Science
NASA rover attempting most difficult Martian touchdown yet – StCatharinesStandard.ca
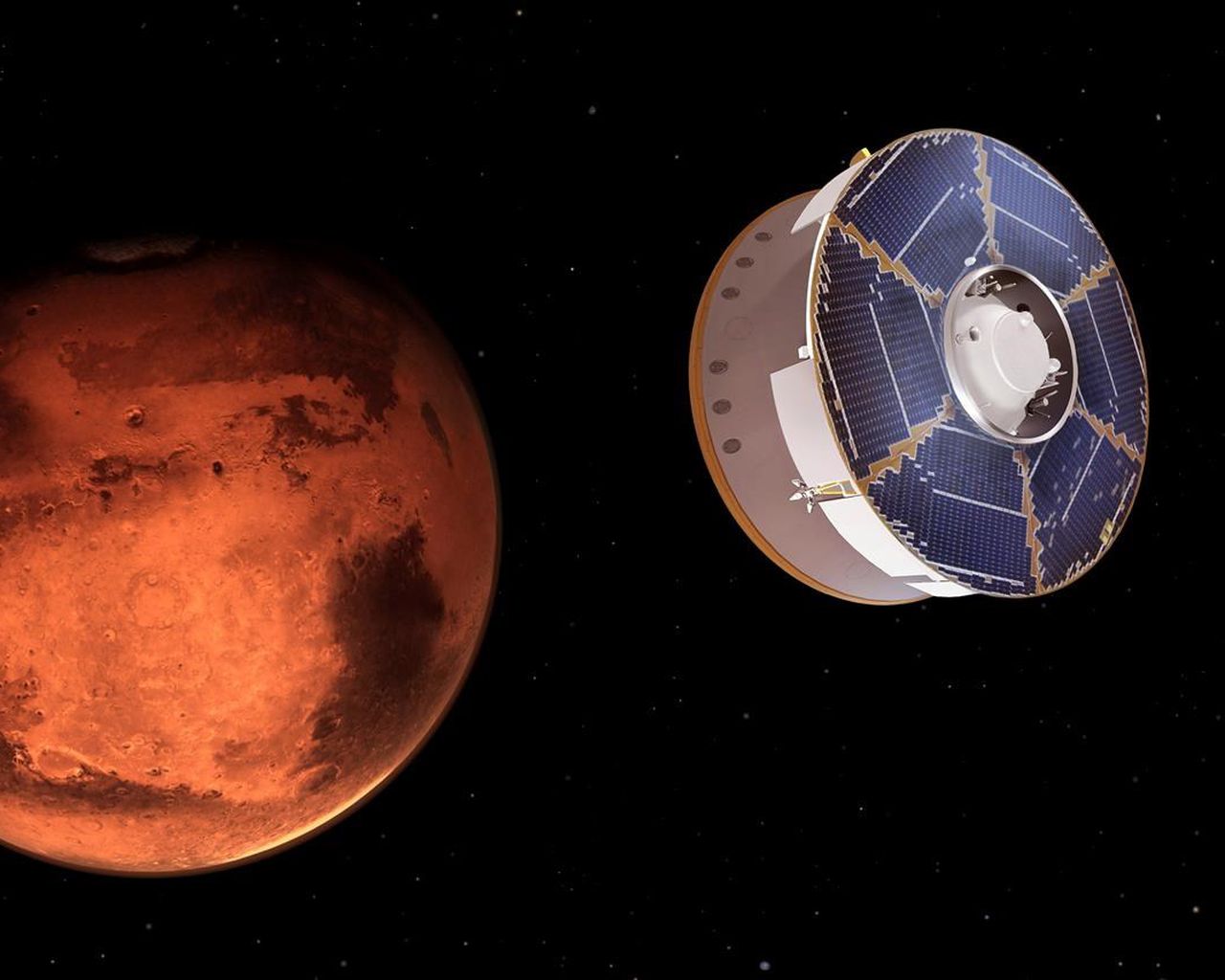
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Spacecraft aiming to land on Mars have skipped past the planet, burned up on entry, smashed into the surface, and made it down amid a fierce dust storm only to spit out a single fuzzy gray picture before dying.
Almost 50 years after the first casualty at Mars, NASA is attempting its hardest Martian touchdown yet.
The rover named Perseverance is headed Thursday for a compact 5-mile-by-4-mile (8-kilometre-by-6.4-kilometre) patch on the edge of an ancient river delta. It’s filled with cliffs, pits, sand dunes and fields of rocks, any of which could doom the $3 billion mission. The once submerged terrain also could hold evidence of past life, all the more reason to gather samples at this spot for return to Earth 10 years from now.
While NASA has done everything possible to ensure success, “there’s always this fear that it won’t work well, it won’t go well,” Erisa Stilley, a landing team engineer, said Tuesday. “We’ve had a pretty good run of successful missions recently and you never want to be the next one that isn’t. It’s heartbreaking when it happens.”
A look at NASA’s latest mission:
MARS MASTER
NASA has nailed eight of nine landing attempts, making the U.S. the only country to achieve a successful touchdown. China hopes to become the second nation in late spring with its own life-seeking rover; its vessel entered orbit around Mars last week along with a United Arab Emirates spacecraft. The red planet’s extremely thin atmosphere makes it hard to get down safely. Russia has piled up the most lander losses at Mars and moon Phobos, beginning in the early 1970s. The European Space Agency also has tried and failed. Two NASA landers are still humming along: 2012’s Curiosity rover and 2018’s InSight. Launched last July, Perseverance will set down some 2,000 miles (3,200 kilometres) away at Jezero Crater, descending by parachute, rocket engines and sky crane.
TOUGHEST LANDING YET
NASA has equipped the 1-ton Perseverance — a beefier version of Curiosity — with the latest landing tech to ace this touchdown. A new autopilot tool will calculate the descending rover’s distance to the targeted location and release the massive parachute at the precise moment. Then another system will scan the surface, comparing observations with on-board maps. The rover could detour up to 2,000 feet (600 metres) while seeking somewhere safe, Neil Armstrong style. Without these gizmos, Jezero Crater would be too risky to attempt. Once down, the six-wheeled Perseverance should be the best driver Mars has ever seen, with more autonomy and range than Curiosity. “Percy’s got a new set of kicks,“ explained chief engineer Adam Steltzner, ”and she is ready for trouble on this Martian surface with her new wheels.”
