Article content
(Bloomberg) — Asset managers love them, while clients seem increasingly wary of them: Article 8 funds.
Asset managers love them, while clients seem increasingly wary of them: Article 8 funds.
(Bloomberg) — Asset managers love them, while clients seem increasingly wary of them: Article 8 funds.
It’s a category within Europe’s ESG investing rulebook that saw huge growth last quarter, as the asset-management industry slapped an Article 8 — also known as “light green” — tag on well over 600 funds that previously weren’t classified as sustainable, according to data provided by Morningstar Inc. At the same time, clients withdrew more than $30 billion from such products. A stricter environmental, social and governance classification — Article 9 — saw $6 billion of inflows.
When an asset manager sells a fund as Article 8, they’re promising clients that their money will go toward “promoting” sustainability. It’s a concept that was enshrined in the EU’s Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation, which started being enforced in March 2021 as the world’s boldest anti-greenwash rulebook to date. But 16 months on, there’s hardly any agreement within the fund industry as to what “promoting” sustainability means. What’s more, even regulators in the EU don’t really see eye to eye.
For investment clients trying to decide where to get the most bang for their ESG buck, it’s now “impossible” to do a meaningful comparison across products, according to Morningstar.
Meanwhile, there continue to be questions around the ESG-ness of Article 8. A Morningstar data analysis found that roughly two-thirds of Article 8 funds target between zero and 10% minimum exposure to sustainable investments.
A new regulatory framework is taking effect that will require financial advisers to make sure they’re taking ESG retail clients’ expectations into account, and explaining the characteristics of financial products in a way that doesn’t lead to misunderstandings. It’s an amendment to the revised Markets in Financial Instruments Directive that law firm Simmons & Simmons, which advises asset managers, has already suggested will add a new layer of risk to the asset-management industry.
“Because of patchy data and a lack of direct comparability between products, financial advisers will struggle to fulfill their new obligations,” according to Morningstar.
NEWS ROUNDUP
Social Taxonomy Shelved | The next milestone in Europe’s efforts to create a global benchmark for ESG investing has been shelved indefinitely as officials balk at devoting resources to a process that’s already marred by deep political division.
Meta Reacts to Data Pact | Meta Platforms Inc. reiterated its threat to pull its popular Facebook and Instagram services from the European Union if a new transatlantic data transfer pact doesn’t materialize. Its latest warning comes amid an imminent data flow ban it already faces from Ireland’s data-protection watchdog, which oversees the tech giants based in the country.
Fashion Probe | The UK’s competition watchdog started a probe into potentially misleading environmental claims made by fashion brands Asos Plc, Boohoo Group Plc and George at Asda, over greenwashing concerns.
ISSB Faces Criticism | The organization aiming to set worldwide climate reporting requirements for decades to come is under fire for putting corporate interests ahead of the planet’s.
Pimco Downgrades ESG Funds | Pacific Investment Management Co. and NN Investment Partners have cut the ESG status of a number of their funds after European authorities clarified rules guiding such classifications.
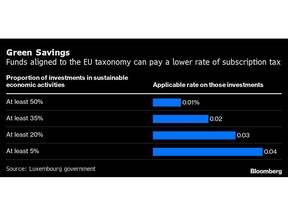
No Tax Break | In Luxembourg, the world’s biggest hub for ESG asset managers, firms have been unable to take advantage of a tax break intended to reward their efforts to do more sustainable investing.
Banks Fall Short | The world’s biggest banks are coming up short in their efforts to rein in global warming, according to an investor group representing more than $50 trillion of assets.
EU Climate Benchmarks | Investment funds tracking EU-regulated climate benchmarks jumped 25% last quarter, as asset managers look for ways to combat greenwashing.
EU Deal to Cut Gas Use | European Union countries reached a political agreement to cut their gas use by 15% through next winter as the prospect of a full cutoff from Russian supplies grows increasingly likely.
Gas and Nuclear | EU lawmakers voted to allow natural gas and nuclear energy to be labeled as green investments, removing the last major barrier to potentially billions of euros of funding from environmental investors.
