Indian Railways, a government entity, announced an increase in ticket prices in December. Its eroding finances apparently left it no choice. Complaints about rising air fares have been circulating since the collapse of Jet Airways last April. India’s mobile-phone operators have raised tariffs sharply after losing a court battle with the government over licence fees and spectrum charges. Despite a collapse in sales, vehicle prices are rising, a result of costly new regulations. Rajiv Bajaj, managing director of Bajaj Auto, a motorcycle-maker, has complained that the government “is killing the industry”.
Economy
India’s economy risks swapping stagnation for stagflation – The Economist
MUMBAI’S CHEFS were quick to spot the latest threat facing India’s economy. As they foraged for ingredients in Crawford market, where hawkers sell fruit, vegetables and other kitchen staples, they began hearing prices quoted not per kilogram, but per quarter-kilo—a forlorn attempt to mask price increases. Returning from a recent shopping spree, one prominent chef checked off the items rising sharply in price: tomatoes, cabbages, aubergines, fish, spices—almost every ingredient, in fact, in the Indian cookbook.
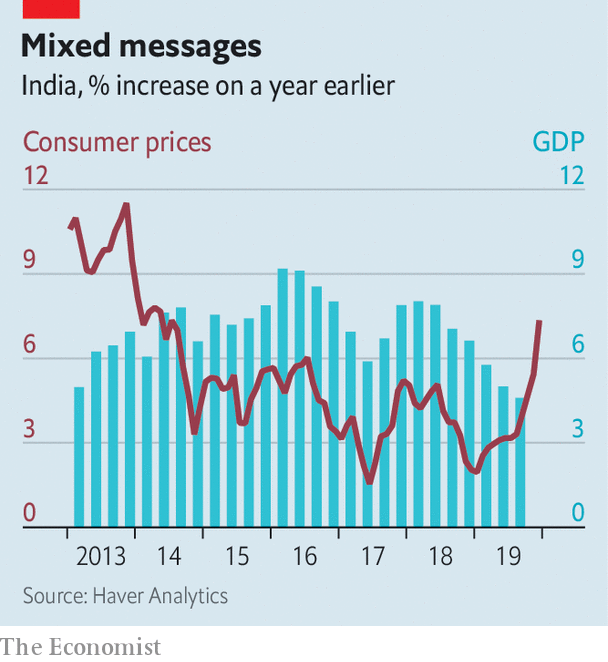
The hawkers had some plausible excuses. The weather has been erratic, and delivery systems unreliable. But although an increase in inflation was widely foreseen, the severity of it was not. Consumer prices rose by over 7.3% in December, compared with a year earlier, the biggest jump since July 2014. Onion prices, up by 328%, contributed 2.1 percentage points to the headline figure all by themselves.
But India’s inflation is not only or everywhere an onion phenomenon. A Mumbai tea-vendors’ association recently recommended a price rise because of the increased cost of sugar and tea leaves, as well as the gas that fuels vendors’ stoves. The National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority allowed sharply higher charges for 21 drugs, including treatments for leprosy, malaria and tuberculosis, which were in short supply because prices had failed to cover rising costs.
This miscellany of misery will complicate the government’s efforts to fight an economic slowdown. India’s GDP grew by only 4.5% in the third quarter compared with a year earlier. That figure would have been as low as 3.1% were it not for a hurried government-spending spree. Yet another splurge is expected in the budget on February 1st. But any increase in demand could prompt an offsetting response from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the central bank. It may choose to prolong stagnation so as to avoid the uglier scenario of stagflation.
Stagflation usually begins with a setback to supply, such as India’s unseasonal rains. These misfortunes both lower output (the “stag” part of the phenomenon) and lift costs (the “flation” part). But once prices have increased sufficiently to reflect the scarcer supply, they should in principle stop rising. Some economists expect inflation to begin falling as soon as February. After all, core inflation, which excludes food and fuel prices, remains below 4%.
The problem is that before inflation disappears, Indians may start believing it will stay, making it more likely to persist. In most rich countries that have adopted inflation-targeting, headline inflation usually falls back into line with core measures, which reflect the strength of demand better. But in India the opposite is true. Core inflation usually converges towards the headline number, which reflects more accurately the drain on people’s pockets.
The RBI’s inflation-targeting framework, which it adopted in 2015, was supposed to fight this tendency. It was meant to convince people that the central bank’s inflation target of 4% was a better guide to future inflation than the prices quoted at Crawford market and other emporiums across the country. But the framework has “yet to be fully tested”, according to a recent lecture by Raghuram Rajan, the former RBI governor who introduced it. Mumbai’s chefs will hope it passes the thorough examination it will now undergo.■
This article appeared in the Finance and economics section of the print edition under the headline “India’s economy risks swapping stagnation for stagflation”
Economy
Canada’s unemployment rate holds steady at 6.5% in October, economy adds 15,000 jobs
OTTAWA – Canada’s unemployment rate held steady at 6.5 per cent last month as hiring remained weak across the economy.
Statistics Canada’s labour force survey on Friday said employment rose by a modest 15,000 jobs in October.
Business, building and support services saw the largest gain in employment.
Meanwhile, finance, insurance, real estate, rental and leasing experienced the largest decline.
Many economists see weakness in the job market continuing in the short term, before the Bank of Canada’s interest rate cuts spark a rebound in economic growth next year.
Despite ongoing softness in the labour market, however, strong wage growth has raged on in Canada. Average hourly wages in October grew 4.9 per cent from a year ago, reaching $35.76.
Friday’s report also shed some light on the financial health of households.
