Economy
OIC nations pledge fund to prevent Afghanistan economic collapse – Al Jazeera English
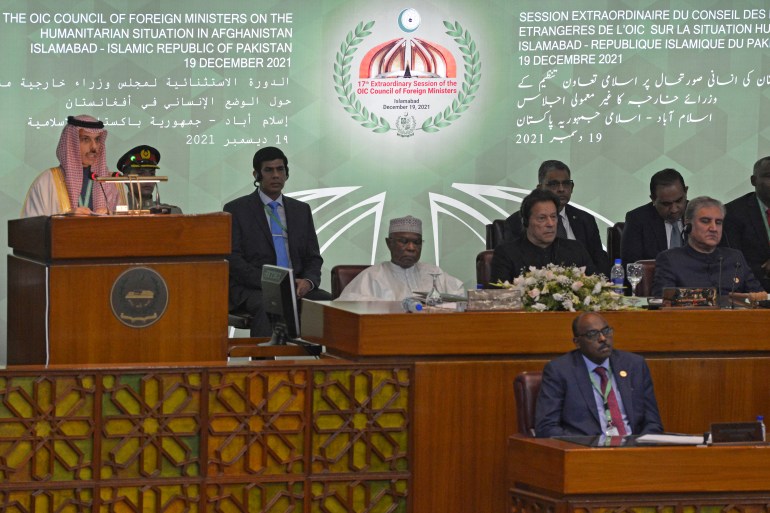
The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) has pledged to set up a humanitarian trust fund for Afghanistan as millions face hunger and poverty.
The crisis is causing alarm with billions of dollars in aid and assets frozen by the international community after the Taliban takeover of the country in August this year.
“Unless action is taken immediately, Afghanistan is heading for chaos,” Prime Minister Imran Khan, of Pakistan – which is holding the summit, told a meeting of foreign ministers from the OIC.
“Any government when it can’t pay its salaries for its public servants, hospitals, doctors, nurses, any government is going to collapse but chaos suits no one, it certainly does not suit the United States.”
1️⃣: @OIC_OCI to establish a Humanitarian Trust Fund, under the aegis of the @isdb_group, to serve as a vehicle to channel humanitarian assistance to #Afghanistan including in partnership with other international actors. pic.twitter.com/Ckw5EUGnYq
— Spokesperson 🇵🇰 MoFA (@ForeignOfficePk) December 19, 2021
An OIC resolution released after the meeting said the Islamic Development Bank would lead the effort to free up assistance by the first quarter of 2022.
It also urged Afghanistan’s rulers to abide by “obligations under international human rights covenants, especially with regards to the rights of women, children, youth, elderly and people with special needs”.
The OIC meeting did not give the new Taliban government any formal international recognition and Afghan Foreign Minister Amir Khan Muttaqi was excluded from the official photograph taken during the event.
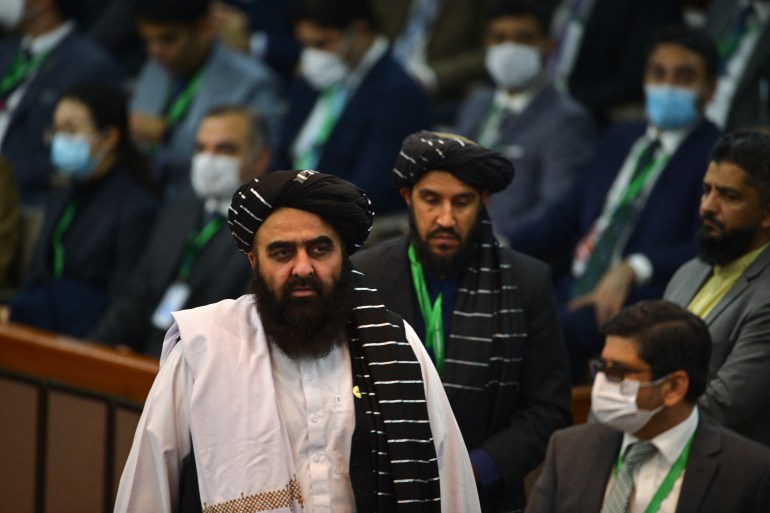