LOOKING FOR SIGNS OF LIFE
Where there was water, there may have been life. That’s why NASA wants Perseverance snooping around Jezero Crater, once home to a lake fed by a river. It’s now bone dry, but 3.5 billion years ago, this Martian lake was as big and wet as Nevada and California’s Lake Tahoe. Perseverance will shoot lasers at rocks judged most likely to contain evidence of past microscopic life, analyzing the emitted vapour, and drill into the best candidates. A few dozen core samples — about a pound’s worth (one-half kilogram) of rock and dust — will be set aside in sealed titanium tubes for future pickup.
ROUND-TRIP TICKET
Scientists have wanted to get hold of Mars rocks ever since NASA’s Mariners provided the first close pictures a half-century ago. NASA is teaming up with the European Space Agency to do just that. The bold plan calls for a rover and return rocket to launch to Mars in 2026, to retrieve Perseverance’s stash of samples. NASA expects to bring back the rocks as early as 2031, several years before the first astronauts might arrive on the scene. The rover’s super sterilized sample tubes are the cleanest components ever sent into space, according to NASA, to avoid any contaminating traces of Earth.
COVID-19 PRECAUTIONS
Speaking of clean, NASA’s Mars Mission Control has never been so spotless. Instead of passing around jars of peanuts right before Perseverance’s landing — a good luck tradition going back decades — masked flight controllers will get their own individual bags. It’s one of many COVID-19 precautions at California’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The landing team will be spread over multiple rooms, with NASA bigwigs and journalists watching remotely. Launched last July, the aptly named Perseverance bears a plaque honouring health care workers battling the virus over the past year.
Loading…
Loading…Loading…Loading…Loading…Loading…
___
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Department of Science Education. The AP is solely responsible for all content.
Science
Giant prehistoric salmon had tusk-like spikes used for defence, building nests: study – CTV News
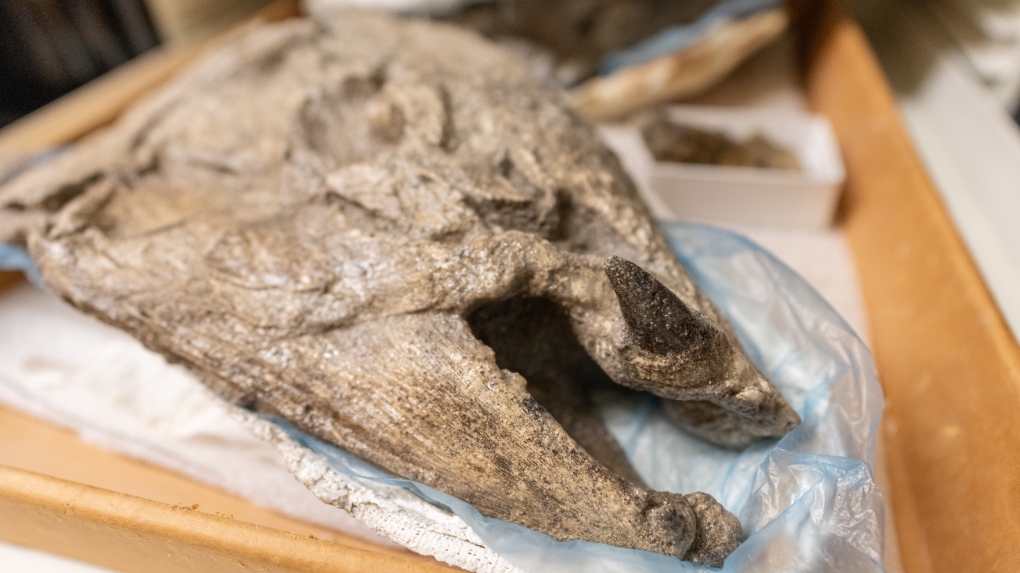


