Economy
Poverty and inflation: Egypt’s economy hit by global turmoil
|
|

DUBAI, United Arab Emirates (AP) — Stores are selling winter clothes from last season in the middle of summer. Repair shops lack spare parts for appliances. There’s a waiting list to buy a new car.
Egypt, a country of more than 103 million people, is running low on foreign currency needed to buy essentials like grain and fuel. To keep U.S. dollars in the country, the government has tightened imports, meaning fewer new cars and summer dresses.
For the nearly third of Egyptians living in poverty, and the millions more in poor conditions, the country’s economic woes mean life is much harder than off-season shopping — they’re finding it harder to put food on the table. A decade after deadly protests and political upheaval rocked the Middle East’s most populous nation, the economy is still staggering and has taken new hits.
Fatima, a 32-year-old cleaner in Cairo, says her family stopped buying red meat five months ago. Chicken also has become a luxury. She’s borrowing from relatives to make ends meet.
She’s worried about the impact of high prices on Egypt’s social fabric. Asking to be identified only by her first name for fear of reprisal, she worries that crime and theft will increase “because people won’t have enough money to feed themselves.”
For decades, most Egyptians have depended on the government to keep basic goods affordable, but that social contract is under pressure due to the impact from Russia’s war in Ukraine. Egypt has sought loans to pay for grain imports for state-subsidized bread. It’s also grappling with surging consumer prices as the currency drops in value. The threat of food insecurity in the world’s largest importer of wheat, 80% of which comes from the war-torn Black Sea region, has raised concerns.
“In terms of, like, bread in exchange for freedom, that contract got violated a long time ago,” said Timothy Kaldas, an economic expert at the Tahrir Institute for Middle East Policy.
Annual inflation climbed to 15.3% in August, compared with just over 6% in the same month last year. The Egyptian pound recently hit a record low against a strengthening U.S. dollar, selling at 19.5 pounds to $1. That has widened trade and budget deficits as foreign reserves needed to buy grain and fuel plunged by nearly 10% in March, shortly after Russia’s invasion sent commodity prices soaring and investors pulled billions of dollars from Egypt.
Egypt has few options to deal with the hole in its finances. As with previous crises, it’s turned to Gulf Arab allies and the International Monetary Fund for a bailout.
A new IMF loan would buoy Egypt’s dwindling foreign reserves, which have fallen to $33 billion from $41 billion in February. A new loan, however, will add to Egypt’s ballooning foreign debt, which climbed from $37 billion in 2010 — before the Arab Spring uprisings — to $158 billion as of March, according to Egyptian central bank figures.
Leaders blame the challenges on the coronavirus pandemic, which hurt the vital tourism industry, and price shocks sparked by the war in Ukraine. They’ve also faulted revolutionaries and those who may have backed the Muslim Brotherhood.
“Why don’t you want to pay the cost of what you did in 2011 and 2013?” President Abdel Fattah el-Sissi said in televised remarks this month. “What you did — didn’t that negatively impact the economy?”
He was referring to protests, which toppled Egypt’s longtime president, ushered in a divisive Muslim Brotherhood presidency, and resulted in a populist-backed power grab by the military and el-Sissi’s ascension to the presidency.
The former military general said the fallout from those years cost Egypt $450 billion — a price, he said, everyone must bear.
“We solve the matter together. I am saying this to all Egyptians … we are going to finish this matter together and pay its price together,” he said.
Critics, however, argue the government has squandered chances to make real reforms and is overspending on superfluous mega-projects as it builds a new administrative capital. The government has touted the construction boom as a job producer and economic engine.
The state’s hold over the economy and the “outsized role of military-related enterprises” have historically crowded out foreign investors and the private sector, said Hasnain Malik, who heads equity research at Tellimer, an emerging-markets investment analysis firm. The government’s plans to sell off minority stakes in some state-owned enterprises “does not necessarily fix this problem,” he said.
Egypt’s elite can withstand rising costs, living comfortably in Nile-view apartments and gated communities beyond the hustle of Cairo. Life for middle-class Egyptians is deteriorating, said Maha, a 38-year-old tech company employee and mother of two who asked to only be identified by her first name to speak freely.
“I think we will eventually move down the social ladder and end up below the poverty line,” she said.
The government took out a $500 million loan from the World Bank this summer and $221 million from the African Development Bank to help buy wheat. That covers around six weeks of a bread subsidy program supporting 70 million low-income Egyptians.
China assisted with a $2.8 billion currency swap. Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates and Qatar stepped in with pledges of $22 billion in short-term deposits and investments.
“Having what they define as stability in Egypt is in their strategic interests. They really don’t want to go through a repeat of 2011 and its aftermath,” said David Butter, an associate fellow at international affairs think tank Chatham House. Gulf Arab states are also making strategic investments in Egypt for the short and long-term, he said.
The government announced an “extraordinary” social protection program to roll out this month, targeting 9 million families with extended cash transfers and food coupons. This is on top of other assistance programs, including pop-up stands selling subsidized food staples. Officials point to how they managed the supply crunch brought on by the pandemic and the war in Ukraine, saying there is enough wheat and other basic food items for six months.
For some, leaving has promised more hope. Egyptians rank behind only Afghans as the top nationality of “irregular arrivals” to Europe so far this year, according to the International Organization for Migration’s flow chart. Most arrive by sea.
As pressure mounts on the Egyptian pound, the government could devalue the currency again.
“It’s going to hurt. It’s going to increase inflation,” said Kaldas, the Tahrir Institute economic expert. “Subsidies on bread is only one line-item in a family’s budget. So, for a lot of families, this is still going to be a lot of pain.”
___
Follow Aya Batrawy on Twitter at www.twitter.com/ayaelb.
Aya Batrawy, The Associated Press
Economy
Poland has EU's second highest emissions in relation to size of economy – Notes From Poland
[unable to retrieve full-text content]
Poland has EU’s second highest emissions in relation to size of economy Notes From Poland