According to the agency, 28.8 per cent of Canadians aged 15 or older were living in a household that had difficulty meeting financial needs – like food and housing – in the previous four weeks.
That was down from 33.1 per cent in October 2023 and 35.5 per cent in October 2022, but still above the 20.4 per cent figure recorded in October 2020.
People living in a rented home were more likely to report difficulty meeting financial needs, with nearly four in 10 reporting that was the case.
That compares with just under a quarter of those living in an owned home by a household member.
Immigrants were also more likely to report facing financial strain last month, with about four out of 10 immigrants who landed in the last year doing so.
That compares with about three in 10 more established immigrants and one in four of people born in Canada.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Nov. 8, 2024.
The Canadian Press. All rights reserved.
Economy
Health-care spending expected to outpace economy and reach $372 billion in 2024: CIHI
The Canadian Institute for Health Information says health-care spending in Canada is projected to reach a new high in 2024.
The annual report released Thursday says total health spending is expected to hit $372 billion, or $9,054 per Canadian.
CIHI’s national analysis predicts expenditures will rise by 5.7 per cent in 2024, compared to 4.5 per cent in 2023 and 1.7 per cent in 2022.
This year’s health spending is estimated to represent 12.4 per cent of Canada’s gross domestic product. Excluding two years of the pandemic, it would be the highest ratio in the country’s history.
While it’s not unusual for health expenditures to outpace economic growth, the report says this could be the case for the next several years due to Canada’s growing population and its aging demographic.
Canada’s per capita spending on health care in 2022 was among the highest in the world, but still less than countries such as the United States and Sweden.
The report notes that the Canadian dental and pharmacare plans could push health-care spending even further as more people who previously couldn’t afford these services start using them.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Nov. 7, 2024.
Canadian Press health coverage receives support through a partnership with the Canadian Medical Association. CP is solely responsible for this content.
The Canadian Press. All rights reserved.
Economy
Trump’s victory sparks concerns over ripple effect on Canadian economy
As Canadians wake up to news that Donald Trump will return to the White House, the president-elect’s protectionist stance is casting a spotlight on what effect his second term will have on Canada-U.S. economic ties.
Some Canadian business leaders have expressed worry over Trump’s promise to introduce a universal 10 per cent tariff on all American imports.
A Canadian Chamber of Commerce report released last month suggested those tariffs would shrink the Canadian economy, resulting in around $30 billion per year in economic costs.
More than 77 per cent of Canadian exports go to the U.S.
Canada’s manufacturing sector faces the biggest risk should Trump push forward on imposing broad tariffs, said Canadian Manufacturers and Exporters president and CEO Dennis Darby. He said the sector is the “most trade-exposed” within Canada.
“It’s in the U.S.’s best interest, it’s in our best interest, but most importantly for consumers across North America, that we’re able to trade goods, materials, ingredients, as we have under the trade agreements,” Darby said in an interview.
“It’s a more complex or complicated outcome than it would have been with the Democrats, but we’ve had to deal with this before and we’re going to do our best to deal with it again.”
American economists have also warned Trump’s plan could cause inflation and possibly a recession, which could have ripple effects in Canada.
It’s consumers who will ultimately feel the burden of any inflationary effect caused by broad tariffs, said Darby.
“A tariff tends to raise costs, and it ultimately raises prices, so that’s something that we have to be prepared for,” he said.
“It could tilt production mandates. A tariff makes goods more expensive, but on the same token, it also will make inputs for the U.S. more expensive.”
A report last month by TD economist Marc Ercolao said research shows a full-scale implementation of Trump’s tariff plan could lead to a near-five per cent reduction in Canadian export volumes to the U.S. by early-2027, relative to current baseline forecasts.
Retaliation by Canada would also increase costs for domestic producers, and push import volumes lower in the process.
“Slowing import activity mitigates some of the negative net trade impact on total GDP enough to avoid a technical recession, but still produces a period of extended stagnation through 2025 and 2026,” Ercolao said.
Since the Canada-United States-Mexico Agreement came into effect in 2020, trade between Canada and the U.S. has surged by 46 per cent, according to the Toronto Region Board of Trade.
With that deal is up for review in 2026, Canadian Chamber of Commerce president and CEO Candace Laing said the Canadian government “must collaborate effectively with the Trump administration to preserve and strengthen our bilateral economic partnership.”
“With an impressive $3.6 billion in daily trade, Canada and the United States are each other’s closest international partners. The secure and efficient flow of goods and people across our border … remains essential for the economies of both countries,” she said in a statement.
“By resisting tariffs and trade barriers that will only raise prices and hurt consumers in both countries, Canada and the United States can strengthen resilient cross-border supply chains that enhance our shared economic security.”
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Nov. 6, 2024.
The Canadian Press. All rights reserved.
-
News24 hours ago
Chrystia Freeland says carbon rebate for small businesses will be tax-free
-
News24 hours ago
FACT FOCUS: Election officials knock down Starlink vote rigging conspiracy theories
-
News24 hours ago
Nova Scotia election promise tracker: What has been promised by three main parties?
-
News24 hours ago
Former B.C. premier John Horgan, who connected with people, dies at 65
-
News24 hours ago
Suncor Energy earnings rise to $2.02 billion in third quarter
-
News24 hours ago
Swearing-in ceremonies at B.C. legislature mark start of new political season
-
News24 hours ago
New Brunswick premier confirms her Liberal government will draft carbon pricing plan
-
News24 hours ago
B.C. teen with bird flu is in critical care, infection source unknown: health officer