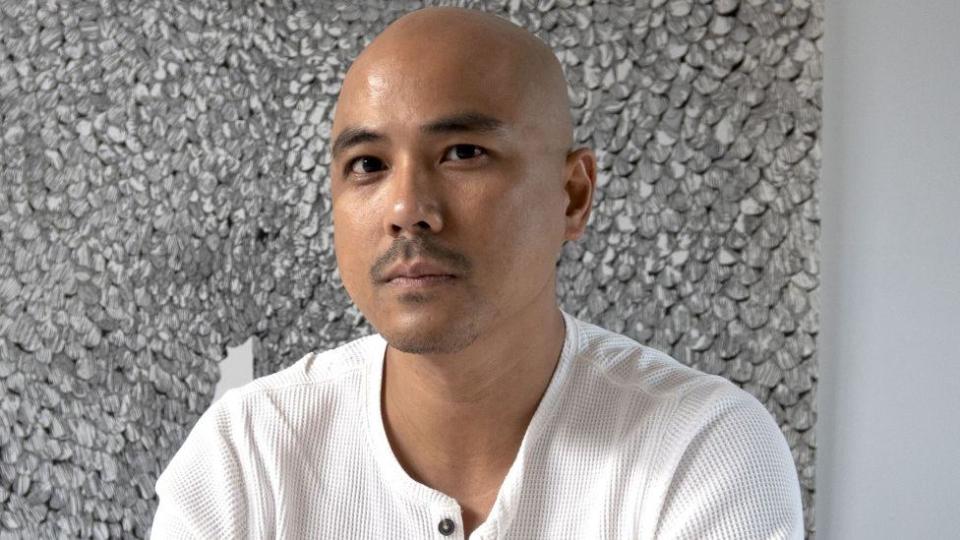
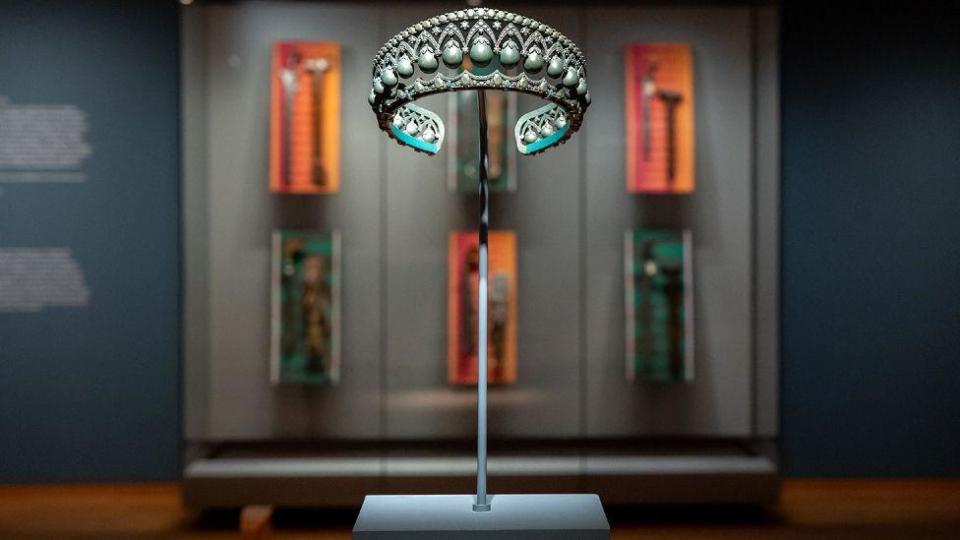




Manila-born Abad’s solo exhibition To Those Sitting in Darkness at the Ashmolean Museum in Oxford included drawings, etchings and sculptures that combined to “ask questions of museums”, according to the jury.
The 40-year-old, who works in London, reflects on colonial history and growing up in the Philippines, where his parents struggled against authoritarianism.
The title of his exhibit is a nod to Mark Twain’s 1901 essay To the Person Sitting In Darkness, which hit out at imperialism.