US Climate Deal | In a breakthrough that surprised much of Washington, Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer and Senator Joe Manchin announced that they agreed on a plan that includes a record $370 billion in spending to fight climate change.
US States Target Banks | West Virginia will restrict BlackRock Inc., Goldman Sachs Group Inc., JPMorgan Chase & Co., Morgan Stanley and Wells Fargo & Co. from state banking contracts after the Republican state treasurer found that the companies engage in a so-called boycott of the fossil-fuels industry.
FSB Warns Banks | Financial institutions should brace for greater scrutiny as the world moves toward a low-carbon economy, the Financial Stability Board said in a report.
EU Targets Insurers | The EU’s top insurance regulator wants national authorities to tighten supervision amid evidence companies are using artificial intelligence to drive up prices unrelated to the risk or cost of service.
BLOOMBERG RESEARCH
Guarding Against Greenwashing | As ESG has increasingly affected investment decisions in Europe, the need for transparent and comparable data has become pivotal. Public-company disclosures can differ drastically, as reporting standards are new and often changing. Bloomberg and MSCI were the most frequently named as the No. 1 or No. 2 source of ESG data among European funds that were surveyed.
Most traders named multiple providers, suggesting they value various data inputs, and there’s room for competition. Almost a quarter of traders surveyed believe greenwashing accounts for more than 50% of ESG. Small funds were surprisingly more pessimistic, as they showed more support for ESG throughout the study.
What percentage of ESG is greenwashing?
US Climate Bill’s Impact | Vestas Wind Systems AS, First Solar Inc., SolarEdge Technologies Inc. and other clean-energy equipment suppliers may see elevated US demand for wind and solar energy in 2023-2025 — with potential upgrades to consensus sales expectations — if the Inflation Reduction Act becomes law.
Carbon Border Tax | This will be a “make or break” year for launching a carbon tariff on imported goods, according to BloombergNEF. The European Commission has proposed levying a tariff on iron and steel, aluminum, fertilizers and cement. In addition, the European Parliament wants to include organic basic chemicals, plastics and hydrogen. With introduction planned for next year, “consensus on devilish questions around coverage, timeline and exports is lacking,” analyst Antoine Vagneur-Jones wrote in a July 27 report.
OFF THE SHELF
ESG Meets Real World | ESG has become a punching bag for the far right, disgruntled corporate executives and even industry insiders.
Taxonomies | Floods, droughts and food shortages are just some of the effects of climate change, while exploitation and corruption drive social injustice around the world. Governments tackling these issues are realizing that to solve them, they need first to define and measure them. Some are turning to so-called taxonomies that establish which economic practices and products are harmful to the planet and which aren’t. The idea is that the price of goods and services must reflect the human and environmental cost of both production and disposal, which in turn would spur much-needed change. But designing a code is fiendishly difficult.
OTHER ESG-F0CUSED FIXTURES
Run NSUB ESG to subscribe to the ESG newsletters listed below:


It’s time to ask a rude question: Is Canada still worth investing in?
Before you rush to deliver an appropriately patriotic response, think about the issue for a moment.
A good place to begin is with the federal government’s announcement this week that it is forming a task force under former Bank of Canada governor Stephen Poloz. The task force’s job will be to find ways to encourage Canadian pension funds to invest more of their assets in Canada.
Wooing pension funds has become a high-priority matter for Ottawa because, at the moment, these big institutional investors don’t invest all that much in Canada. The Canada Pension Plan Investment Board, for instance, had a mere 14 per cent of its massive $570-billion portfolio in Canadian assets at the end of its last fiscal year.
Other major Canadian pension plans have similar allocations, especially if you look beyond their holdings of government bonds and consider only their investments in stocks, infrastructure and real assets. When it comes to such risky assets, these big, sophisticated players often see more potential for good returns outside of Canada than at home.
This leads to a simple question: If the CPPIB and other sophisticated investors aren’t overwhelmed by Canada’s investment appeal, why should you and I be?
It’s not as if Canadian stocks have a record of outstanding success. Over the past decade, they have lagged far behind the juicy returns of the U.S.-based S&P 500.