Muttaqi said his government “has the right to be officially recognised”.
“The current Afghanistan government is cooperating with every foreign organisation,” he told reporters, adding that sanctions “must be removed”.
In a speech to delegates, he said the US freezing of assets “is a clear violation of the human rights of Afghans, and can be interpreted as enmity with an entire nation”.
Economy in ‘free fall’
While some countries and organisations have begun delivering aid, a near-collapse of the country’s banking system has complicated their work.
United Nations’ Undersecretary-General on Humanitarian Affairs Martin Griffiths was also present at the OIC meeting and warned that Afghanistan’s economy was “now in free fall”.
“If we don’t act decisively and with compassion, I fear this fall will pull the entire population with it,” he said in his remarks.
I am encouraged by the support for the people of Afghanistan and the sense of urgency voiced unanimously by OIC member states today.
My remarks: https://t.co/dYuLLxqGbi
— Martin Griffiths (@UNReliefChief) December 19, 2021
“Twenty-three million people are already facing hunger; health facilities are overflowing with malnourished children; some 70 percent of teachers are not getting paid and millions of children, Afghanistan’s future are out of school.”
Pakistan’s Foreign Minister Shah Mahmood Qureshi said unlocking financial and banking channels was essential “because the economy can’t function and people can’t be helped without a banking system”.


Beyond immediate aid, Afghanistan needs help ensuring longer-term economic stability.
Much will depend on whether Washington is willing to unfreeze billions of dollars in central bank reserves and lift sanctions that have caused many institutions and governments to shy away from direct dealings with the Taliban.
Muttaqi reiterated the Taliban would not allow Afghanistan to be used as a base for attacks on other countries and he said no reprisals would be carried out against officials of the former government.
However, the Taliban has faced heavy criticism for keeping women and girls out of employment and education and excluding broad sections of Afghan society from government.
They have also been accused of trampling on human rights and, despite their promise of amnesty, targeting officials of the former administration.
Economy
Poland has EU's second highest emissions in relation to size of economy – Notes From Poland
[unable to retrieve full-text content]
Poland has EU’s second highest emissions in relation to size of economy Notes From Poland





Source link
Economy
IMF's Georgieva warns "there's plenty to worry about'' in world economy — including inflation, debt – Yahoo Canada Finance

WASHINGTON (AP) — The head of the International Monetary Fund said Thursday that the world economy has proven surprisingly resilient in the face of higher interest rates and the shock of war in Ukraine and Gaza, but “there is plenty to worry about,” including stubborn inflation and rising levels of government debt.
“ Inflation is down but not gone,” Kristalina Georgieva told reporters at the spring meeting of the IMF and its sister organization, the World Bank. In the United States, she said, “the flipside” of unexpectedly strong economic growth is that it ”taking longer than expected” to bring inflation down.
Georgieva also warned that government debts are growing around the world. Last year, they ticked up to 93% of global economic output — up from 84% in 2019 before the response to the COVID-19 pandemic pushed governments to spend more to provide healthcare and economic assistance. She urged countries to more efficiently collect taxes and spend public money. “In a world where the crises keep coming, countries must urgently build fiscal resilience to be prepared for the next shock,” she said.
On Tuesday, the IMF said it expects to the global economy to grow 3.2% this year, a modest upgrade from the forecast it made in January and unchanged from 2023. It also expects a third straight year of 3.2% growth in 2025.
ADVERTISEMENT
The world economy has proven unexpectedly sturdy, but it remains weak by historical standards: Global growth averaged 3.8% from 2000 to 2019.
One reason for sluggish global growth, Georgieva said, is disappointing improvement in productivity. She said that countries had not found ways to most efficiently match workers and technology and that years of low interest rates — that only ended after inflation picked up in 2021 — had allowed “firms that were not competitive to stay afloat.”
She also cited in many countries an aging “labor force that doesn’t bring the dynamism” needed for faster economic growth.
The United States has been an exception to the weak productivity gains over the past year. Compared to Europe, Georgieva said, America makes it easier for businesses to bring innovations to the marketplace and has lower energy costs.
She said countries could help their economies by slashing bureaucratic red tape and getting more women into the job market.
Paul Wiseman, The Associated Press
Economy
Nigeria’s Economy, Once Africa’s Biggest, Slips to Fourth Place – BNN Bloomberg
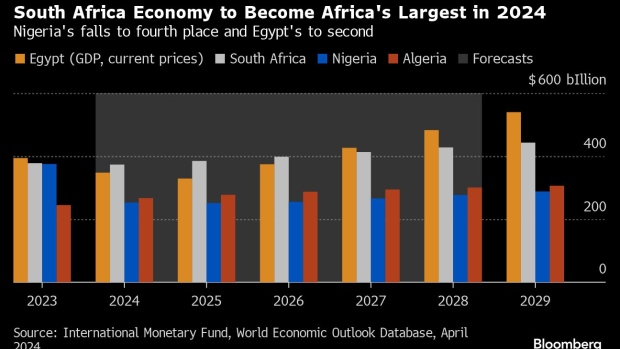