Jasleen Kaur
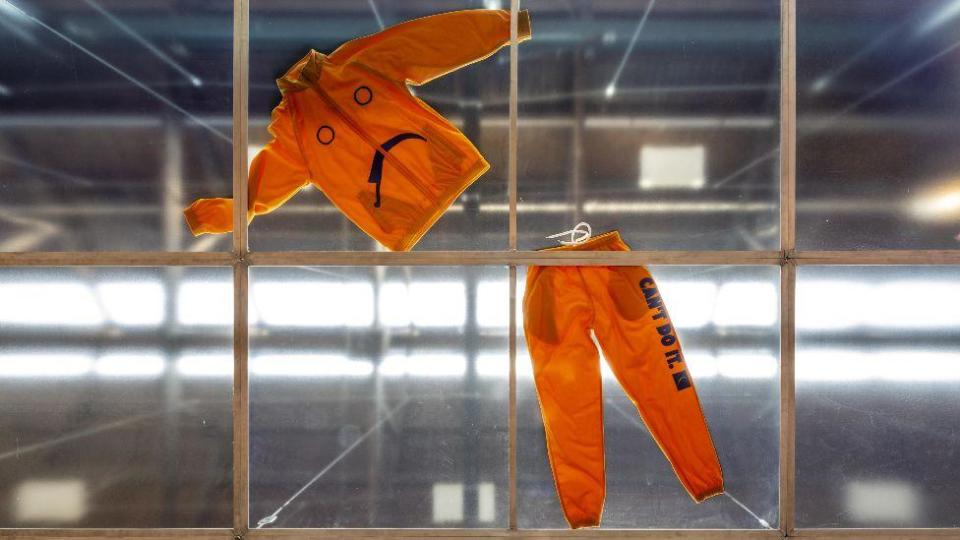
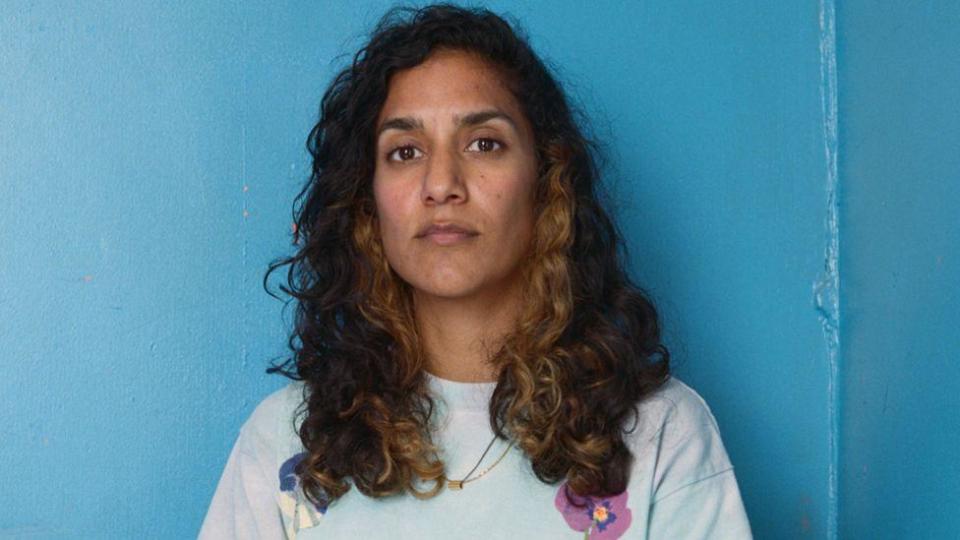
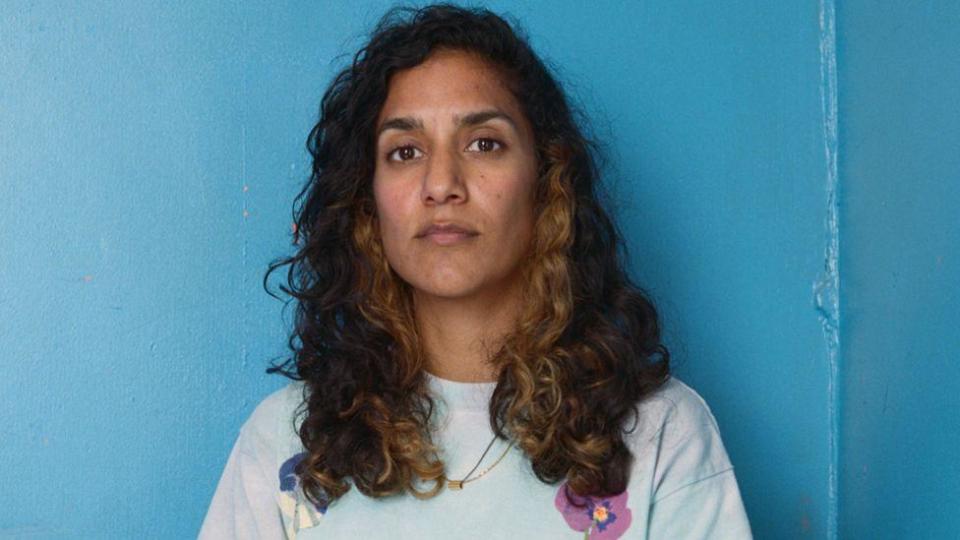


Kaur is on the list for Alter Altar at Tramway, Glasgow, which included family photos, an Axminster carpet, a classic Ford Escort covered in a giant doily, Irn-Bru and kinetic handbells.
The 37-year-old, who lives in London, had previously showcased her work at the Victoria and Albert Museum by looking at popular Indian cinema.
Delaine Le Bas
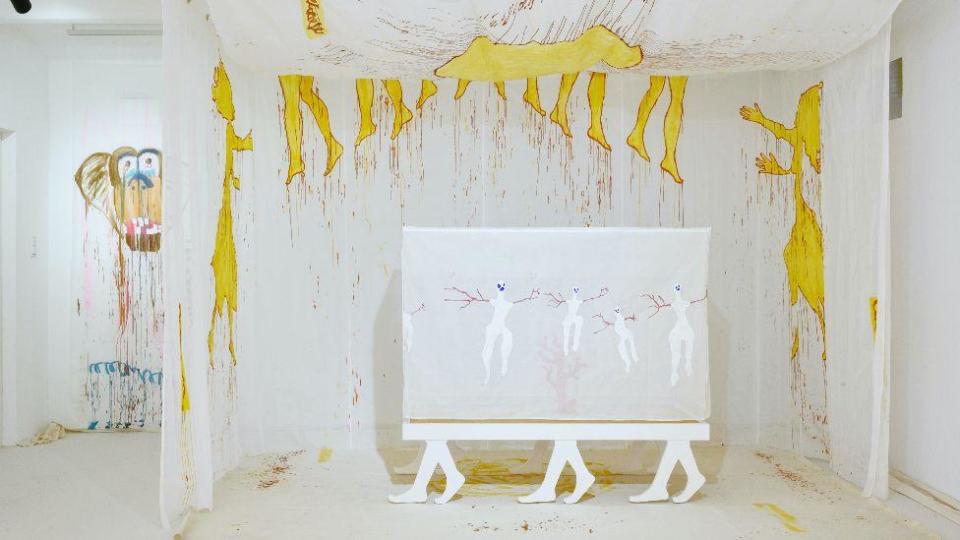




Worthing-born Le Bas is nominated for an exhibition titled Incipit Vita Nova. Here Begins The New Life/A New Life Is Beginning. Staged at the Secession art institute in Vienna, Austria, it saw painted fabrics hung, with theatrical costumes and sculptures also part of the exhibit.
The 58-year-old artist was inspired by the death of her grandmother and the history of the Roma people.
The jury said they “were impressed by the energy and immediacy present in this exhibition, and its powerful expression of making art in a time of chaos”.