To be fair, other countries have also fallen short of Wall Street’s glorious run. Still, Canadian stocks have only a middling record over the past 10 years even when measured against other non-U.S. peers. They have trailed French and Japanese stocks and achieved much the same results as their Australian counterparts. There is no obvious Canadian edge.
There are also no obvious reasons to think this middle-of-the-pack record will suddenly improve.
A generation of mismanagement by both major Canadian political parties has spawned a housing crisis and kneecapped productivity growth. It has driven household debt burdens to scary levels.
Policy makers appear unwilling to take bold action on many long-standing problems. Interprovincial trade barriers remain scandalously high, supply-managed agriculture continues to coddle inefficient small producers, and tax policy still pushes people to invest in homes rather than in productive enterprises.
From an investor’s perspective, the situation is not that appetizing. A handful of big banks, a cluster of energy producers and a pair of railways dominate Canada’s stock market. They are solid businesses, yes, but they are also mature industries, with less than thrilling growth prospects.
What is largely missing from the Canadian stock scene are big companies with the potential to expand and innovate around the globe. Shopify Inc. SHOP-T and Brookfield Corp. BN-T qualify. After that, the pickings get scarce, especially in areas such as health care, technology and retailing.
So why hold Canadian stocks at all? Four rationales come to mind:
How compelling you find these rationales will depend upon your personal circumstances. Based strictly on the numbers, Canadian stocks look like ho-hum investments – they’re reasonable enough places to put your money, but they fail to stand out compared with what is available globally.
Canadians, though, have always displayed a striking fondness for homebrew. Canadian stocks make up only a smidgen of the global market – about 3 per cent, to be precise – but Canadians typically pour more than half of their total stock market investments into Canadian stocks, according to the International Monetary Fund. This home market bias is hard to justify on any rational basis.
What is more reasonable? Vanguard Canada crunched the historical data in a report last year and concluded that Canadian investors could achieve the best balance between risk and reward by devoting only about 30 per cent of their equity holdings to Canadian stocks.
This seems to be more or less in line with what many Canadian pension funds currently do. They have about half their portfolio in equities, so devoting 30 per cent of that half to domestic stocks works out to holding about 15 per cent of their total portfolio in Canadian equities.
That modest allocation to Canadian stocks is a useful model for Canadian investors of all sizes. And if Ottawa doesn’t like it? Perhaps it could do more to make Canada an attractive investment destination.
You might not think it’s possible to outperform the average Wall Street professional with just a single investment. Fund managers are highly educated and steeped in market data. They get paid a lot of money to make smart investments.
But the truth is, most of them may not be worth the money. With the right steps, individual investors can outperform the majority of active large-cap mutual fund managers over the long run. You don’t need a doctorate or MBA, and you certainly don’t need to follow the everyday goings-on in the stock market. You just need to buy a single investment and hold it forever.
That’s because 88% of active large-cap fund managers have underperformed the S&P 500 index over the last 15 years thru Dec. 31, 2023, according to S&P Global’s most recent SPIVA (S&P Indices Versus Active) scorecard. So if you buy a simple S&P 500 index fund like the Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (NYSEMKT: VOO), chances are that your investment will outperform the average active mutual fund in the long run.

It’s a good bet that the average fund manager is hardworking and well-trained. But there are at least two big factors working against active fund managers.
The first is that institutional investors make up roughly 80% of all trading in the U.S. stock market — far higher than it was years ago when retail investors dominated the market. That means a professional investor is mostly trading shares with another manager who is also very knowledgeable, making it much harder to gain an edge and outperform the benchmark index.
The more basic problem, though, is that fund managers don’t just need to outperform their benchmark index. They need to beat the index by a wide enough margin to justify the fees they charge. And that reduces the odds that any given large-cap fund manager will be able to outperform an S&P 500 index fund by a significant amount.
The SPIVA scorecard found that just 40% of large-cap fund managers outperformed the S&P 500 in 2023 once you factor in fees. So if the odds of outperforming fall to 40-60 for a single year, you can see how the odds of beating the index consistently over the long run could go way down.
