Economy
How Sanctions on Russia Are Affecting the Global Economy – The New York Times


The price of energy has already shot higher, and the conflict imperils supply chains, factors that could exacerbate inflation and suppress growth.
In the span of just a few days, the global economic outlook has darkened while troops battled in Ukraine and unexpectedly potent financial sanctions rocked Russia’s economy and threatened to further fuel worldwide inflation.
The price of oil, natural gas and other staples spiked on Monday. At the same time, the groaning weight on supply chains, still laboring from the pandemic, rose as the United States, Europe and their allies tightened the screws on Russia’s financial transactions and froze hundreds of billions of dollars of the central bank’s assets that are held abroad.
Russia has long been a relatively minor player in the global economy, accounting for just 1.7 percent of the world’s total output despite its enormous energy exports. President Vladimir V. Putin has moved to further insulate it in recent years, building up a storehouse of foreign exchange reserves, reducing national debt and even banning cheese and other food imports from Europe.
But while Mr. Putin has ignored a slate of international norms, he cannot ignore a modern and mammoth financial system that is largely controlled by governments and bankers outside his country. He has mobilized tens of thousands of his troops, and, in response, allied governments have mobilized their vast financial power.
Now, “it’s a gamble between a financial clock and a military clock, to vaporize the resources to conduct a war,” said Julia Friedlander, director of the economic statecraft initiative at the Atlantic Council.
Together, the invasion and the sanctions inject a huge dose of uncertainty and volatility into economic decision-making, heightening the risk to the global outlook.
The sanctions were designed to avoid disrupting essential energy exports, which Europe, in particular, relies on to heat homes, power factories and fill gas tanks. That helped dampen, but did not erase, a surge in energy prices caused by war and anxieties about disruptions in the flow of oil and gas.
Worries about shortages also pushed up the price of some grains and metals, which would inflict higher costs on consumers and businesses. Russia and Ukraine are also large exporters of wheat and corn, as well as essential metals, like palladium, aluminum and nickel, that are used in everything from mobile phones to automobiles.
Already eye-popping transport costs are also expected to soar.
“We are going to see rates skyrocket for ocean and air,” said Glenn Koepke, general manager of network collaboration at FourKites, a supply chain consultancy in Chicago. He warned that ocean rates could double or triple to $30,000 a container from $10,000 a container, and that airfreight costs were expected to jump even higher.
Russia closed its airspace to 36 countries, which means shipping planes will have to divert to roundabout routes, leading them to spend more on fuel and possibly encouraging them to reduce the size of their loads.
“We’re also going to see more product shortages,” Mr. Koepke said. While it’s a slower season now, he said, “companies are ramping up for summer volume, and that’s going to have a major impact on our supply chain.”
In a flurry of updates on Monday, several Wall Street analysts and economists acknowledged that they had underestimated the extent of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and the international response. With events rapidly piling up, assessments of the potential economic fallout ranged from the mild to the severe.
Inflation was already a concern, running in the United States at the highest it has been since the 1980s. Now questions about how much more inflation might rise — and how the Federal Reserve and other central banks respond — hovered over every scenario.
“The Fed is in a box, inflation is running at 7.5 percent, but they know if they raise interest rates, that will tank markets,” said Desmond Lachman, a senior fellow at the American Enterprise Institute. “The policy choices aren’t good, so I don’t see how this has a happy outcome.”
Others were more cautious about the spillover effects given the isolation of Russia’s economy.
Adam Posen, president of the Peterson Institute for International Economics, said there were vexing questions, particularly in Europe, about what the conflict would mean for inflation — and whether it posed the prospect of stagflation, in which economic growth slows and prices rise quickly.
But overall, he said, “the damage is likely to be small.”
That doesn’t mean there won’t be intense pain in spots. Mr. Posen noted that a handful of banks in Europe could suffer from their exposures to the Russian financial system, and that Eastern European companies might lose access to money in the country.
Thousands of people fleeing Ukraine are also streaming into neighboring countries like Poland, Moldova and Romania, which could add to their costs.
Turkey’s economy, which is already struggling, is likely to take a hit. Oxford Economics lowered its forecast for Turkey’s annual growth by 0.4 percentage points to 2.1 percent because of rises in energy prices, disruptions to financial markets and declines in tourism.
Russia’s Attack on Ukraine and the Global Economy
A rising concern. Russia’s attack on Ukraine could cause dizzying spikes in prices for energy and food and could spook investors. The economic damage from supply disruptions and economic sanctions would be severe in some countries and industries and unnoticed in others.
In 2021, 19 percent of its visitors came from Russia, and 8.3 percent came from Ukraine. Inflation, already at a two-decade high of nearly 50 percent, is now estimated to reach 60 percent, Oxford said.
In the United States, the chair of the Biden administration’s Council of Economic Advisers, Cecilia Rouse, said the biggest impact on the American economy from the war was rising gas prices. “This has definitely clouded the outlook,” she said at a forum in Washington.
Gasoline prices are roughly a dollar higher than a year ago, with a national average of $3.61 a gallon, according to AAA.
Rising energy prices are tough on consumers, although good for producers — and the U.S. economy has both.
Other oil-producing nations will also see a rise in revenues. And for Iran, which has been shut out of the global economy for years, the demand for oil from other sources could help smooth negotiations to lift sanctions.
Over the longer term, the current conflict is likely to have effects on several countries’ future budget decisions. Germany’s chancellor, Olaf Scholz, announced that he would increase military spending to 2 percent of its economic output.
“Defense spending has fallen consistently in the post-WWII world,” Jim Reid, managing director of Deutsche Bank, wrote in a note on Monday. Now, with this shift in “the geopolitical tectonic plates,” he said, priorities are changing, and “those levels are likely to rise.”
In Russia, the central bank and government took a series of actions, including doubling a key interest rates to 20 percent to increase the ruble’s appeal, barring people from transferring money to overseas accounts, and closing the stock market to contain the damage and tamp down panic.
“What’s happening right now is we’re looking at the dismemberment of one of the largest economies on the planet,” said Carl Weinberg, chief economist at High Frequency Economics. “And from what I know about tactics, this is a dangerous tactic.”
Peter S. Goodman and Jeanna Smialek contributed reporting.
Economy
Opinion: Higher capital gains taxes won't work as claimed, but will harm the economy – The Globe and Mail
Canada’s Prime Minister Justin Trudeau and Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland hold the 2024-25 budget, on Parliament Hill in Ottawa, on April 16.Patrick Doyle/Reuters
Alex Whalen and Jake Fuss are analysts at the Fraser Institute.
Amid a federal budget riddled with red ink and tax hikes, the Trudeau government has increased capital gains taxes. The move will be disastrous for Canada’s growth prospects and its already-lagging investment climate, and to make matters worse, research suggests it won’t work as planned.
Currently, individuals and businesses who sell a capital asset in Canada incur capital gains taxes at a 50-per-cent inclusion rate, which means that 50 per cent of the gain in the asset’s value is subject to taxation at the individual or business’s marginal tax rate. The Trudeau government is raising this inclusion rate to 66.6 per cent for all businesses, trusts and individuals with capital gains over $250,000.
The problems with hiking capital gains taxes are numerous.
First, capital gains are taxed on a “realization” basis, which means the investor does not incur capital gains taxes until the asset is sold. According to empirical evidence, this creates a “lock-in” effect where investors have an incentive to keep their capital invested in a particular asset when they might otherwise sell.
For example, investors may delay selling capital assets because they anticipate a change in government and a reversal back to the previous inclusion rate. This means the Trudeau government is likely overestimating the potential revenue gains from its capital gains tax hike, given that individual investors will adjust the timing of their asset sales in response to the tax hike.
Second, the lock-in effect creates a drag on economic growth as it incentivizes investors to hold off selling their assets when they otherwise might, preventing capital from being deployed to its most productive use and therefore reducing growth.
Budget’s capital gains tax changes divide the small business community
And Canada’s growth prospects and investment climate have both been in decline. Canada currently faces the lowest growth prospects among all OECD countries in terms of GDP per person. Further, between 2014 and 2021, business investment (adjusted for inflation) in Canada declined by $43.7-billion. Hiking taxes on capital will make both pressing issues worse.
Contrary to the government’s framing – that this move only affects the wealthy – lagging business investment and slow growth affect all Canadians through lower incomes and living standards. Capital taxes are among the most economically damaging forms of taxation precisely because they reduce the incentive to innovate and invest. And while taxes on capital gains do raise revenue, the economic costs exceed the amount of tax collected.
Previous governments in Canada understood these facts. In the 2000 federal budget, then-finance minister Paul Martin said a “key factor contributing to the difficulty of raising capital by new startups is the fact that individuals who sell existing investments and reinvest in others must pay tax on any realized capital gains,” an explicit acknowledgment of the lock-in effect and costs of capital gains taxes. Further, that Liberal government reduced the capital gains inclusion rate, acknowledging the importance of a strong investment climate.
At a time when Canada badly needs to improve the incentives to invest, the Trudeau government’s 2024 budget has introduced a damaging tax hike. In delivering the budget, Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland said “Canada, a growing country, needs to make investments in our country and in Canadians right now.” Individuals and businesses across the country likely agree on the importance of investment. Hiking capital gains taxes will achieve the exact opposite effect.
Economy
Nigeria's Economy, Once Africa's Biggest, Slips to Fourth Place – Bloomberg