A new paper says a giant salmon that lived five million years ago in the coastal waters of the Pacific Northwest used tusk-like spikes as defense mechanisms and for building nests to spawn.
The initial fossil discoveries of the 2.7-metre-long salmon in Oregon in the 1970s were incomplete and led researchers to suggest the fish had fang-like teeth.
The now-extinct fish was dubbed the “saber-tooth salmon,” but the study published in the peer-reviewed journal PLOS One today renames it the “spike-toothed salmon” and says both males and females possessed the “multifunctional” feature.
Study co-author Edward Davis says the revelation about the tusk-like teeth came after the discovery of fossilized skulls at a site in Oregon in 2014.
Davis, an associate professor in the department of earth sciences at the University of Oregon, says he was surprised to see the skulls had “sideways teeth.”
Contrary to the belief since the 1970s, he says the teeth couldn’t have been used for any kind of biting.
“That was definitely a surprising moment,” Davis says of the fossil discovery in 2014. “I realized that all of the artwork and all of the publicity materials … we had just made two months prior, for the new exhibit, were all out of date.”
This report by The Canadian Press was first published April 24, 2024.
Science
SpaceX sends 23 Starlink satellites into low-Earth orbit


|
|
April 23 (UPI) — SpaceX launched 23 Starlink satellites into low-Earth orbit Tuesday evening from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
Liftoff occurred at 6:17 EDT with a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket sending the payload of 23 Starlink satellites into orbit.
The Falcon 9 rocket’s first-stage booster landed on an autonomous drone ship in the Atlantic Ocean after separating from the rocket’s second stage and its payload.
The entire mission was scheduled to take about an hour and 5 minutes to complete from launch to satellite deployment.
The mission was the ninth flight for the first-stage booster that previously completed five Starlink satellite-deployment missions and three other missions.





Science
NASA Celebrates As 1977’s Voyager 1 Phones Home At Last


|
|
Voyager 1 has finally returned usable data to NASA from outside the solar system after five months offline.
Launched in 1977 and now in its 46th year, the probe has been suffering from communication issues since November 14. The same thing also happened in 2022. However, this week, NASA said that engineers were finally able to get usable data about the health and status of its onboard engineering systems.
Slow Work
Fixing Voyager 1 has been slow work. It’s currently over 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, which means a radio message takes about 22.5 hours to reach it—and the same again to receive an answer.
The problem appears to have been its flight data subsystem, one of one of the spacecraft’s three onboard computers. Its job is to package the science and engineering data before it’s sent to Earth. Since the computer chip that stores its memory and some of its code is broken, engineers had to re-insert that code into a new location.
Next up for engineers at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California is to adjust other parts of the FDS software so Voyager 1 can return to sending science data.
Beyond The ‘Heliopause’
The longest-running and most distant spacecraft in history, Voyager 1, was launched on September 5, 1977, while its twin spacecraft, Voyager 2, was launched a little earlier on August 20, 1977. Voyager 2—now 12 billion miles away and traveling more slowly—continues to operate normally.
Both are now beyond what astronomers call the heliopause—a protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields created by the sun, which is thought to represent the sun’s farthest influence. Voyager 1 got to the heliopause in 2012 and Voyager 2 in 2018.
The Pale Blue Dot is a photograph of Earth taken Feb. 14, 1990, by NASA’s Voyager 1 at a distance of … [+]
NASA/JPL-Caltech
Pale Blue Dot
Since their launch from Cape Canaveral, Florida, aboard Titan-Centaur rockets, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 have had glittering careers. Both photographed Jupiter and Saturn in 1979 and 1980 before going their separate ways. Voyager 1 could have visited Pluto, but that was sacrificed so scientists could get images of Saturn’s moon, Titan, a maneuver that made it impossible for it to reach any other body in the solar system. Meanwhile, Voyager 2 took slingshots around the planets to also image Uranus in 1986 and Neptune in 1989—the only spacecraft ever to image the two outer planets.
On February 14, 1990, when 3.7 billion miles from Earth, Voyager 1 turned its cameras back towards the sun and took an image that included our planet as “a mote of dust suspended in a sunbeam.” Known as the “Pale Blue Dot,” it’s one of the most famous photos ever taken. It was remastered in 2019.





-



 Health19 hours ago
Health19 hours agoRemnants of bird flu virus found in pasteurized milk, FDA says
-



 Health23 hours ago
Health23 hours agoBird flu virus found in grocery milk as officials say supply still safe
-
News16 hours ago
Amid concerns over ‘collateral damage’ Trudeau, Freeland defend capital gains tax change
-



 Investment24 hours ago
Investment24 hours agoTaxes should not wag the tail of the investment dog, but that’s what Trudeau wants
-
Art20 hours ago
Random: We’re In Awe of Metaphor: ReFantazio’s Box Art
-
News24 hours ago
Peel police chief met Sri Lankan officer a court says ‘participated’ in torture – Global News
-
Art13 hours ago
The unmissable events taking place during London’s Digital Art Week
-
Media19 hours ago
Vaughn Palmer: B.C. premier gives social media giants another chance




