Article content
It’s taken months, but Middlesex-London officially passed the magical threshold of 90 per cent coverage for two doses of COVID-19 vaccine.
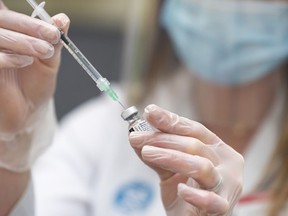
It’s taken months, but Middlesex-London officially passed the magical threshold of 90 per cent coverage for two doses of COVID-19 vaccine.
It’s taken months, but Middlesex-London officially passed the magical threshold of 90 per cent coverage for two doses of COVID-19 vaccine.
In a latest vaccine coverage statistical report, the health unit posted that 90.2 per cent of eligible people age 12 and older were fully vaccinated. Bravo.
But there are two areas where Middlesex-London continues to slog along. Only 47.2 per cent of people older than 12 have boosters. The other is the lack of uptake among kids younger than 12.
Two months after shots started going into arms of children age five to 11 years old, the first-dose vaccination coverage rate is 56.3 per cent, up just 2.3 percentage points from a week before when children were preparing to head back to class.
Now, a glass-half-full reaction might be that it’s encouraging to see so many kids have rolled up their sleeves. But my concern is, in an average elementary school classroom, statistically, almost half haven’t.
Though many of the political arguments have focused on schools having proper masks, testing and ventilation, particularly with super-contagious Omicron, a vaccination is still the best first line of defence.
There was a signal nationally Tuesday that might convince more parents to get shots in their kids’ arms. The National Advisory Committee on Immunization (NACI) beefed up its child vaccine recommendation, changing its advice from saying children “may” be vaccinated to “should” be vaccinated.
That subtle change “reflects the fact that the more we give this vaccine, the more it’s clear that the benefits far, far, far outweigh any risk,” said Alex Summers, Middlesex-London’s acting medical officer of health.
But, there still appears to be hefty hesitation. Stephen Wetmore, chair of the department of family medicine at Western University’s Schulich school of medicine and dentistry, said parents often “have a little more reluctance when it comes to vaccination of children and treatments in general for their children.”
Many adults hesitated before getting their own primary series of shots last year until they had more advice from public health and their doctors. Their hesitation about getting vaccinated then, might be behind their “reticence for their children getting vaccinated,” Wetmore said.
Summers said some point to the fact children who get COVID-19 do well, most of the time, “which may lead a parent to ask: ‘Why would I take any risk of the vaccine if my kid, if they do get exposed, is going to do fine?’”
“My response to that question would be that the risks of a child getting COVID, even if small, are still greater than any risks associated with the child getting vaccinated,” he said, adding the risks with getting vaccinated are “infinitesimally small.”
On the other hand, Wetmore pointed out cases of serious COVID-19 disease, long-haul COVID symptoms and multi-system inflammatory disease, though extremely rare, are documented in unvaccinated children. And there’s always the potential spread of the virus from kids to other vulnerable family members who may be more at risk because they are elderly or immune-compromised.
Summers said, on a larger scale, more vaccine coverage means less strain on the health-care system and less likelihood of public health restrictions. For kids, that’s not just a return to school, but getting back to hockey, dance, swimming, sleep-overs and everything else they’re missing.
The age group who got the memo is the 12- to 17-year-old cohort in the region who are 93.3 per cent vaccinated with two doses and are still waiting for booster approvals.
“I think the teenagers also looked at their activities and thought, ‘Hey, I actually value that activity and I know getting vaccinated makes it less likely that those activities aren’t going to happen,’” Summers said.
But public health still has work to do on the persuasion side both for adult boosters and children’s shots. Next week, the health unit will announce some in-school clinics in targeted areas and work will continue through family doctors, pharmacies and mobile clinics to get people protected.
And, Summers said, with NACI’s increased confidence in the vaccine, what might soon start are more conversations about proof-of vaccination requirements for children, similar to what helped increase uptake in adults last year.
“What mechanisms helped us essentially not have a Delta wave, I think, are very informative for the mechanisms that will help us move out of the Omicron wave,” he said.
And they might just get more shots in the arms of our kids.
