Science
Rate of scientific breakthroughs slowing over time: Study
|
|
The rate of ground-breaking scientific discoveries and technological innovation is slowing down despite an ever-growing amount of knowledge, according to an analysis released Wednesday of millions of research papers and patents.
While previous research has shown downturns in individual disciplines, the study is the first that “emphatically, convincingly documents this decline of disruptiveness across all major fields of science and technology,” lead author Michael Park told AFP.
Park, a doctoral student at the University of Minnesota’s Carlson School of Management, called disruptive discoveries those that “break away from existing ideas” and “push the whole scientific field into new territory.”
The researchers gave a “disruptiveness score” to 45 million scientific papers dating from 1945 to 2010, and to 3.9 million US-based patents from 1976 to 2010.
From the start of those time ranges, research papers and patents have been increasingly likely to consolidate or build upon previous knowledge, according to results published in the journal Nature.
The ranking was based on how the papers were cited in other studies five years after publication, assuming that the more disruptive the research was, the less its predecessors would be cited.
The biggest decrease in disruptive research came in physical sciences such as physics and chemistry.
“The nature of research is shifting” as incremental innovations become more common, senior study author Russell Funk said.
Burden of knowledge
One theory for the decline is that all the “low-hanging fruit” of science has already been plucked.
If that were the case, disruptiveness in various scientific fields would have fallen at different speeds, Park said.
But instead “the declines are pretty consistent in their speeds and timing across all major fields,” Park said, indicating that the low-hanging fruit theory is not likely to be the culprit.
Instead, the researchers pointed to what has been dubbed “the burden of research,” which suggests there is now so much that scientists must learn to master a particular field they have little time left to push boundaries.
This causes scientists and inventors to “focus on a narrow slice of the existing knowledge, leading them to just come up with something more consolidating rather than disruptive,” Park said.
Another reason could be that “there’s increasing pressure in academia to publish, publish, publish, because that’s the metric that academics are assessed on,” he added.
The researchers called on universities and funding agencies to focus more on quality, rather than quantity, and consider full subsidies for year-long sabbaticals to allow academics to read and think more deeply.
“We’re not getting any less innovative as a species,” Park emphasized, pointing to recent breakthroughs such as the use of mRNA technology in COVID-19 vaccines, or the measurement of gravity waves in 2015.
Jerome Lamy, a historian and expert in the sociology of science at France’s CNRS research agency, who was not involved in the research, said it showed that “ultra-specialization” and the pressure to publish had increased over the years.
He blamed a global trend of academics being “forced to slice up their papers” to increase their number of publications, saying it had led to “a dulling of research.”
More information:
Michael Park et al, Papers and patents are becoming less disruptive over time, Nature (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-05543-x
© 2023 AFP
Citation:
Rate of scientific breakthroughs slowing over time: Study (2023, January 4)
retrieved 4 January 2023
from https://phys.org/news/2023-01-scientific-breakthroughs.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.





Science
Exploring ecological networks in a digital world | News | Vancouver Island University | Canada – Vancouver Island University News


