Economy
Modi’s Nationalism Masks a Bad Economy

|
|
(Bloomberg) — Through some of the coldest nights in a century, the students of New Delhi gathered outside the city’s police headquarters. They chanted anti-government slogans, recited Pakistani resistance poets, and flashed witty posters to make a stand against a new citizenship law that excludes Muslims.
As the confrontations continue across the country, though, they’ve morphed into a wider protest against economic prospects and financial disparities. Violence flared at campuses as the authorities cracked down on the demonstrations that have become Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s biggest test since he won power more than five years ago.
“Their handling of the economy is disastrous,” said Akshay Bajaj, 29, a post-doctoral student who helped organize protests at the Indian Institute of Technology in Kanpur. “There are no jobs, falling growth and rocketing prices for vegetables.”
Like so many of the protests across the world that have defined the last 12 months, the contentious legislation in India was effectively just a tipping point for the under 30s. With tear gas clouds sweeping across Beirut again this week and regular clashes in Hong Kong, the students in New Delhi and Mumbai have added to the sense of global malaise.
The protests were triggered by a new law called the Citizenship Amendment Act that fast-tracks religious minorities from three neighboring countries, except for Muslims. They intensified after police stormed the Jamia Millia Islamia university in December to crush what it said were acts of vandalism.
In solidarity, students spilled out of colleges across the capital and even elite management and technology schools to protest against Modi and his confidante Amit Shah, India’s powerful minister for internal security.
“Nationalism, far from being reversed, made further headway,” billionaire philanthropist George Soros told the World Economic Forum in Davos last week, according to excerpts from his speech. The biggest and “most frightening setback,” he said, was in India.
Protesters say the law undermines India’s Constitution, which treats all religions equally. They fear it will be misused, together with a proposed National Citizens’ Register, to disenfranchise poor Muslims who lack the documents to prove their residency. The government instead should have expended its energy on reversing the worst economic slump in a decade and the highest unemployment rate in 45 years.
“The government doesn’t attempt to answer the grievances of the people, it is instead distracting us with these kind of issues,” said Mihir Jain, 26, a chartered accountant who last month participated in his first ever public protest. “If today we allow them to go ahead with this, we don’t know what will come next.”
Peaceful protests continued last week, with at least two dozen rallies and sit-ins in Mumbai and New Delhi and several others scattered across the country. The Supreme Court on Wednesday deferred a hearing on cases challenging the constitutional validity of the citizenship law. A human chain is planned for Jan. 30, the anniversary of the slaying of Mahatma Gandhi by a Hindu fundamentalist, according to messages being shared on college WhatsApp groups.