Source link
Economy
IMF's Georgieva warns "there's plenty to worry about'' in world economy — including inflation, debt – Yahoo Canada Finance

WASHINGTON (AP) — The head of the International Monetary Fund said Thursday that the world economy has proven surprisingly resilient in the face of higher interest rates and the shock of war in Ukraine and Gaza, but “there is plenty to worry about,” including stubborn inflation and rising levels of government debt.
“ Inflation is down but not gone,” Kristalina Georgieva told reporters at the spring meeting of the IMF and its sister organization, the World Bank. In the United States, she said, “the flipside” of unexpectedly strong economic growth is that it ”taking longer than expected” to bring inflation down.
Georgieva also warned that government debts are growing around the world. Last year, they ticked up to 93% of global economic output — up from 84% in 2019 before the response to the COVID-19 pandemic pushed governments to spend more to provide healthcare and economic assistance. She urged countries to more efficiently collect taxes and spend public money. “In a world where the crises keep coming, countries must urgently build fiscal resilience to be prepared for the next shock,” she said.
On Tuesday, the IMF said it expects to the global economy to grow 3.2% this year, a modest upgrade from the forecast it made in January and unchanged from 2023. It also expects a third straight year of 3.2% growth in 2025.
ADVERTISEMENT
The world economy has proven unexpectedly sturdy, but it remains weak by historical standards: Global growth averaged 3.8% from 2000 to 2019.
One reason for sluggish global growth, Georgieva said, is disappointing improvement in productivity. She said that countries had not found ways to most efficiently match workers and technology and that years of low interest rates — that only ended after inflation picked up in 2021 — had allowed “firms that were not competitive to stay afloat.”
She also cited in many countries an aging “labor force that doesn’t bring the dynamism” needed for faster economic growth.
The United States has been an exception to the weak productivity gains over the past year. Compared to Europe, Georgieva said, America makes it easier for businesses to bring innovations to the marketplace and has lower energy costs.
She said countries could help their economies by slashing bureaucratic red tape and getting more women into the job market.
Paul Wiseman, The Associated Press
Economy
Nigeria’s Economy, Once Africa’s Biggest, Slips to Fourth Place – BNN Bloomberg
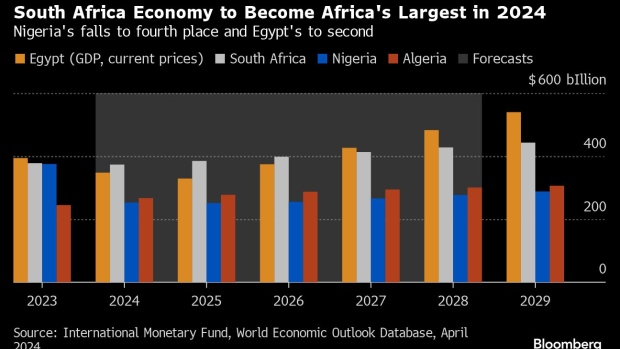

