Science
The detection of phosphine in Venus' clouds is a big deal – here's how we can find out if it really is life – The Conversation US
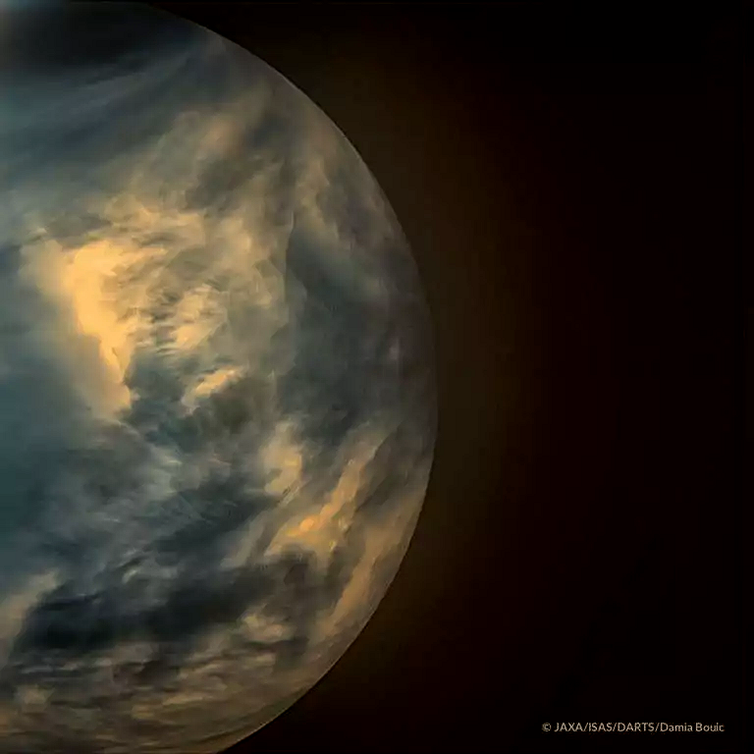

On Sept. 14, 2020, a new planet was added to the list of potentially habitable worlds in the Solar System: Venus.
Phosphine, a toxic gas made up of one phosphorus and three hydrogen atoms (PH₃), commonly produced by organic life forms but otherwise difficult to make on rocky planets, was discovered in the middle layer of the Venus atmosphere. This raises the tantalizing possibility that something is alive on our planetary neighbor. With this discovery, Venus joins the exalted ranks of Mars and the icy moons Enceladus and Europa among planetary bodies where life may once have existed, or perhaps might even still do so today.
I’m a planetary scientist and something of a Venus evangelical. This discovery is one of the most exciting made about Venus in a very long time — and opens up a new set of possibilities for further exploration in search of life in the Solar System.
JAXA/ISAS/DARTS/Damia Bouic
Atmospheric mysteries
First, it’s critical to point out that this detection does not mean that astronomers have found alien life in the clouds of Venus. Far from it, in fact.
Although the discovery team identified phosphine at Venus with two different telescopes, helping to confirm the initial detection, phosphine gas can result from several processes that are unrelated to life, such as lightning, meteor impacts or even volcanic activity.
However, the quantity of phosphine detected in the Venusian clouds seems to be far greater than those processes are capable of generating, allowing the team to rule out numerous inorganic possibilities. But our understanding of the chemistry of Venus’ atmosphere is sorely lacking: Only a handful of missions have plunged through the inhospitable, carbon dioxide-dominated atmosphere to take samples among the global layer of sulfuric acid clouds.
So we planetary scientists are faced with two possibilities: Either there is some sort of life in the Venus clouds, generating phosphine, or there is unexplained and unexpected chemistry taking place there. How do we find out which it is?


Daderot
First and foremost, we need more information about the abundance of PH₃ in the Venus atmosphere, and we can learn something about this from Earth. Just as the discovery team did, existing telescopes capable of detecting phosphine around Venus can be used for follow-up observations, to both definitively confirm the initial finding and figure out if the amount of PH₃ in the atmosphere changes with time. In parallel, there is now a huge opportunity to carry out lab work to better understand the types of chemical reactions that might be possible on Venus — for which we have very limited information at present.