Economic anxiety served as the kindling for the protests while the new legislation was the spark, said Milan Vaishnav, director for the South Asia program at the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace. Then as food prices spiked, the demonstrations turned into a focal point for many strands of disenchantment with the government, he said.
Modi’s governing Bharatiya Janata Party says the new law will offer refuge to persecuted minorities from India’s neighboring countries and it won’t impact any Indian citizen. It sees the rebellion as a reflection of how the law is misunderstood.
Party member Baijayant Panda told Bloomberg Television on Thursday that the government has started an outreach program to explain it more clearly. “You’ve had TV bites where they aren’t able to say why exactly they are protesting,” said Panda. “Some think they are protesting against inflation.”
While India’s economy ballooned to about $3 trillion since the nation adopted its constitution in 1950, much of the population remains left behind. Modi swept to power in 2014 promising India’s poor and middle classes he’d restore their ” dignity” after years of inequality.
Yet Swiss bank Credit Suisse Group AG estimated the richest 10% of Indians held 74% of the country’s wealth in 2019, up from 62% in 2012. S. Subramanian, a member of the advisory board of the World Bank’s Commission on Global Poverty, said underlying data from a government report leaked in November indicate that an even larger share of Indians have slipped into poverty. The government says it has concerns about the quality of this database.
About 30% of Indian youth aged 15-29 are not in employment, education or training, according to data from the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development, more than double the average. India’s economy is forecast to grow 5% in the year ending March 2020, the slowest pace since 2009, and inflation accelerated last month to the fastest since 2014.
Modi’s administration will present its annual budget on Feb. 1 and analysts say it’s unlikely to have adequate tools to combat the economic slowdown as the deficit swells. Meanwhile the pushback is being led by the very people who were considered a potential new support base for Modi and are now disenchanted with the lurch toward Hindu nationalism.
His campaign in 2019 was fueled by a combination of Hindu nationalism, economic populism and air strikes against arch-rival Pakistan. The new citizenship laws were among Modi’s promises; he won the vote with a massive majority.
Shrishti Parihar, 19, said the legislation acts as a convenient smokescreen for the government. Until recently, she was discussing job security with her friends, but now Modi and Shah talk of nothing but religion, she said.
“The economy is in such bad shape–that should be our main concern,” said Parihar. “Instead, we are talking Hindu-Muslim.”
To contact the authors of this story: Jeanette Rodrigues in Mumbai at jrodrigues26@bloomberg.netArchana Chaudhary in New Delhi at achaudhary2@bloomberg.netRonojoy Mazumdar in Mumbai at rmazumdar7@bloomberg.net
By Jeanette Rodrigues
Economy
China Wants Everyone to Trade In Their Old Cars, Fridges to Help Save Its Economy
|
|
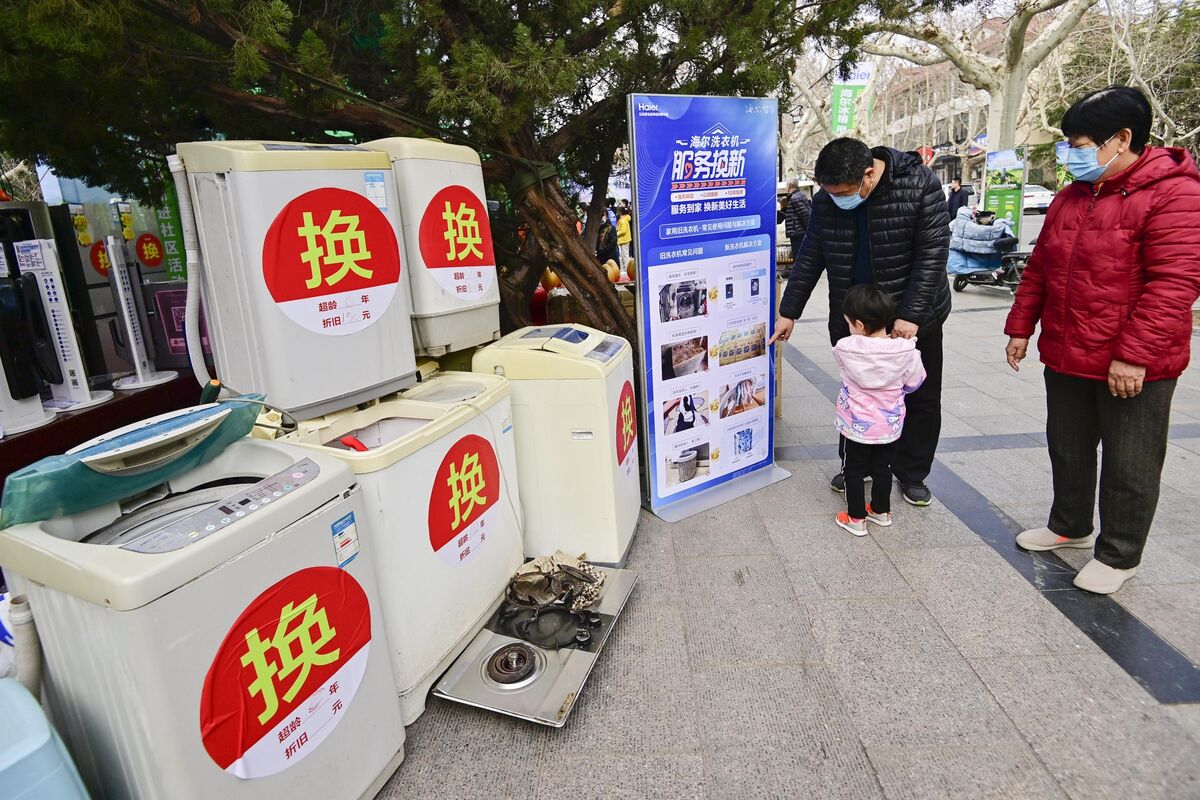