(Bloomberg) — Nigeria’s economy, which ranked as Africa’s largest in 2022, is set to slip to fourth place this year and Egypt, which held the top position in 2023, is projected to fall to second behind South Africa after a series of currency devaluations, International Monetary Fund forecasts show.
The IMF’s World Economic Outlook estimates Nigeria’s gross domestic product at $253 billion based on current prices this year, lagging energy-rich Algeria at $267 billion, Egypt at $348 billion and South Africa at $373 billion.
Africa’s most industrialized nation will remain the continent’s largest economy until Egypt reclaims the mantle in 2027, while Nigeria is expected to remain in fourth place for years to come, the data released this week shows.
Nigeria and Egypt’s fortunes have dimmed as they deal with high inflation and a plunge in their currencies.
Bola Tinubu has announced significant policy reforms since he became Nigeria’s president at the end of May 2023, including allowing the currency to float more freely, scrapping costly energy and gasoline subsidies and taking steps to address dollar shortages. Despite a recent rebound, the naira is still 50% weaker against the greenback than what it was prior to him taking office after two currency devaluations.
Read More: Why Nigeria’s Currency Rebounded and What It Means: QuickTake
Egypt, one of the emerging world’s most-indebted countries and the IMF’s second-biggest borrower after Argentina, has also allowed its currency to float, triggering an almost 40% plunge in the pound’s value against the dollar last month to attract investment.
The IMF had been calling for a flexible currency regime for many months and the multilateral lender rewarded Egypt’s government by almost tripling the size of a loan program first approved in 2022 to $8 billion. This was a catalyst for a further influx of around $14 billion in financial support from the European Union and the World Bank.
Read More: Egypt Avoided an Economic Meltdown. What Next?: QuickTake
Unlike Nigeria’s naira and Egypt’s pound, the value of South Africa’s rand has long been set in the financial markets and it has lost about 4% of its value against the dollar this year. Its economy is expected to benefit from improvements to its energy supply and plans to tackle logistic bottlenecks.
Algeria, an OPEC+ member has been benefiting from high oil and gas prices caused first by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and now tensions in the Middle East. It stepped in to ease some of Europe’s gas woes after Russia curtailed supplies amid its war in Ukraine.
©2024 Bloomberg L.P.
-



 Tech23 hours ago
Tech23 hours agoCytiva Showcases Single-Use Mixing System at INTERPHEX 2024 – BioPharm International
-



 Health19 hours ago
Health19 hours agoSupervised consumption sites urgently needed, says study – Sudbury.com
-



 Science5 hours ago
Science5 hours agoJeremy Hansen – The Canadian Encyclopedia
-
News19 hours ago
Canada's 2024 budget announces 'halal mortgages'. Here's what to know – National Post
-
News18 hours ago
2024 federal budget's key takeaways: Housing and carbon rebates, students and sin taxes – CBC News
-



 Investment5 hours ago
Investment5 hours agoUK Mulls New Curbs on Outbound Investment Over Security Risks – BNN Bloomberg
-



 Tech21 hours ago
Tech21 hours agoNew EV features for Google Maps have arrived. Here’s how to use them. – The Washington Post
-



 Science18 hours ago
Science18 hours agoGiant, 82-foot lizard fish discovered on UK beach could be largest marine reptile ever found – Livescience.com




