Economy
Opinion: Waves of sanctions were supposed to crush the Russian economy, but it is still showing signs of resilience – The Globe and Mail
:format(jpeg)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/tgam/G63S4CMKENOZTAG6ORAWW7V34E.JPG)
:format(jpeg)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/tgam/G63S4CMKENOZTAG6ORAWW7V34E.JPG)
Valves near a drilling rig at a gas processing facility on the Arctic Yamal peninsula, Russia, on May 21, 2019.MAXIM SHEMETOV/Reuters
Near the start of the war, as the sanctions piled up, the Russian economy was thought to be doomed, possibly forcing President Vladimir Putin to sue for early peace. Almost three months later, there is no sign that a peace deal is about to be negotiated, nor is there much sign that the Russian economy is collapsing. The two may be related.
Yes, the Russian economy is hurting and no doubt in recession. But the economy is also showing annoying signs of resilience, in good part because oil and natural gas revenues are climbing even as Europe tries to wean itself off Mr. Putin’s hydrocarbons as punishment for having launched an unprovoked war that is killing an alarming number of civilians and triggering war crimes investigations.
Last week, the International Energy Agency said that Russia’s oil revenues are up 50 per cent this year even though some refiners are refusing to take Russian shipments. But other refiners are buying as much as they can – China and India are gobbling up the cargoes no longer wanted in Europe and North America. Moscow has been earning about US$20-billion this year – money that is used to fund the war – from the sale of crude and refined products.
At the same time, the sanctions, coupled with the proposed embargo on Russian oil exports to Europe, are putting the Europeans into a low-grade panic that is intensifying by the day as energy prices soar and across-the-board inflation takes off – always a popularity-shredding recipe for any ruling politician.
This week Italian Prime Minister Mario Draghi, calling for a ceasefire and the start of peace talks, indicated that the country’s support for the war is waning. Italy was one of the European countries most dependent on Russian energy and one of the biggest exporters to Russia – until the war began. Recent polls say nearly half of Italians now oppose sending arms to Ukraine and a similar proportion say that Russia should be handed Crimea and the eastern parts of Ukraine it now occupies, if doing so is what it takes to end the war. The figure is double the level of those who think Ukraine should fight to reclaim the territories lost to the Russians.
Sanctions and embargoes are tricky, often hazardous, pursuits. The working idea is that those on the receiving end should suffer far more than those delivering them. In this case, the pain is shared by both sides, though Russia is suffering more. Still, as energy writer Irina Slav points out, Europe’s assumption – that Russia needs to sell Europe its hydrocarbons more than Europe needs to buy them – may not hold true.