Claudette Johnson
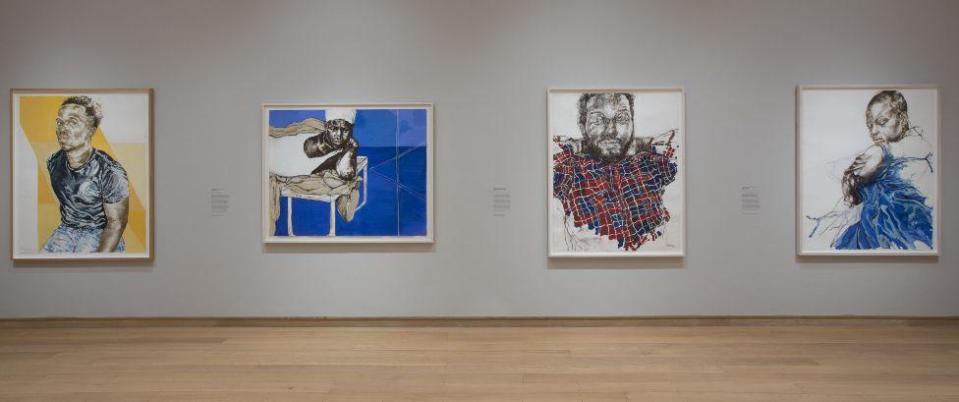




Manchester-born Johnson has been given the nod for her solo exhibition Presence at the Courtauld Gallery in London, and Drawn Out at Ortuzar Projects, New York.
She uses portraits of black women and men in a combination of pastels, gouache and watercolour, and was praised by the judges for her “sensitive and dramatic use of line, colour, space and scale to express empathy and intimacy with her subjects”.
Johnson, 65, was appointed an MBE in 2022 after being named on the New Year Honours list for her services to the arts.





Art
Turner Prize: Shortlisted artist showcases Scottish Sikh community
|
|
Turner Prize shortlist includes art showcasing Scottish Sikh community
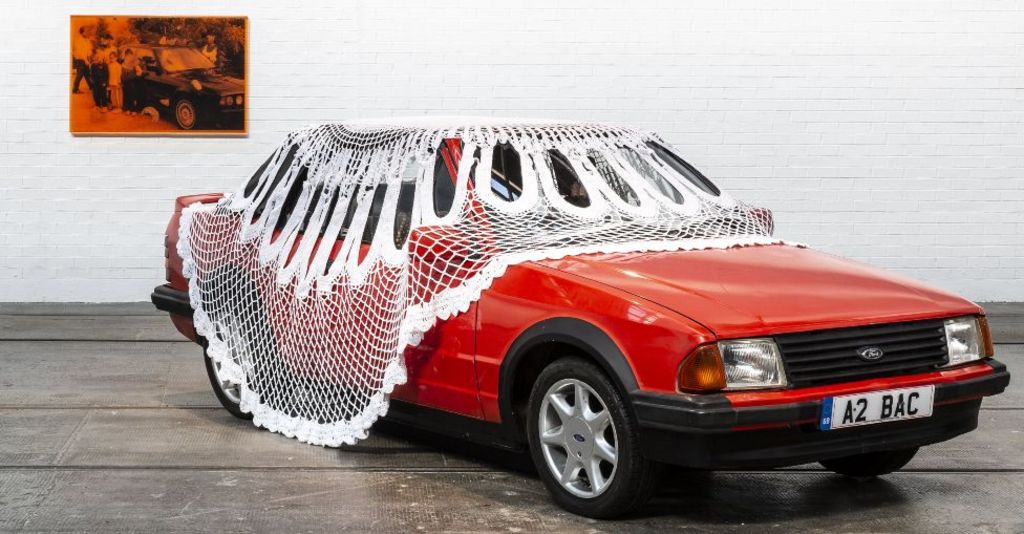


A Scottish artist who uses cars, worship bells and Irn-Bru in her work is among the nominees for this year’s Turner Prize.
Glasgow-born Jasleen Kaur’s work reflects her life growing up in the city’s Sikh community.
She is up for the prestigious art award, now in its 40th year, alongside Pio Abad, Claudette Johnson and Delaine Le Bas.
Turner Prize jury chairman Alex Farquharson described it as a “fantastic shortlist of artists”
Works by the nominated artists will go on show at London’s Tate Britain gallery from 25 September.
They will receive £10,000 each, while the winner, to be announced on 3 December, will get £25,000.