Nigeria’s economy, which ranked as Africa’s largest in 2022, is set to slip to fourth place this year and Egypt, which held the top position in 2023, is projected to fall to second behind South Africa after a series of currency devaluations, International Monetary Fund forecasts show.
The IMF’s World Economic Outlook estimates Nigeria’s gross domestic product at $253 billion based on current prices this year, lagging energy-rich Algeria at $267 billion, Egypt at $348 billion and South Africa at $373 billion.
Economy
IMF Sees OPEC+ Oil Output Lift From July in Saudi Economic Boost – BNN Bloomberg
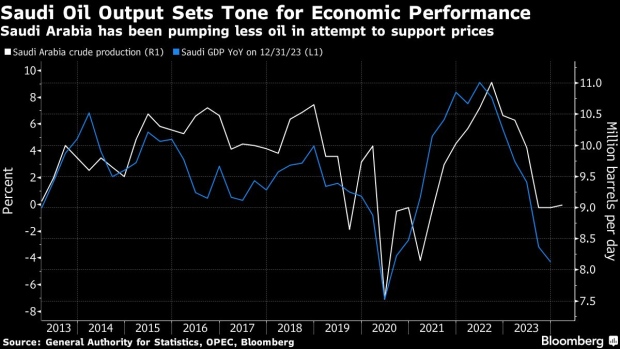

