Economy
National child-care system would boost women's job numbers and economy, report says – CP24 Toronto's Breaking News


Jordan Press, The Canadian Press
Published Wednesday, November 25, 2020 7:31AM EST
OTTAWA – A new report estimates that hundreds of thousands of women could get back into the labour force if the Liberals follow through on a pledge to create a national child care system.
The paper to be released Wednesday makes the case that federal spending to create a national program would “pay for itself” in the form of extra income tax, extra spending and reduced social costs as more parents entered the workforce.
There is also the potential for tens of thousands of construction jobs as new centres and spaces are built, along with an employment boost in the child-care sector as it expands.
Report author and economist Jim Stanford says the lack of accessible and affordable daycare is a key reason why fewer women in their 30s and 40s are in the workforce than men the same age.
He estimates that between 363,000 and 726,000 women in the “prime parenting age cohort” between 25 and 50 could join the labour force over a 10-year period as a national child-care program is developed.
Among them would be up to 250,000 women moving into full-time jobs.
Stanford’s paper builds on previous research into the economic spinoffs of Quebec’s publicly funded daycare system, but develops estimates based on how a national system might look.
The Liberals have promised to make a long-term spending commitment to create a national child-care system, seeing it as a key avenue to help women harder hit during the pandemic in what has been dubbed a “she-cession.”
“Economists have agreed for years that child care has huge economic benefits, but we just can’t seem to get the ball over the line in Canada,” says Stanford, director of the Centre for Future Work.
“I finally think the ducks are being lined up here and we can actually make this happen,” he adds.
“This really is the moment when we can finally move forward, and it is a moment when Canada’s economy needs every job that it can get.”