In a statement, Farquharson said: “All four make work that is full of life.
“They show how contemporary art can fascinate, surprise and move us, and how it can speak powerfully of complex identities and memories, often through the subtlest of details.
“In the Turner Prize’s 40th year, this shortlist proves that British artistic talent is as rich and vibrant as ever.”
The shortlisted artists are:
Pio Abad
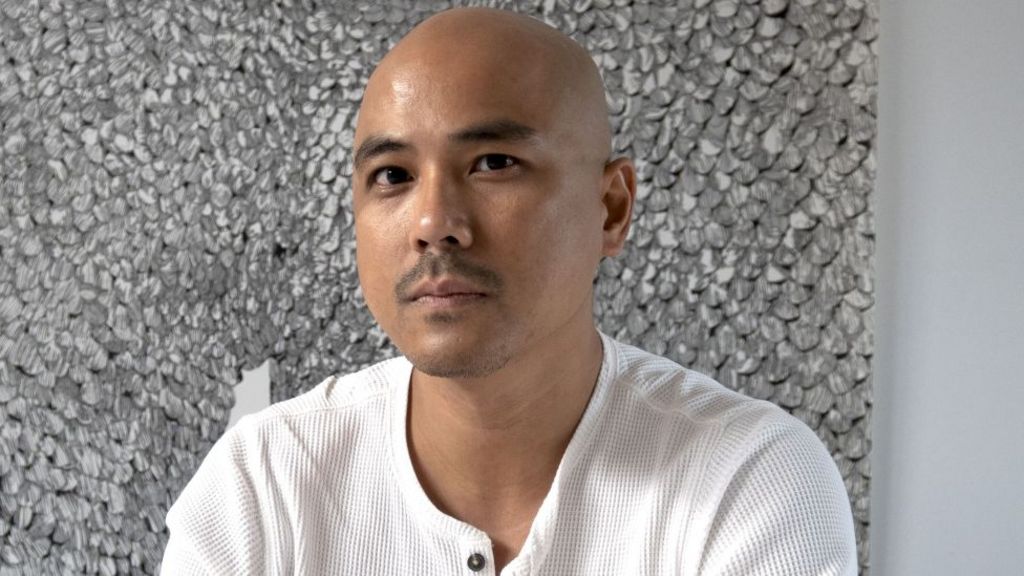




Manila-born Abad’s solo exhibition To Those Sitting in Darkness at the Ashmolean Museum in Oxford included drawings, etchings and sculptures that combined to “ask questions of museums”, according to the jury.