(Bloomberg) — The International Monetary Fund expects OPEC and its partners to start increasing oil output gradually from July, a transition that’s set to catapult Saudi Arabia back into the ranks of the world’s fastest-growing economies next year.
“We are assuming the full reversal of cuts is happening at the beginning of 2025,” Amine Mati, the lender’s mission chief to the kingdom, said in an interview in Washington, where the IMF and the World Bank are holding their spring meetings.
The view explains why the IMF is turning more upbeat on Saudi Arabia, whose economy contracted last year as it led the OPEC+ alliance alongside Russia in production cuts that squeezed supplies and pushed up crude prices. In 2022, record crude output propelled Saudi Arabia to the fastest expansion in the Group of 20.
Under the latest outlook unveiled this week, the IMF improved next year’s growth estimate for the world’s biggest crude exporter from 5.5% to 6% — second only to India among major economies in an upswing that would be among the kingdom’s fastest spurts over the past decade.
The fund projects Saudi oil output will reach 10 million barrels per day in early 2025, from what’s now a near three-year low of 9 million barrels. Saudi Arabia says its production capacity is around 12 million barrels a day and it’s rarely pumped as low as today’s levels in the past decade.
Mati said the IMF slightly lowered its forecast for Saudi economic growth this year to 2.6% from 2.7% based on actual figures for 2023 and the extension of production curbs to June. Bloomberg Economics predicts an expansion of 1.1% in 2024 and assumes the output cuts will stay until the end of this year.
Worsening hostilities in the Middle East provide the backdrop to a possible policy shift after oil prices topped $90 a barrel for the first time in months. The Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries and its allies will gather on June 1 and some analysts expect the group may start to unwind the curbs.
After sacrificing sales volumes to support the oil market, Saudi Arabia may instead opt to pump more as it faces years of fiscal deficits and with crude prices still below what it needs to balance the budget.
Saudi Arabia is spending hundreds of billions of dollars to diversify an economy that still relies on oil and its close derivatives — petrochemicals and plastics — for more than 90% of its exports.
Restrictive US monetary policy won’t necessarily be a drag on Saudi Arabia, which usually moves in lockstep with the Federal Reserve to protect its currency peg to the dollar.
Mati sees a “negligible” impact from potentially slower interest-rate cuts by the Fed, given the structure of the Saudi banks’ balance sheets and the plentiful liquidity in the kingdom thanks to elevated oil prices.
The IMF also expects the “non-oil sector growth momentum to remain strong” for at least the next couple of years, Mati said, driven by the kingdom’s plans to develop industries from manufacturing to logistics.
The kingdom “has undertaken many transformative reforms and is doing a lot of the right actions in terms of the regulatory environment,” Mati said. “But I think it takes time for some of those reforms to materialize.”
©2024 Bloomberg L.P.
-



 Investment23 hours ago
Investment23 hours agoUK Mulls New Curbs on Outbound Investment Over Security Risks – BNN Bloomberg
-



 Sports21 hours ago
Sports21 hours agoAuston Matthews denied 70th goal as depleted Leafs lose last regular-season game – Toronto Sun
-
Media2 hours ago
DJT Stock Rises. Trump Media CEO Alleges Potential Market Manipulation. – Barron's
-
Business20 hours ago
BC short-term rental rules take effect May 1 – CityNews Vancouver
-
Media4 hours ago
Trump Media alerts Nasdaq to potential market manipulation from 'naked' short selling of DJT stock – CNBC
-
Art20 hours ago
Collection of First Nations art stolen from Gordon Head home – Times Colonist
-



 Investment20 hours ago
Investment20 hours agoBenjamin Bergen: Why would anyone invest in Canada now? – National Post
-



 Tech22 hours ago
Tech22 hours agoSave $700 Off This 4K Projector at Amazon While You Still Can – CNET