Getting to know Samantha Letourneau
By day, Samantha Letourneau is Vancouver Island University’s Canada Learning Bond project lead and Volunteer Tutor Coordinator. She’s also a musician and dancer and for the past two years, she’s been collaborating with Swedish artist Mårten Spångberg, thanks to funding obtained through Crimson Coast Dance, to create a digital art installation that goes live on Friday, April 26. A launch event takes place at Black Rabbit restaurant in the Old City Quarter that night. Samantha is also hosting a creative process workshop on April 27 and 28.
Can you share a bit about your background as an artist and how you got into it?
I have been working in art for a very long time, as a musician and dancer as well as an art administrator and program coordinator. I started music at the age of 11 and dance came later in my life in my early 20s. I always wanted to do dance, but I grew up in a small community in Yellowknife and at that time the only dance classes available were highland dancing, which I was not very interested in.
In my early 20s while living in Vancouver, I took classes in contemporary dance and was fortunate to land a small part in the Karen Jameison Dance company for a piece called The River. The River was about rivers and connection between the reality of a real and physical outdoor river and the different reality of “the river within.” It was both a piece of art and outreach for the community. It included working with the S’pak’wus Slu’lum Dancers of the Squamish Nation. Somewhat ground-breaking for 1998.
From there I was hooked and wanted to do more in dance. I studied a lot and took many classes. Fast forward to now, I have been involved with productions and performances with Crimson Coast Dance for more than 15 years and greatly appreciate the talent and innovation that Artistic Director Holly Bright has brought to this community. She is amazing and very supportive of artists in Nanaimo.
How did this international exchange come about?
The Nordic/Nanaimo exchange is one of the innovative projects Holly created. At the height of the pandemic, funded by BC Arts Council and Made In BC, Crimson Coast Dance embarked on a project that explored the ways in which Nanaimo artists could participate in online exchanges.
Two artists in Nanaimo – myself and Genevieve Johnson – were introduced to artists from Europe and supported through this international exchange. My collaborator, Mårten Spångberg, is a Swedish artist living and working in Berlin. An extension of that exchange is funded by Canada Council for the Arts – Digital Now.
What brought Mårten and myself together – and I quote Mårten here – is “questions around climate change, ecology and the influence contemporary society has on its environments. We are not interested in making art about the ecological crises or informing our audience about the urgency that climate change implies, but instead through our research develop work that in itself proposes, practices and engages in alternative ecologies.”
We share an understanding that art is a unique place, in the sense of practice, activation, performance and event, through which alternative ecologies can emerge and be probed and analyzed.
Tell us about the launch event.
We are launching the digital art installation that Mårten and I created on April 26 at The Attic at Black Rabbit Restaurant. The event is free to attend but people must sign up as seating is limited. I produced video art with soundscapes that I recorded mixing field recordings with voice and instrumentation. Marten explores text, imagery and AI.
My focus is on the evolving and ongoing process of how we communicate with each other and to nature within a digital context.
During our collaboration, Mårten and I talked about networks, though not just the expansive digital network of the internet but of nature. We shared thoughts on mycelium, a network of fungal threads or hyphae, that lately has received much attention on the importance of its function for the environment, including human beings.
Building off this concept, ideas of digital and ecological landscapes being connected emerged. From this we worked both collaboratively and individually to produce material for this digital project. Mårten will be there via Zoom as well and we will talk about this two-year process and the work we created together.
Science
Voyager 1 transmitting data again after Nasa remotely fixes 46-year-old probe – The Guardian