Warren Buffett is one of the smartest investors around, and he can’t think of a single better investment than an S&P 500 index fund. He recommends it even above his own company, Berkshire Hathaway.
In his 2016 letter to shareholders, Buffett shared a rough calculation that the search for superior investment advice had cost investors, in aggregate, $100 billion over the previous decade relative to investing in a simple index fund.
Even Berkshire Hathaway holds two small positions in S&P 500 index funds. You’ll find shares of the Vanguard S&P 500 ETF and the SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust (NYSEMKT: SPY) in Berkshire’s quarterly disclosures. Both are great options for index investors, offering low expense ratios and low tracking errors (a measure of how closely an ETF price follows the underlying index). There are plenty of other solid index funds you could buy, but either of the above is an excellent option as a starting point.
Before you buy stock in Vanguard S&P 500 ETF, consider this:
The Motley Fool Stock Advisor analyst team just identified what they believe are the 10 best stocks for investors to buy now… and Vanguard S&P 500 ETF wasn’t one of them. The 10 stocks that made the cut could produce monster returns in the coming years.
Consider when Nvidia made this list on April 15, 2005… if you invested $1,000 at the time of our recommendation, you’d have $514,887!*
Stock Advisor provides investors with an easy-to-follow blueprint for success, including guidance on building a portfolio, regular updates from analysts, and two new stock picks each month. The Stock Advisor service has more than quadrupled the return of S&P 500 since 2002*.
*Stock Advisor returns as of April 15, 2024
Adam Levy has no position in any of the stocks mentioned. The Motley Fool has positions in and recommends Vanguard S&P 500 ETF. The Motley Fool has a disclosure policy.
Want to Outperform 88% of Professional Fund Managers? Buy This 1 Investment and Hold It Forever. was originally published by The Motley Fool


The numbers from the Department of Finance suggest they have struck taxation gold. But they’ve been wrong before
“99.87 per cent of Canadians will not pay a cent more,” the prime minister said this week, in reference to the budget announcement that his government will raise the inclusion rate on capital gains tax in June.
The move will be limited to 40,000 wealthy taxpayers. “We’re going to make them pay a little bit more,” Justin Trudeau said.
Article content
But it’s hard to see how that number can be true when the budget document also says 307,000 corporations will also be caught in the dragnet that raises the inclusion rate on capital gains to 66 per cent from 50 per cent.
Advertisement 2
Article content
Many of those corporations are holding companies set up by professionals and small-business owners who are relying on their portfolios for their retirement.
The budget offers the example of the nurse earning $70,000 who faces a combined federal-provincial marginal rate of 29.7 per cent on his or her income. “In comparison, a wealthy individual in Ontario with $1 million in income would face a marginal rate of 26.86 per cent on their capital gain,” it says.
Policy wonks argue that the change improves the efficiency and equity of the tax system, meaning capital gains are now taxed at a similar level to dividends, interest and paid income. The Department of Finance is an enthusiastic supporter of this view, which should have set alarm bells ringing on the political side.
That’s not to say it’s not a valid argument. But against it you could put forward the counterpoint that capital gains tax is a form of double taxation, the income having already been taxed at the individual and corporate level, which explains why the inclusion rate is not 100 per cent.
The prospect of capital gains is an incentive to invest particularly for people who, unlike wage earners, usually do not have pensions or other employment benefits.
Article content
Advertisement 3
Article content
Recommended from Editorial
That was recognized by Bill Morneau, Trudeau’s former finance minister, who said increasing the capital gains rate was proposed when he was in politics but he resisted the proposal.
Morneau criticized the new tax hike as “a disincentive for investment … I don’t think there’s any way to sugar-coat it.”
Regardless of the high-minded policy explanations that are advanced about neutrality in the tax system, it is clear that the impetus for the tax increase was the need to raise revenues by a government with a spending addiction, and to engage in wedge politics for one with a popularity problem.
The most pressing question right now is: how many people are affected — or, just as importantly, think they might be affected?