ESO/C. Malin.
Once more unto the breach
But measurements on and from Earth can take us only so far. To really get to the heart of this mystery, we need to go back to Venus. Spacecraft equipped with spectrometers that can detect phosphine from orbit could be dispatched to the second planet with the express purpose of characterizing where, and how much, of this gas is there. Because spacecraft can survive for many years in Venus’ orbit, we could obtain continuous observations with a dedicated orbiter over a much longer period than with telescopes on Earth.
But even orbital data can’t tell us the whole story. To fully get a handle on what’s happening at Venus, we have to actually get into the atmosphere. And that’s where aerial platforms come in. Capable of operating above much of the acidic cloud layer – where the temperature and pressure are almost Earthlike – for potentially months at a time, balloons or flying wings could take detailed atmospheric composition measurements there. These craft could even carry the kinds of instruments being developed to look for life on Europa. At that point, humanity might finally be able to definitively tell if we share our Solar System with Venusian life.


NASA/JPL-Caltech
A new dawn for Venus exploration?
Thirty-one years have elapsed since the United States last sent a dedicated mission to Venus. That could soon change as NASA considers two of four missions in the late 2020s targeting Venus. One, called VERITAS, would carry a powerful radar to peer through the thick clouds and return unprecedented high-resolution images of the surface. The other, DAVINCI+, would plunge through the atmosphere, sampling the air as it descended, perhaps even able to sniff any phosphine present. NASA plans to pick at least one mission in April 2021.
[Deep knowledge, daily. Sign up for The Conversation’s newsletter.]
I have argued before for a return to Venus, and will continue to do so. Even without this latest scientific discovery, Venus is a compelling exploration target, with tantalizing evidence that the planet once had oceans and perhaps even suffered a hellish fate at the hands of its own volcanic eruptions.
But with the detection of a potential biomarker in Venus’ atmosphere, we now have yet another major reason to return to the world ancient Greek astronomers called Phosphorus — a name for Venus that, it turns out, is wonderfully prescient.
Science
An extra moon may be orbiting Earth — and scientists think they know exactly where it came from – Livescience.com