(Bloomberg) — Nigeria’s economy, which ranked as Africa’s largest in 2022, is set to slip to fourth place this year and Egypt, which held the top position in 2023, is projected to fall to second behind South Africa after a series of currency devaluations, International Monetary Fund forecasts show.
The IMF’s World Economic Outlook estimates Nigeria’s gross domestic product at $253 billion based on current prices this year, lagging energy-rich Algeria at $267 billion, Egypt at $348 billion and South Africa at $373 billion.
Africa’s most industrialized nation will remain the continent’s largest economy until Egypt reclaims the mantle in 2027, while Nigeria is expected to remain in fourth place for years to come, the data released this week shows.
Nigeria and Egypt’s fortunes have dimmed as they deal with high inflation and a plunge in their currencies.
Bola Tinubu has announced significant policy reforms since he became Nigeria’s president at the end of May 2023, including allowing the currency to float more freely, scrapping costly energy and gasoline subsidies and taking steps to address dollar shortages. Despite a recent rebound, the naira is still 50% weaker against the greenback than what it was prior to him taking office after two currency devaluations.
Read More: Why Nigeria’s Currency Rebounded and What It Means: QuickTake
Egypt, one of the emerging world’s most-indebted countries and the IMF’s second-biggest borrower after Argentina, has also allowed its currency to float, triggering an almost 40% plunge in the pound’s value against the dollar last month to attract investment.
The IMF had been calling for a flexible currency regime for many months and the multilateral lender rewarded Egypt’s government by almost tripling the size of a loan program first approved in 2022 to $8 billion. This was a catalyst for a further influx of around $14 billion in financial support from the European Union and the World Bank.
Read More: Egypt Avoided an Economic Meltdown. What Next?: QuickTake
Unlike Nigeria’s naira and Egypt’s pound, the value of South Africa’s rand has long been set in the financial markets and it has lost about 4% of its value against the dollar this year. Its economy is expected to benefit from improvements to its energy supply and plans to tackle logistic bottlenecks.
Algeria, an OPEC+ member has been benefiting from high oil and gas prices caused first by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and now tensions in the Middle East. It stepped in to ease some of Europe’s gas woes after Russia curtailed supplies amid its war in Ukraine.
©2024 Bloomberg L.P.
-



 Tech22 hours ago
Tech22 hours agoCytiva Showcases Single-Use Mixing System at INTERPHEX 2024 – BioPharm International
-



 Health18 hours ago
Health18 hours agoSupervised consumption sites urgently needed, says study – Sudbury.com
-
News24 hours ago
Tim Hortons says 'technical errors' falsely told people they won $55K boat in Roll Up To Win promo – CBC.ca
-



 Tech24 hours ago
Tech24 hours agoAaron Sluchinski adds Kyle Doering to lineup for next season – Sportsnet.ca
-



 Tech20 hours ago
Tech20 hours agoNew EV features for Google Maps have arrived. Here’s how to use them. – The Washington Post
-
News16 hours ago
2024 federal budget's key takeaways: Housing and carbon rebates, students and sin taxes – CBC News
-
Tech23 hours ago
Nintendo Indie World Showcase April 2024 – Every Announcement, Game Reveal & Trailer – Nintendo Life
-
News17 hours ago
Canada's 2024 budget announces 'halal mortgages'. Here's what to know – National Post