|
Give the gift of great skin this holiday season Skinstitut Holiday Gift Kits take the stress out of gifting Toronto, October 31, 2024 – Beauty gifts are at the top of holiday wish lists this year, and Laser Clinics Canada, a leader in advanced beauty treatments and skincare, is taking the pressure out of seasonal shopping. Today, Laser Clincs Canada announces the arrival of its 2024 Holiday Gift Kits, courtesy of Skinstitut, the exclusive skincare line of Laser Clinics Group. In time for the busy shopping season, the limited-edition Holiday Gifts Kits are available in Laser Clinics locations in the GTA and Ottawa. Clinics are conveniently located in popular shopping centers, including Hillcrest Mall, Square One, CF Sherway Gardens, Scarborough Town Centre, Rideau Centre, Union Station and CF Markville. These limited-edition Kits are available on a first come, first served basis. “These kits combine our best-selling products, bundled to address the most relevant skin concerns we’re seeing among our clients,” says Christina Ho, Senior Brand & LAM Manager at Laser Clinics Canada. “With several price points available, the kits offer excellent value and suit a variety of gift-giving needs, from those new to cosmeceuticals to those looking to level up their skincare routine. What’s more, these kits are priced with a savings of up to 33 per cent so gift givers can save during the holiday season. There are two kits to select from, each designed to address key skin concerns and each with a unique theme — Brightening Basics and Hydration Heroes. Brightening Basics is a mix of everyday essentials for glowing skin for all skin types. The bundle comes in a sleek pink, reusable case and includes three full-sized products: 200ml gentle cleanser, 50ml Moisture Defence (normal skin) and 30ml1% Hyaluronic Complex Serum. The Brightening Basics kit is available at $129, a saving of 33 per cent. Hydration Heroes is a mix of hydration essentials and active heroes that cater to a wide variety of clients. A perfect stocking stuffer, this bundle includes four deluxe products: Moisture 15 15 ml Defence for normal skin, 10 ml 1% Hyaluronic Complex Serum, 10 ml Retinol Serum and 50 ml Expert Squalane Cleansing Oil. The kit retails at $59. In addition to the 2024 Holiday Gifts Kits, gift givers can easily add a Laser Clinic Canada gift card to the mix. Offering flexibility, recipients can choose from a wide range of treatments offered by Laser Clinics Canada, or they can expand their collection of exclusive Skinstitut products.
|
||
|
Brightening Basics 2024 Holiday Gift Kit by Skinstitut, available exclusively at Laser Clincs Canada clinics and online at skinstitut.ca. |
||
|
Hydration Heroes 2024 Holiday Gift Kit by Skinstitut – available exclusively at Laser Clincs Canada clinics and online at skinstitut.ca. |
LONDON (AP) — Most people have accumulated a pile of data — selfies, emails, videos and more — on their social media and digital accounts over their lifetimes. What happens to it when we die?
It’s wise to draft a will spelling out who inherits your physical assets after you’re gone, but don’t forget to take care of your digital estate too. Friends and family might treasure files and posts you’ve left behind, but they could get lost in digital purgatory after you pass away unless you take some simple steps.
Here’s how you can prepare your digital life for your survivors:
Apple
The iPhone maker lets you nominate a “ legacy contact ” who can access your Apple account’s data after you die. The company says it’s a secure way to give trusted people access to photos, files and messages. To set it up you’ll need an Apple device with a fairly recent operating system — iPhones and iPads need iOS or iPadOS 15.2 and MacBooks needs macOS Monterey 12.1.
For iPhones, go to settings, tap Sign-in & Security and then Legacy Contact. You can name one or more people, and they don’t need an Apple ID or device.
You’ll have to share an access key with your contact. It can be a digital version sent electronically, or you can print a copy or save it as a screenshot or PDF.
Take note that there are some types of files you won’t be able to pass on — including digital rights-protected music, movies and passwords stored in Apple’s password manager. Legacy contacts can only access a deceased user’s account for three years before Apple deletes the account.
Google takes a different approach with its Inactive Account Manager, which allows you to share your data with someone if it notices that you’ve stopped using your account.
When setting it up, you need to decide how long Google should wait — from three to 18 months — before considering your account inactive. Once that time is up, Google can notify up to 10 people.
You can write a message informing them you’ve stopped using the account, and, optionally, include a link to download your data. You can choose what types of data they can access — including emails, photos, calendar entries and YouTube videos.
There’s also an option to automatically delete your account after three months of inactivity, so your contacts will have to download any data before that deadline.
Facebook and Instagram
Some social media platforms can preserve accounts for people who have died so that friends and family can honor their memories.
When users of Facebook or Instagram die, parent company Meta says it can memorialize the account if it gets a “valid request” from a friend or family member. Requests can be submitted through an online form.
The social media company strongly recommends Facebook users add a legacy contact to look after their memorial accounts. Legacy contacts can do things like respond to new friend requests and update pinned posts, but they can’t read private messages or remove or alter previous posts. You can only choose one person, who also has to have a Facebook account.
You can also ask Facebook or Instagram to delete a deceased user’s account if you’re a close family member or an executor. You’ll need to send in documents like a death certificate.
TikTok
The video-sharing platform says that if a user has died, people can submit a request to memorialize the account through the settings menu. Go to the Report a Problem section, then Account and profile, then Manage account, where you can report a deceased user.
Once an account has been memorialized, it will be labeled “Remembering.” No one will be able to log into the account, which prevents anyone from editing the profile or using the account to post new content or send messages.