Take Hungary. The European Union is struggling to ban oil imports from Russia because Hungary is completely dependent on Russian oil; its economy would shut down without them, all the more so since most of its refineries are incapable of processing non-Russian oil. About two-thirds of Hungary’s oil, and more than 80 per cent of its gas, come from Russia.
And because much of the rest of Europe is addicted to Russian hydrocarbons too, the sanctions are taking on a two-sided flavour. Finland revealed Friday that Gazprom, the Kremlin-controlled gas giant that holds a monopoly on Russian gas exports, will cease gas supplies to Finland on Saturday (since Russia supplies only 5 per cent of Finnish gas, the move won’t hurt much but will act as a warning to the European heavyweight economies far more reliant on Russian gas, notably Germany and Italy).
The sanctions and embargo wars, like the war in Ukraine itself, are getting ugly, with no obvious winners or losers. The West is still waiting for the Russian economic implosion.
In March, shortly after war started, JPMorgan predicted a 35 per cent fall in second-quarter Russian GDP over the same period in 2021. Earlier this month, the Wall Street bank said the GDP hit would likely be less severe than it had forecast. They wrote that the data “do not point to an abrupt plunge in activity, at least for now.”
One of the reasons for Russia’s relative rude health is the country’s oil and gas export revenues are not only intact – they’re rising – even as the EU tries to curtail, and ultimately stop, imports of those fuels (the United States and Canada have already banned Russian oil and refined oil products).
Russia was making fortunes from oil and gas revenues even before the war started as global demand rose. Oil began to surge about this time last year as pandemic restrictions eased off and economies bounced back to life. Brent crude, the international benchmark, is up 73 per cent in a year; OPEC undershooting its oil production target is certainly adding to the upward price pressure, much to the irritation of the Americans. Mr. Putin is not complaining.
As Russia’s hydrocarbon revenues rise, its current-account surplus, which includes trade and some financial flows, is hitting record levels. The Institute of International Finance recently estimated that Russia’s surplus could hit US$250-billion this year, about double the figure recorded in 2021. Meanwhile the Russian ruble, which got slaughtered in the early days of the war, has rallied and is one of the top performing currencies in the world, in part due to capital controls and Moscow’s insistence that Gazprom be paid in rubles, not dollars or euros.
To be sure, Russia is suffering. Various Russian and international forecasts predict Russian GDP will shrink by 10 per cent this year. Russia’s central bank is hobbled by the sanctions on its foreign exchange reserves and Western companies are leaving in droves (though Russian companies are picking up some of those discarded assets at fire sale prices). But the country is not suffering enough to be motivated to end the war to save its economy. That may change, but probably not anytime soon.
Economy
China Wants Everyone to Trade In Their Old Cars, Fridges to Help Save Its Economy
|
|
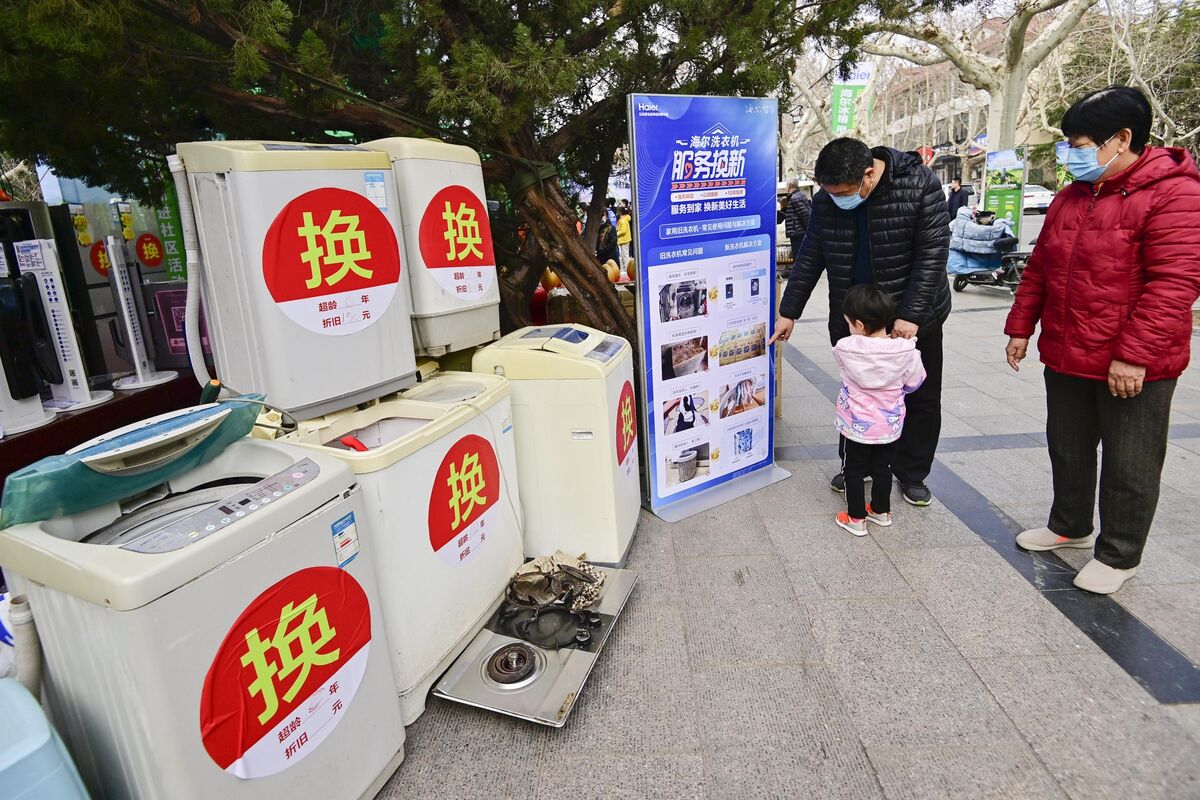