Earth’s most distant spacecraft, Voyager 1, has started communicating properly again with Nasa after engineers worked for months to remotely fix the 46-year-old probe.
Nasa’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), which makes and operates the agency’s robotic spacecraft, said in December that the probe – more than 15bn miles (24bn kilometres) away – was sending gibberish code back to Earth.
In an update released on Monday, JPL announced the mission team had managed “after some inventive sleuthing” to receive usable data about the health and status of Voyager 1’s engineering systems. “The next step is to enable the spacecraft to begin returning science data again,” JPL said. Despite the fault, Voyager 1 had operated normally throughout, it added.
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 was designed with the primary goal of conducting close-up studies of Jupiter and Saturn in a five-year mission. However, its journey continued and the spacecraft is now approaching a half-century in operation.
Voyager 1 crossed into interstellar space in August 2012, making it the first human-made object to venture out of the solar system. It is currently travelling at 37,800mph (60,821km/h).
The recent problem was related to one of the spacecraft’s three onboard computers, which are responsible for packaging the science and engineering data before it is sent to Earth. Unable to repair a broken chip, the JPL team decided to move the corrupted code elsewhere, a tricky job considering the old technology.
The computers on Voyager 1 and its sister probe, Voyager 2, have less than 70 kilobytes of memory in total – the equivalent of a low-resolution computer image. They use old-fashioned digital tape to record data.
The fix was transmitted from Earth on 18 April but it took two days to assess if it had been successful as a radio signal takes about 22 and a half hours to reach Voyager 1 and another 22 and a half hours for a response to come back to Earth. “When the mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on 20 April, they saw that the modification worked,” JPL said.
Alongside its announcement, JPL posted a photo of members of the Voyager flight team cheering and clapping in a conference room after receiving usable data again, with laptops, notebooks and doughnuts on the table in front of them.
The Retired Canadian astronaut Chris Hadfield, who flew two space shuttle missions and acted as commander of the International Space Station, compared the JPL mission to long-distance maintenance on a vintage car.
“Imagine a computer chip fails in your 1977 vehicle. Now imagine it’s in interstellar space, 15bn miles away,” Hadfield wrote on X. “Nasa’s Voyager probe just got fixed by this team of brilliant software mechanics.
Voyager 1 and 2 have made numerous scientific discoveries, including taking detailed recordings of Saturn and revealing that Jupiter also has rings, as well as active volcanism on one of its moons, Io. The probes later discovered 23 new moons around the outer planets.
As their trajectory takes them so far from the sun, the Voyager probes are unable to use solar panels, instead converting the heat produced from the natural radioactive decay of plutonium into electricity to power the spacecraft’s systems.
Nasa hopes to continue to collect data from the two Voyager spacecraft for several more years but engineers expect the probes will be too far out of range to communicate in about a decade, depending on how much power they can generate. Voyager 2 is slightly behind its twin and is moving slightly slower.
In roughly 40,000 years, the probes will pass relatively close, in astronomical terms, to two stars. Voyager 1 will come within 1.7 light years of a star in the constellation Ursa Minor, while Voyager 2 will come within a similar distance of a star called Ross 248 in the constellation of Andromeda.
Science
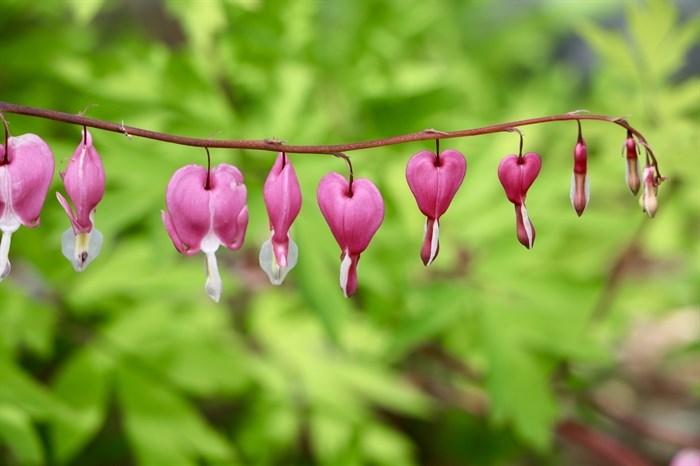
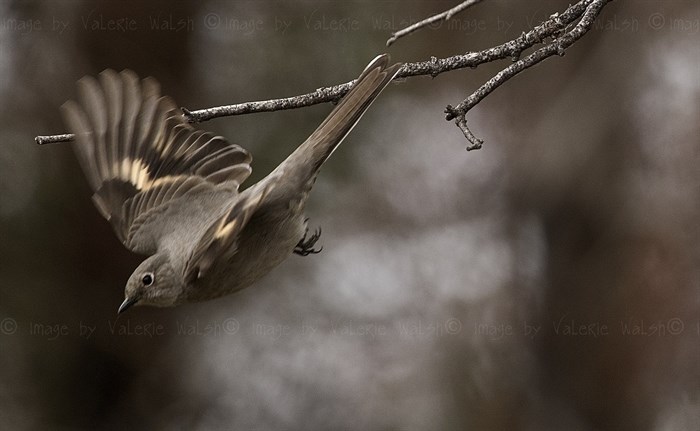
iN PHOTOS: Nature lovers celebrate flora, fauna for Earth Day in Kamloops, Okanagan | iNFOnews | Thompson-Okanagan's News Source – iNFOnews
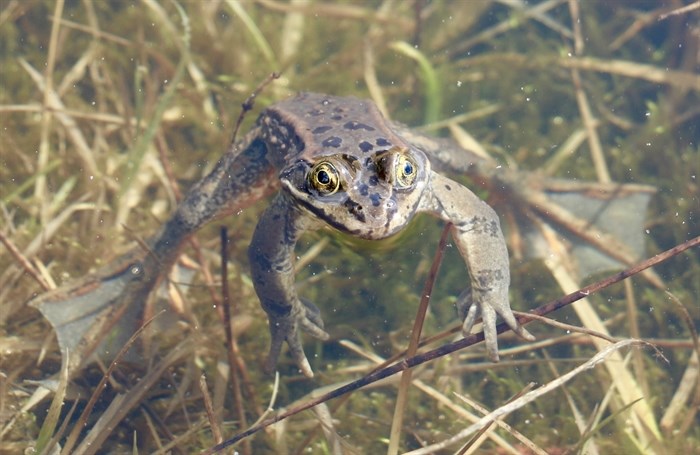