A recent report by RBC economists Dawn Desjardins and Carrie Freestone calculated that 20,600 women fell out of the labour force between February and October even as 68,000 more men joined it.
The situation was most acute for women ages 20 to 24, and 35 to 39; one of the reasons the duo cited for the sharper drop was the pandemic-caused closure of child-care centres.
Child-care centres, which often run on tight margins and rely on steep parental fees, couldn’t keep up with costs during spring shutdowns and shed about 35,000 jobs between February and July. Some centres have closed for good.
The worry Stanford notes is that many of the job losses will become permanent and more centres will close without financial assistance from governments.
Scotiabank economists Jean-Francois Perrault and Rebekah Young suggested in September that creating nationally what Quebec has provincially would cost $11.5 billion a year.
Their analysis also suggested federal coffers could reap billions in new tax revenue as women in particular would get into the workforce in greater numbers, offsetting some of the overall cost.
Stanford’s estimate is for a boost to government revenues of between $18 billion and $30 billion per year, split between federal and provincial governments.
“This literally is a social program that pays for itself,” Stanford says.
“The economic benefits of giving this first-class care to early-age children, and getting their mothers in the labour market working to their full potential, are enormous.”
He argues that provinces, mired in a fiscal quagmire worse than the federal government’s, shouldn’t stand in the way of “reasonable demands” from the federal government to create a national system.
Provinces have responsibility for child-care delivery. Stanford says they cannot afford to look this gift horse of new revenues in the mouth given the federal government would foot most of the bill.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Nov. 25, 2020.
Economy
China Wants Everyone to Trade In Their Old Cars, Fridges to Help Save Its Economy – Bloomberg
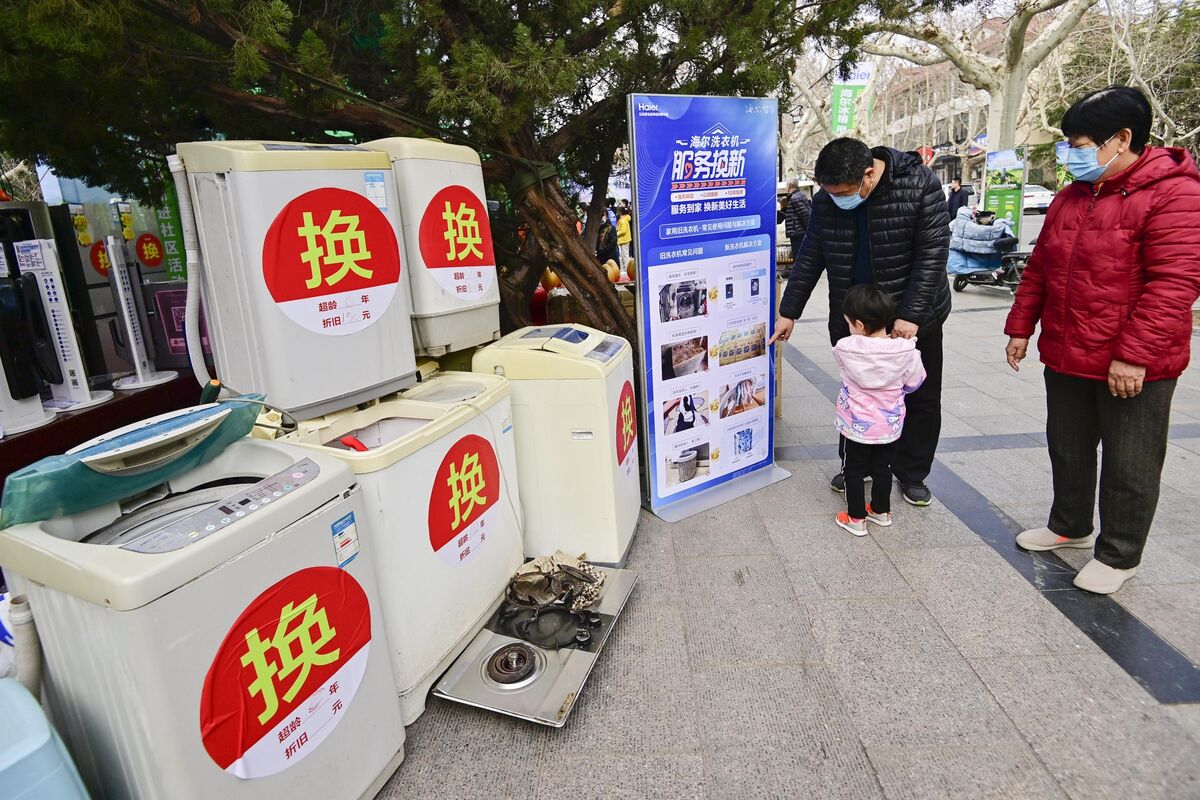