The 40-year-old, who works in London, reflects on colonial history and growing up in the Philippines, where his parents struggled against authoritarianism.
The title of his exhibit is a nod to Mark Twain’s 1901 essay To the Person Sitting In Darkness, which hit out at imperialism.
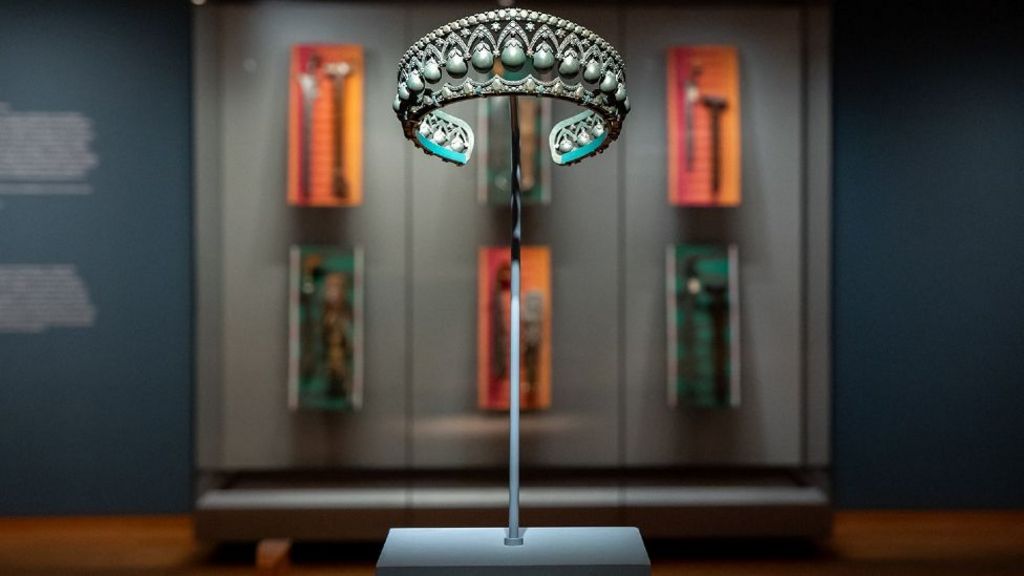
Jasleen Kaur
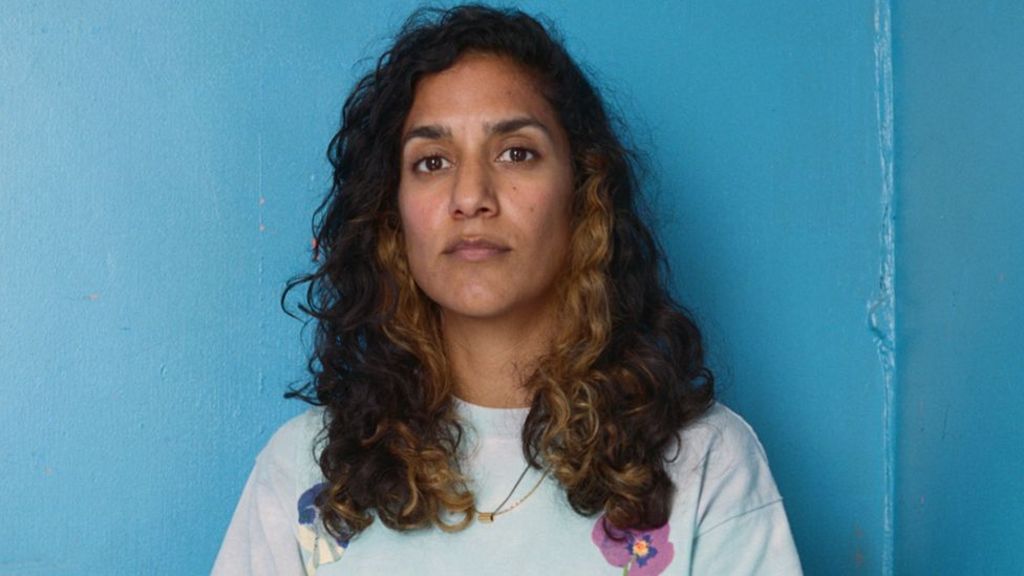




Kaur is on the list for Alter Altar at Tramway, Glasgow, which included family photos, an Axminster carpet, a classic Ford Escort covered in a giant doily, Irn-Bru and kinetic handbells.
The 37-year-old, who lives in London, had previously showcased her work at the Victoria and Albert Museum by looking at popular Indian cinema.