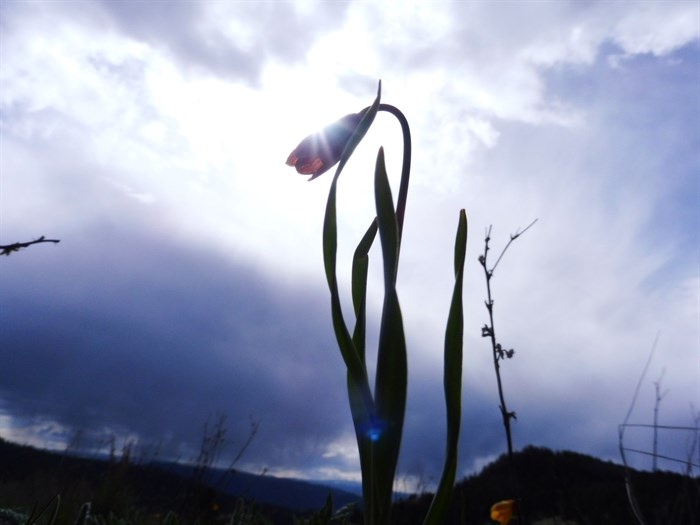
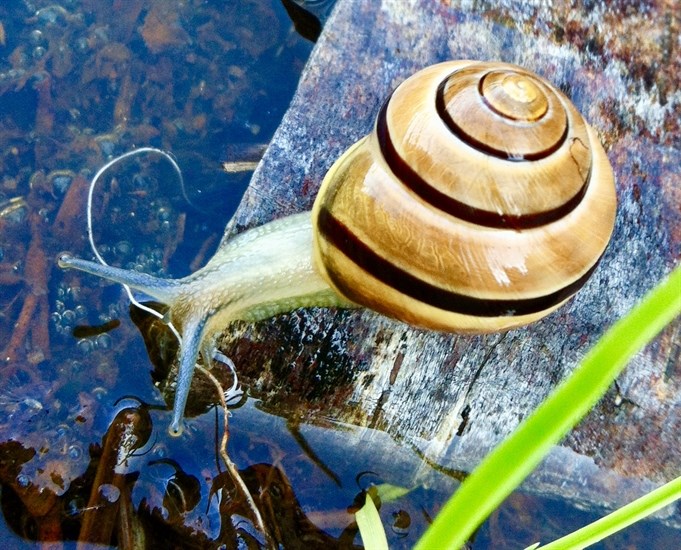
Photographers are sharing their favourite photos of flora and fauna captured in Kamloops and the Okanagan in celebration of Earth Day.
First started in the United States in the 70s, the special day on April 22 continues to be acknowledged around the globe. It’s a day to celebrate the planet and a reminder of the need for environmental conservation and sustainability, according to EarthDay.org.
These stunning nature photos show life in ponds and forests, in skies and on mountains, capturing the beauty and wonder of our local natural environments.
Area photographers shared some of their favourite finds and artistic captures. From frogs to flowers, the great outdoors is teeming with life.
If you have nature photos you want to share, send them to news@infonews.ca.








To contact a reporter for this story, email Shannon Ainslie or call 250-819-6089 or email the editor. You can also submit photos, videos or news tips to the newsroom and be entered to win a monthly prize draw.
We welcome your comments and opinions on our stories but play nice. We won’t censor or delete comments unless they contain off-topic statements or links, unnecessary vulgarity, false facts, spam or obviously fake profiles. If you have any concerns about what you see in comments, email the editor in the link above. SUBSCRIBE to our awesome newsletter here.


-



 Health24 hours ago
Health24 hours agoIt's possible to rely on plant proteins without sacrificing training gains, new studies say – The Globe and Mail
-



 Tech24 hours ago
Tech24 hours agoMeta Expands VR Operating System to Third-Party Hardware Makers – MacRumors
-



 Science23 hours ago
Science23 hours agoNASA's Voyager 1 resumes sending engineering updates to Earth – Phys.org
-
Art5 hours ago
Mayor's youth advisory council seeks submissions for art gala – SooToday
-
Art17 hours ago
Made Right Here: Woodworking art – CTV News Kitchener
-



 Sports15 hours ago
Sports15 hours agoAuston Matthews turns it up with three-point night as Maple Leafs slay Bruins in Game 2 – Toronto Sun
-



 Science13 hours ago
Science13 hours ago"Hi, It's Me": NASA's Voyager 1 Phones Home From 15 Billion Miles Away – NDTV
-
News23 hours ago
CTV National News: Honda's big move in Canada – CTV News