China’s world-beating electric vehicle industry, at the heart of growing trade tensions with the US and Europe, is set to receive a big boost from the government’s latest effort to accelerate growth.
That’s one takeaway from what Beijing has revealed about its plan for incentives that will encourage Chinese businesses and households to adopt cleaner technologies. It’s widely expected to be one of this year’s main stimulus programs, though question-marks remain — including how much the government will spend.
Economy
German Business Outlook Hits One-Year High as Economy Heals – BNN Bloomberg
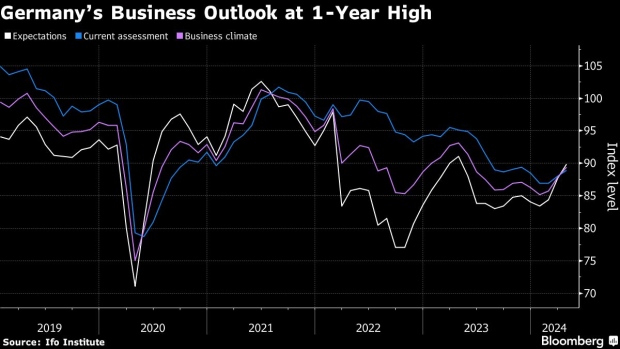

(Bloomberg) — German business sentiment improved to its highest level in a year — reinforcing recent signs that Europe’s largest economy is exiting two years of struggles.
An expectations gauge by the Ifo institute rose to 89.9. in April from a revised 87.7 the previous month. That exceeds the 88.9 median forecast in a Bloomberg survey. A measure of current conditions also advanced.
“Sentiment has improved at companies in Germany,” Ifo President Clemens Fuest said. “Companies were more satisfied with their current business. Their expectations also brightened. The economy is stabilizing, especially thanks to service providers.”
A stronger global economy and the prospect of looser monetary policy in the euro zone are helping drag Germany out of the malaise that set in following Russia’s attack on Ukraine. European Central Bank President Christine Lagarde said last week that the country may have “turned the corner,” while Chancellor Olaf Scholz has also expressed optimism, citing record employment and retreating inflation.
There’s been a particular shift in the data in recent weeks, with the Bundesbank now estimating that output rose in the first quarter, having only a month ago foreseen a contraction that would have ushered in a first recession since the pandemic.
Even so, the start of the year “didn’t go great,” according to Fuest.
“What we’re seeing at the moment confirms the forecasts, which are saying that growth will be weak in Germany, but at least it won’t be negative,” he told Bloomberg Television. “So this is the stabilization we expected. It’s not a complete recovery. But at least it’s a start.”
Monthly purchasing managers’ surveys for April brought more cheer this week as Germany returned to expansion for the first time since June 2023. Weak spots remain, however — notably in industry, which is still mired in a slump that’s being offset by a surge in services activity.
“We see an improving worldwide economy,” Fuest said. “But this doesn’t seem to reach German manufacturing, which is puzzling in a way.”
Germany, which was the only Group of Seven economy to shrink last year and has been weighing on the wider region, helped private-sector output in the 20-nation euro area strengthen this month, S&P Global said.
–With assistance from Joel Rinneby, Kristian Siedenburg and Francine Lacqua.
(Updates with more comments from Fuest starting in sixth paragraph.)
©2024 Bloomberg L.P.
Economy
Parallel economy: How Russia is defying the West’s boycott
|
|


When Moscow resident Zoya, 62, was planning a trip to Italy to visit her daughter last August, she saw the perfect opportunity to buy the Apple Watch she had long dreamed of owning.
Officially, Apple does not sell its products in Russia.
The California-based tech giant was one of the first companies to announce it would exit the country in response to Russian President Vladimir Putin’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine on February 24, 2022.
But the week before her trip, Zoya made a surprise discovery while browsing Yandex.Market, one of several Russian answers to Amazon, where she regularly shops.
Not only was the Apple Watch available for sale on the website, it was cheaper than in Italy.
Zoya bought the watch without a moment’s delay.
The serial code on the watch that was delivered to her home confirmed that it was manufactured by Apple in 2022 and intended for sale in the United States.
“In the store, they explained to me that these are genuine Apple products entering Russia through parallel imports,” Zoya, who asked to be only referred to by her first name, told Al Jazeera.
“I thought it was much easier to buy online than searching for a store in an unfamiliar country.”
Nearly 1,400 companies, including many of the most internationally recognisable brands, have since February 2022 announced that they would cease or dial back their operations in Russia in protest of Moscow’s military aggression against Ukraine.
But two years after the invasion, many of these companies’ products are still widely sold in Russia, in many cases in violation of Western-led sanctions, a months-long investigation by Al Jazeera has found.
Aided by the Russian government’s legalisation of parallel imports, Russian businesses have established a network of alternative supply chains to import restricted goods through third countries.
The companies that make the products have been either unwilling or unable to clamp down on these unofficial distribution networks.





-



 Health14 hours ago
Health14 hours agoRemnants of bird flu virus found in pasteurized milk, FDA says
-
Art20 hours ago
Mayor's youth advisory council seeks submissions for art gala – SooToday
-



 Health19 hours ago
Health19 hours agoBird flu virus found in grocery milk as officials say supply still safe
-



 Investment19 hours ago
Investment19 hours agoTaxes should not wag the tail of the investment dog, but that’s what Trudeau wants
-



 Science23 hours ago
Science23 hours agoiN PHOTOS: Nature lovers celebrate flora, fauna for Earth Day in Kamloops, Okanagan | iNFOnews | Thompson-Okanagan's News Source – iNFOnews
-
News19 hours ago
Peel police chief met Sri Lankan officer a court says ‘participated’ in torture – Global News
-
Media14 hours ago
Vaughn Palmer: B.C. premier gives social media giants another chance
-
Art20 hours ago
An exhibition with a cause: Montreal's 'Art by the Water' celebrates 15 years – CityNews Montreal