China’s world-beating electric vehicle industry, at the heart of growing trade tensions with the US and Europe, is set to receive a big boost from the government’s latest effort to accelerate growth.
That’s one takeaway from what Beijing has revealed about its plan for incentives that will encourage Chinese businesses and households to adopt cleaner technologies. It’s widely expected to be one of this year’s main stimulus programs, though question-marks remain — including how much the government will spend.




Economy
German Business Outlook Hits One-Year High as Economy Heals
|
|
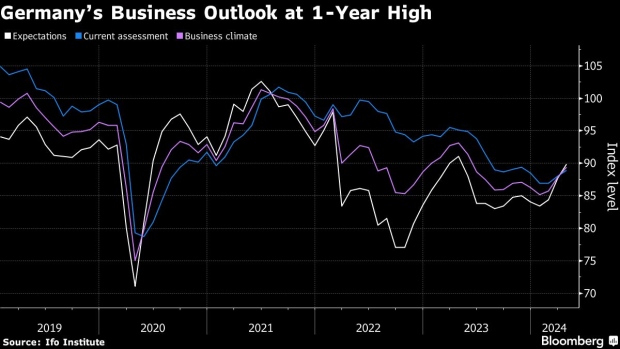

German business sentiment improved to its highest level in a year — reinforcing recent signs that Europe’s largest economy is exiting two years of struggles.
An expectations gauge by the Ifo institute rose to 89.9. in April from a revised 87.7 the previous month. That exceeds the 88.9 median forecast in a Bloomberg survey. A measure of current conditions also advanced.
“Sentiment has improved at companies in Germany,” Ifo President Clemens Fuest said. “Companies were more satisfied with their current business. Their expectations also brightened. The economy is stabilizing, especially thanks to service providers.”
A stronger global economy and the prospect of looser monetary policy in the euro zone are helping drag Germany out of the malaise that set in following Russia’s attack on Ukraine. European Central Bank President Christine Lagarde said last week that the country may have “turned the corner,” while Chancellor Olaf Scholz has also expressed optimism, citing record employment and retreating inflation.
There’s been a particular shift in the data in recent weeks, with the Bundesbank now estimating that output rose in the first quarter, having only a month ago foreseen a contraction that would have ushered in a first recession since the pandemic.
Even so, the start of the year “didn’t go great,” according to Fuest.
“What we’re seeing at the moment confirms the forecasts, which are saying that growth will be weak in Germany, but at least it won’t be negative,” he told Bloomberg Television. “So this is the stabilization we expected. It’s not a complete recovery. But at least it’s a start.”
Monthly purchasing managers’ surveys for April brought more cheer this week as Germany returned to expansion for the first time since June 2023. Weak spots remain, however — notably in industry, which is still mired in a slump that’s being offset by a surge in services activity.
“We see an improving worldwide economy,” Fuest said. “But this doesn’t seem to reach German manufacturing, which is puzzling in a way.”
Germany, which was the only Group of Seven economy to shrink last year and has been weighing on the wider region, helped private-sector output in the 20-nation euro area strengthen this month, S&P Global said.
–With assistance from Joel Rinneby, Kristian Siedenburg and Francine Lacqua.
(Updates with more comments from Fuest starting in sixth paragraph.)




Economy
Parallel economy: How Russia is defying the West’s boycott
|
|


When Moscow resident Zoya, 62, was planning a trip to Italy to visit her daughter last August, she saw the perfect opportunity to buy the Apple Watch she had long dreamed of owning.
Officially, Apple does not sell its products in Russia.
The California-based tech giant was one of the first companies to announce it would exit the country in response to Russian President Vladimir Putin’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine on February 24, 2022.
But the week before her trip, Zoya made a surprise discovery while browsing Yandex.Market, one of several Russian answers to Amazon, where she regularly shops.
Not only was the Apple Watch available for sale on the website, it was cheaper than in Italy.
Zoya bought the watch without a moment’s delay.
The serial code on the watch that was delivered to her home confirmed that it was manufactured by Apple in 2022 and intended for sale in the United States.
“In the store, they explained to me that these are genuine Apple products entering Russia through parallel imports,” Zoya, who asked to be only referred to by her first name, told Al Jazeera.
“I thought it was much easier to buy online than searching for a store in an unfamiliar country.”
Nearly 1,400 companies, including many of the most internationally recognisable brands, have since February 2022 announced that they would cease or dial back their operations in Russia in protest of Moscow’s military aggression against Ukraine.
But two years after the invasion, many of these companies’ products are still widely sold in Russia, in many cases in violation of Western-led sanctions, a months-long investigation by Al Jazeera has found.
Aided by the Russian government’s legalisation of parallel imports, Russian businesses have established a network of alternative supply chains to import restricted goods through third countries.
The companies that make the products have been either unwilling or unable to clamp down on these unofficial distribution networks.




-



 Health17 hours ago
Health17 hours agoRemnants of bird flu virus found in pasteurized milk, FDA says
-
Art23 hours ago
Mayor's youth advisory council seeks submissions for art gala – SooToday
-



 Health21 hours ago
Health21 hours agoBird flu virus found in grocery milk as officials say supply still safe
-



 Investment21 hours ago
Investment21 hours agoTaxes should not wag the tail of the investment dog, but that’s what Trudeau wants
-
News13 hours ago
Amid concerns over ‘collateral damage’ Trudeau, Freeland defend capital gains tax change
-
Art17 hours ago
Random: We’re In Awe of Metaphor: ReFantazio’s Box Art
-
News22 hours ago
Peel police chief met Sri Lankan officer a court says ‘participated’ in torture – Global News
-
Art22 hours ago
An exhibition with a cause: Montreal's 'Art by the Water' celebrates 15 years – CityNews Montreal