Delaine Le Bas
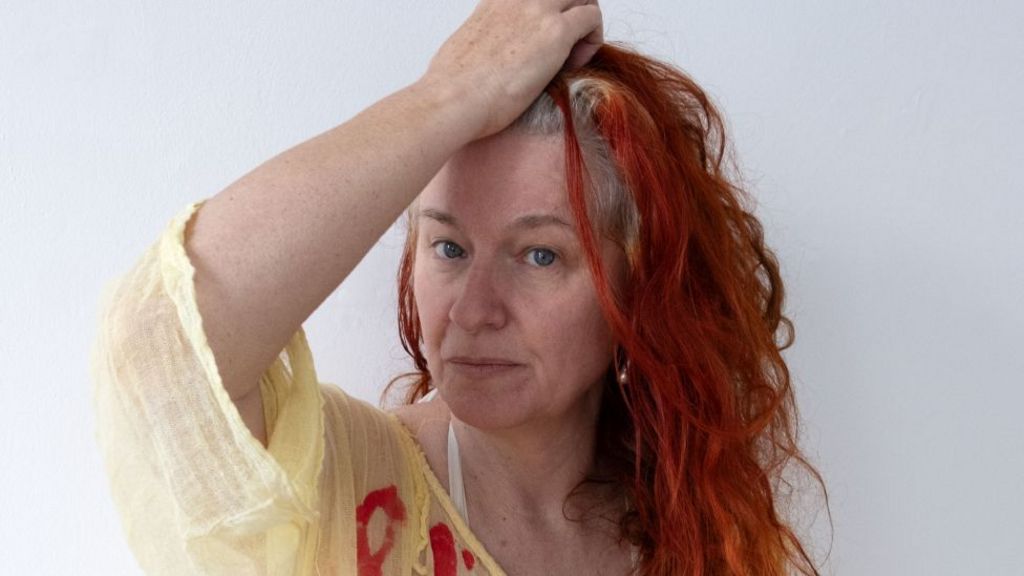
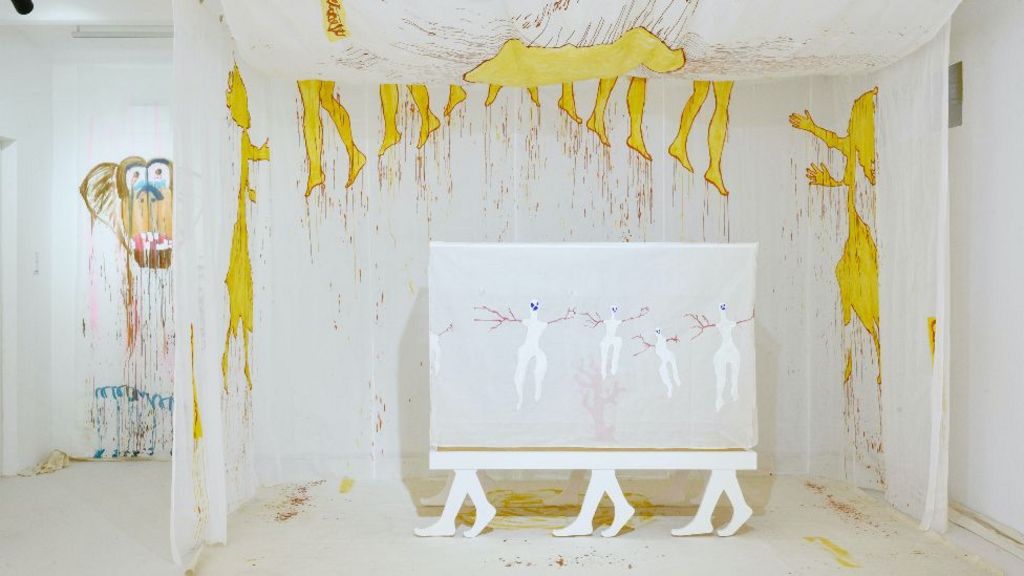




Worthing-born Le Bas is nominated for an exhibition titled Incipit Vita Nova. Here Begins The New Life/A New Life Is Beginning. Staged at the Secession art institute in Vienna, Austria, it saw painted fabrics hung, with theatrical costumes and sculptures also part of the exhibit.
The 58-year-old artist was inspired by the death of her grandmother and the history of the Roma people.
The jury said they “were impressed by the energy and immediacy present in this exhibition, and its powerful expression of making art in a time of chaos”.