One recent Leger poll said 78 per cent of Canadians would support a new tax on people with wealth over $10 million.
But what about those regular folks who stand to make a once-in-a-lifetime windfall by selling the family cottage? We will need to wait a few weeks before it becomes clear how many people feel they might be affected.
Advertisement 4
Article content
The numbers supplied to Trudeau by the Department of Finance suggest they have struck taxation gold: plucking the largest amount of feathers ($21.9 billion in new revenues over five years) with the least amount of hissing (impacting just 0.13 per cent of taxpayers).
The worry for Trudeau and Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland is that Finance has been wrong before.
Political veterans recall former Conservative finance minister Jim Flaherty’s volte face in 2007, when he was forced to drop a proposal to cancel the ability of Canadian companies to deduct the interest costs on money they borrowed to expand abroad.
“Tax officials vastly underestimated the number of taxpayers affected when it came to corporations,” said one person who was there, pointing out that such miscalculations tend to happen when Finance has been pushing a particular policy for years.
Trudeau’s government has some experience of this phenomenon, having been obliged to reverse itself after introducing a range of measures in 2017, aimed at dissuading professionals from incorporating in order to pay less tax. It was a defensible public policy objective but the blowback from small-business owners and professionals who felt they were unfairly being labelled tax cheats precipitated an ignoble retreat.
Advertisement 5
Article content
Speaking after the budget was delivered, Freeland was unperturbed about the prospect of blowback. “No one likes to pay more tax, even — or perhaps more particularly — those who can afford it the most,” she said.
She’d best hope such sanguinity is justified: failure to raise the promised sums will blow a hole in her budget and cut loose her fiscal anchors of declining deficits and a tumbling debt-to-GDP ratio.
That probably won’t be apparent for a year or so: the government projected that $6.9 billion in capital gains revenue will be recorded this fiscal year, largely because the implementation date has been delayed until the end of June. We are likely to see a flood of transactions before then, so that investors can sell before the inclusion rate goes up.
After that, you can imagine asset sales will be minimized, particularly if the Conservatives promise to lower the rate again (though on that front, it was noticeable that during question period this week, not one Conservative raised the new $21 billion tax hike).
The calculated nature of the timing is in line with the surreptitious nature of the narrative: presenting a blatant revenue grab as a principled fight for “fairness.” The move has the added attraction of inflicting pain on the highest earners, a desirable end in itself for an ultra-progressive government that views wealth creation as a wrong that should be punished.
Advertisement 6
Article content
Trudeau’s biggest problem is that not many voters still associate him with principles, particularly after he sold out his own climate policy with the home heating oil exemption.
The tax hike smacks of a shift inspired by polling that indicates that Canadians prefer that any new taxes only affect the people richer than them.
Success or failure may depend on the number of unaffected Canadians being close to the 99.87-per-cent number supplied by the Finance Department.
History suggests that may be a shaky foundation on which to build a budget.
National Post
Twitter.com/IvisonJ
Get more deep-dive National Post political coverage and analysis in your inbox with the Political Hack newsletter, where Ottawa bureau chief Stuart Thomson and political analyst Tasha Kheiriddin get at what’s really going on behind the scenes on Parliament Hill every Wednesday and Friday, exclusively for subscribers. Sign up here.
Article content
DJT Stock Rises. Trump Media CEO Alleges Potential Market Manipulation. – Barron's
Trump Media alerts Nasdaq to potential market manipulation from 'naked' short selling of DJT stock – CNBC
Private equity gears up for potential National Football League investments – Financial Times
DJT Stock Jumps. The Truth Social Owner Is Showing Stockholders How to Block Short Sellers. – Barron's




Type 2 diabetes is not one-size-fits-all: Subtypes affect complications and treatment options – The Conversation
Tofino, Pemberton among communities opting in to B.C.'s new short-term rental restrictions – Vancouver Sun
A sunken boat dream has left a bad taste in this Tim Hortons customer's mouth – CBC.ca
Best in Canada: Jets Beat Canucks to Finish Season as Top Canadian Club – The Hockey News
Comments