China’s world-beating electric vehicle industry, at the heart of growing trade tensions with the US and Europe, is set to receive a big boost from the government’s latest effort to accelerate growth.
That’s one takeaway from what Beijing has revealed about its plan for incentives that will encourage Chinese businesses and households to adopt cleaner technologies. It’s widely expected to be one of this year’s main stimulus programs, though question-marks remain — including how much the government will spend.





Economy
German Business Outlook Hits One-Year High as Economy Heals
|
|
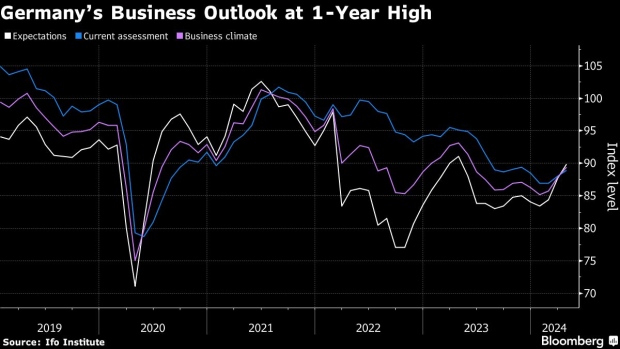

German business sentiment improved to its highest level in a year — reinforcing recent signs that Europe’s largest economy is exiting two years of struggles.
An expectations gauge by the Ifo institute rose to 89.9. in April from a revised 87.7 the previous month. That exceeds the 88.9 median forecast in a Bloomberg survey. A measure of current conditions also advanced.
“Sentiment has improved at companies in Germany,” Ifo President Clemens Fuest said. “Companies were more satisfied with their current business. Their expectations also brightened. The economy is stabilizing, especially thanks to service providers.”
A stronger global economy and the prospect of looser monetary policy in the euro zone are helping drag Germany out of the malaise that set in following Russia’s attack on Ukraine. European Central Bank President Christine Lagarde said last week that the country may have “turned the corner,” while Chancellor Olaf Scholz has also expressed optimism, citing record employment and retreating inflation.
There’s been a particular shift in the data in recent weeks, with the Bundesbank now estimating that output rose in the first quarter, having only a month ago foreseen a contraction that would have ushered in a first recession since the pandemic.
Even so, the start of the year “didn’t go great,” according to Fuest.
“What we’re seeing at the moment confirms the forecasts, which are saying that growth will be weak in Germany, but at least it won’t be negative,” he told Bloomberg Television. “So this is the stabilization we expected. It’s not a complete recovery. But at least it’s a start.”
Monthly purchasing managers’ surveys for April brought more cheer this week as Germany returned to expansion for the first time since June 2023. Weak spots remain, however — notably in industry, which is still mired in a slump that’s being offset by a surge in services activity.
“We see an improving worldwide economy,” Fuest said. “But this doesn’t seem to reach German manufacturing, which is puzzling in a way.”
Germany, which was the only Group of Seven economy to shrink last year and has been weighing on the wider region, helped private-sector output in the 20-nation euro area strengthen this month, S&P Global said.
–With assistance from Joel Rinneby, Kristian Siedenburg and Francine Lacqua.
(Updates with more comments from Fuest starting in sixth paragraph.)





Economy
Parallel economy: How Russia is defying the West’s boycott
|
|


When Moscow resident Zoya, 62, was planning a trip to Italy to visit her daughter last August, she saw the perfect opportunity to buy the Apple Watch she had long dreamed of owning.
Officially, Apple does not sell its products in Russia.
The California-based tech giant was one of the first companies to announce it would exit the country in response to Russian President Vladimir Putin’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine on February 24, 2022.
But the week before her trip, Zoya made a surprise discovery while browsing Yandex.Market, one of several Russian answers to Amazon, where she regularly shops.
Not only was the Apple Watch available for sale on the website, it was cheaper than in Italy.
Zoya bought the watch without a moment’s delay.
The serial code on the watch that was delivered to her home confirmed that it was manufactured by Apple in 2022 and intended for sale in the United States.
“In the store, they explained to me that these are genuine Apple products entering Russia through parallel imports,” Zoya, who asked to be only referred to by her first name, told Al Jazeera.
“I thought it was much easier to buy online than searching for a store in an unfamiliar country.”
Nearly 1,400 companies, including many of the most internationally recognisable brands, have since February 2022 announced that they would cease or dial back their operations in Russia in protest of Moscow’s military aggression against Ukraine.
But two years after the invasion, many of these companies’ products are still widely sold in Russia, in many cases in violation of Western-led sanctions, a months-long investigation by Al Jazeera has found.
Aided by the Russian government’s legalisation of parallel imports, Russian businesses have established a network of alternative supply chains to import restricted goods through third countries.
The companies that make the products have been either unwilling or unable to clamp down on these unofficial distribution networks.





-



 Health21 hours ago
Health21 hours agoRemnants of bird flu virus found in pasteurized milk, FDA says
-
News18 hours ago
Amid concerns over ‘collateral damage’ Trudeau, Freeland defend capital gains tax change
-
Art22 hours ago
Random: We’re In Awe of Metaphor: ReFantazio’s Box Art
-
Art15 hours ago
The unmissable events taking place during London’s Digital Art Week
-



 Politics20 hours ago
Politics20 hours agoHow Michael Cohen and Trump went from friends to foes
-
Tech22 hours ago
Surprise Apple Event Hints at First New iPads in Years
-
Science21 hours ago
NASA hears from Voyager 1, the most distant spacecraft from Earth, after months of quiet
-
Media21 hours ago
Vaughn Palmer: B.C. premier gives social media giants another chance