X
It’s not possible to nominate a legacy contact on Elon Musk’s social media site. But family members or an authorized person can submit a request to deactivate a deceased user’s account.
Passwords
Besides the major online services, you’ll probably have dozens if not hundreds of other digital accounts that your survivors might need to access. You could just write all your login credentials down in a notebook and put it somewhere safe. But making a physical copy presents its own vulnerabilities. What if you lose track of it? What if someone finds it?
Instead, consider a password manager that has an emergency access feature. Password managers are digital vaults that you can use to store all your credentials. Some, like Keeper,Bitwarden and NordPass, allow users to nominate one or more trusted contacts who can access their keys in case of an emergency such as a death.
But there are a few catches: Those contacts also need to use the same password manager and you might have to pay for the service.
___
Is there a tech challenge you need help figuring out? Write to us at onetechtip@ap.org with your questions.
The Canadian Paediatric Society says doctors should regularly screen children for reading difficulties and dyslexia, calling low literacy a “serious public health concern” that can increase the risk of other problems including anxiety, low self-esteem and behavioural issues, with lifelong consequences.
New guidance issued Wednesday says family doctors, nurses, pediatricians and other medical professionals who care for school-aged kids are in a unique position to help struggling readers access educational and specialty supports, noting that identifying problems early couldhelp kids sooner — when it’s more effective — as well as reveal other possible learning or developmental issues.
The 10 recommendations include regular screening for kids aged four to seven, especially if they belong to groups at higher risk of low literacy, including newcomers to Canada, racialized Canadians and Indigenous Peoples. The society says this can be done in a two-to-three-minute office-based assessment.
Other tips encourage doctors to look for conditions often seen among poor readers such as attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder; to advocate for early literacy training for pediatric and family medicine residents; to liaise with schools on behalf of families seeking help; and to push provincial and territorial education ministries to integrate evidence-based phonics instruction into curriculums, starting in kindergarten.
Dr. Scott McLeod, one of the authors and chair of the society’s mental health and developmental disabilities committee, said a key goal is to catch kids who may be falling through the cracks and to better connect families to resources, including quicker targeted help from schools.
“Collaboration in this area is so key because we need to move away from the silos of: everything educational must exist within the educational portfolio,” McLeod said in an interview from Calgary, where he is a developmental pediatrician at Alberta Children’s Hospital.
“Reading, yes, it’s education, but it’s also health because we know that literacy impacts health. So I think that a statement like this opens the window to say: Yes, parents can come to their health-care provider to get advice, get recommendations, hopefully start a collaboration with school teachers.”
McLeod noted that pediatricians already look for signs of low literacy in young children by way of a commonly used tool known as the Rourke Baby Record, which offers a checklist of key topics, such as nutrition and developmental benchmarks, to cover in a well-child appointment.
But he said questions about reading could be “a standing item” in checkups and he hoped the society’s statement to medical professionals who care for children “enhances their confidence in being a strong advocate for the child” while spurring partnerships with others involved in a child’s life such as teachers and psychologists.
The guidance said pediatricians also play a key role in detecting and monitoring conditions that often coexist with difficulty reading such as attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, but McLeod noted that getting such specific diagnoses typically involves a referral to a specialist, during which time a child continues to struggle.
He also acknowledged that some schools can be slow to act without a specific diagnosis from a specialist, and even then a child may end up on a wait list for school interventions.
“Evidence-based reading instruction shouldn’t have to wait for some of that access to specialized assessments to occur,” he said.
“My hope is that (by) having an existing statement or document written by the Canadian Paediatric Society … we’re able to skip a few steps or have some of the early interventions present,” he said.
McLeod added that obtaining specific assessments from medical specialists is “definitely beneficial and advantageous” to know where a child is at, “but having that sort of clear, thorough assessment shouldn’t be a barrier to intervention starting.”
McLeod said the society was partly spurred to act by 2022’s “Right to Read Inquiry Report” from the Ontario Human Rights Commission, which made 157 recommendations to address inequities related to reading instruction in that province.
He called the new guidelines “a big reminder” to pediatric providers, family doctors, school teachers and psychologists of the importance of literacy.
“Early identification of reading difficulty can truly change the trajectory of a child’s life.”
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Oct. 23, 2024.
Trudeau, Freeland embrace a second Trump presidency
In this Florida school district, some parents are pushing back against a cellphone ban
Canadanewsmedia news November 07, 2024: Canada’s health-care spending to reach $372 billion in 2024
A tiny grain of nuclear fuel is pulled from ruined Japanese nuclear plant, in a step toward cleanup
Things for Canada to watch following Trump victory in U.S.
Saskatchewan’s Jason Ackerman improves to 6-0 at mixed curling nationals
Health-care spending expected to outpace economy and reach $372 billion in 2024: CIHI
DeMar DeRozan scores 27 points to lead the Kings past the Raptors 122-107