Claudette Johnson
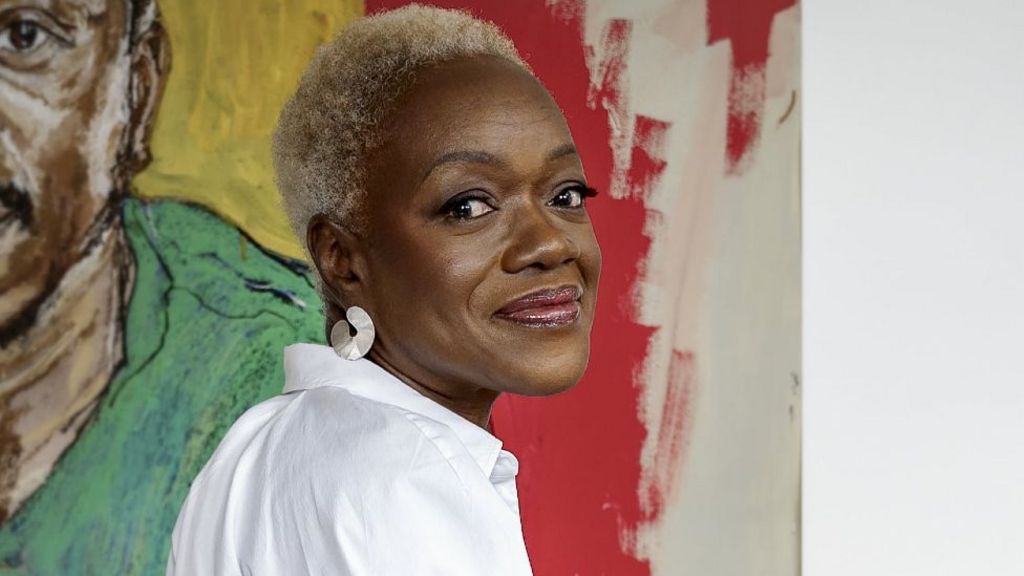
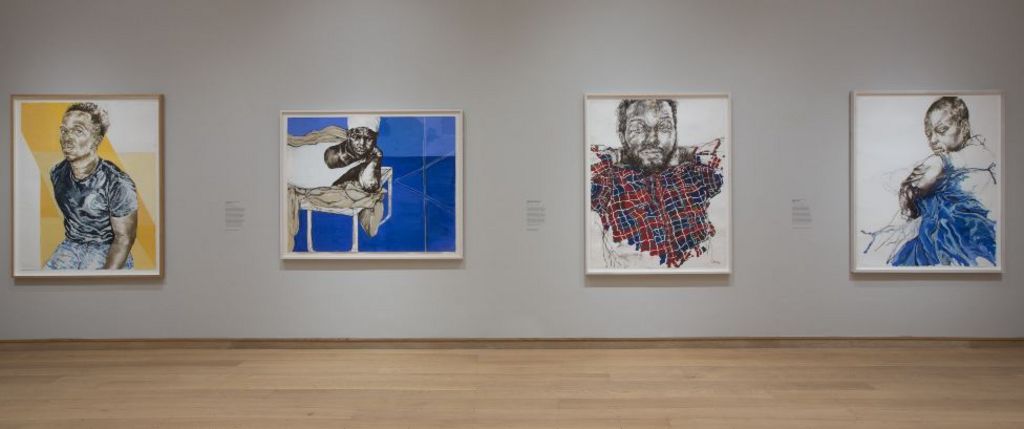




Manchester-born Johnson has been given the nod for her solo exhibition Presence at the Courtauld Gallery in London, and Drawn Out at Ortuzar Projects, New York.
She uses portraits of black women and men in a combination of pastels, gouache and watercolour, and was praised by the judges for her “sensitive and dramatic use of line, colour, space and scale to express empathy and intimacy with her subjects”.
Johnson, 65, was appointed an MBE in 2022 after being named on the New Year Honours list for her services to the arts.





-



 Politics22 hours ago
Politics22 hours agoOpinion: Fear the politicization of pensions, no matter the politician
-



 Politics21 hours ago
Politics21 hours agoPecker’s Trump Trial Testimony Is a Lesson in Power Politics
-



 Science21 hours ago
Science21 hours agoNASA Celebrates As 1977’s Voyager 1 Phones Home At Last
-
Media14 hours ago
B.C. online harms bill on hold after deal with social media firms
-
Media20 hours ago
B.C. puts online harms bill on hold after agreement with social media companies
-
Business20 hours ago
Oil Firms Doubtful Trans Mountain Pipeline Will Start Full Service by May 1st
-
Real eState20 hours ago
Judge Approves $418 Million Settlement That Will Change Real Estate Commissions
-
Media19 hours ago
Trump poised to clinch US$1.3-billion social media company stock award