A fast-spinning asteroid that orbits in time with Earth may be a wayward chunk of the moon. Now, scientists think they know exactly which lunar crater it came from.
A new study, published April 19 in the journal Nature Astronomy, finds that the near-Earth asteroid 469219 Kamo’oalewa may have been flung into space when a mile-wide (1.6 kilometers) space rock hit the moon, creating the Giordano Bruno crater.
Kamo’oalewa’s light reflectance matches that of weathered lunar rock, and its size, age and spin all match up with the 13.6-mile-wide (22 km) crater, which sits on the far side of the moon, the study researchers reported.
China plans to launch a sample-return mission to the asteroid in 2025. Called Tianwen-2, the mission will return pieces of Kamo’oalewa about 2.5 years later, according to Live Science’s sister site Space.com.
“The possibility of a lunar-derived origin adds unexpected intrigue to the [Tianwen-2] mission and presents additional technical challenges for the sample return,” Bin Cheng, a planetary scientist at Tsinghua University and a co-author of the new study, told Science.
Related: How many moons does Earth have?
Kamo’oalewa was discovered in 2016 by researchers at Haleakala Observatory in Hawaii. It has a diameter of about 100 to 200 feet (approximately 30 to 60 meters, or about the size of a large Ferris wheel) and spins at a rapid clip of one rotation every 28 minutes. The asteroid orbits the sun in a similar path to Earth, sometimes approaching within 10 million miles (16 million km).
window.sliceComponents = window.sliceComponents || ;
externalsScriptLoaded.then(() => {
window.reliablePageLoad.then(() => {
var componentContainer = document.querySelector(“#slice-container-newsletterForm-articleInbodyContent-UG4KJ7zrhxAytcHZQxVzXK”);
if (componentContainer)
var data = “layout”:”inbodyContent”,”header”:”Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now”,”tagline”:”Get the worldu2019s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.”,”formFooterText”:”By submitting your information you agree to the Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy and are aged 16 or over.”,”successMessage”:”body”:”Thank you for signing up. You will receive a confirmation email shortly.”,”failureMessage”:”There was a problem. Please refresh the page and try again.”,”method”:”POST”,”inputs”:[“type”:”hidden”,”name”:”NAME”,”type”:”email”,”name”:”MAIL”,”placeholder”:”Your Email Address”,”required”:true,”type”:”hidden”,”name”:”NEWSLETTER_CODE”,”value”:”XLS-D”,”type”:”hidden”,”name”:”LANG”,”value”:”EN”,”type”:”hidden”,”name”:”SOURCE”,”value”:”60″,”type”:”hidden”,”name”:”COUNTRY”,”type”:”checkbox”,”name”:”CONTACT_OTHER_BRANDS”,”label”:”text”:”Contact me with news and offers from other Future brands”,”type”:”checkbox”,”name”:”CONTACT_PARTNERS”,”label”:”text”:”Receive email from us on behalf of our trusted partners or sponsors”,”type”:”submit”,”value”:”Sign me up”,”required”:true],”endpoint”:”https://newsletter-subscribe.futureplc.com/v2/submission/submit”,”analytics”:[“analyticsType”:”widgetViewed”],”ariaLabels”:;
var triggerHydrate = function()
window.sliceComponents.newsletterForm.hydrate(data, componentContainer);
if (window.lazyObserveElement)
window.lazyObserveElement(componentContainer, triggerHydrate);
else
triggerHydrate();
}).catch(err => console.log(‘Hydration Script has failed for newsletterForm-articleInbodyContent-UG4KJ7zrhxAytcHZQxVzXK Slice’, err));
}).catch(err => console.log(‘Externals script failed to load’, err));
Follow-up studies suggested that the light spectra reflected by Kamo’oalewa was very similar to the spectra reflected by samples brought back to Earth by lunar missions, as well as to meteorites known to come from the moon.
Cheng and his colleagues first calculated what size object and what speed of impact would be necessary to eject a fragment like Kamo’oalewa from the lunar surface, as well as what size crater would be left behind. They figured out that the asteroid could have resulted from a 45-degree impact at about 420,000 mph (18 kilometers per second) and would have left a 6-to-12-mile-wide (10 to 20 km) crater.
There are tens of thousands of craters that size on the moon, but most are ancient, the researchers wrote in their paper. Near-Earth asteroids usually last only about 10 million years, or at most up to 100 million years before they crash into the sun or a planet or get flung out of the solar system entirely. By looking at young craters, the team narrowed down the contenders to a few dozen options.
The researchers focused on Giordano Bruno, which matched the requirements for both size and age. They found that the impact that formed Giordano Bruno could have created as many as three still-extant Kamo’oalewa-like objects. This makes Giordano Bruno crater the most likely source of the asteroid, the researchers concluded.
“It’s like finding out which tree a fallen leaf on the ground came from in a vast forest,” Cheng wrote on X, formerly known as Twitter.
Confirmation will come after the Tianwen-2 mission brings a piece of Kamo’oalewa back to Earth. Scientists already have a sample of what is believed to be ejecta from Giordano Bruno crater in the Luna 24 sample, a bit of moon rock brought back to Earth in a 1976 NASA mission. By comparing the two, researchers could verify Kamo’oalewa’s origin.
Editor’s note: This article’s headline was updated on April 23 at 10 a.m. ET.
Science
"Hi, It's Me": NASA's Voyager 1 Phones Home From 15 Billion Miles Away – NDTV


<!–
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 was mankind’s first spacecraft to enter the interstellar medium
Washington, United States:
NASA’s Voyager 1 probe — the most distant man-made object in the universe — is returning usable information to ground control following months of spouting gibberish, the US space agency announced Monday.
The spaceship stopped sending readable data back to Earth on November 14, 2023, even though controllers could tell it was still receiving their commands.
In March, teams working at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory discovered that a single malfunctioning chip was to blame, and devised a clever coding fix that worked within the tight memory constraints of its 46-year-old computer system.
window._rrCode = window._rrCode || [];_rrCode.push(function() (function(v,d,o,ai)ai=d.createElement(“script”);ai.defer=true;ai.async=true;ai.src=v.location.protocol+o;d.head.appendChild(ai);)(window, document, “//a.vdo.ai/core/v-ndtv/vdo.ai.js”); );
“Voyager 1 spacecraft is returning usable data about the health and status of its onboard engineering systems,” the agency said.
Hi, it’s me. – V1 https://t.co/jgGFBfxIOe
— NASA Voyager (@NASAVoyager) April 22, 2024
“The next step is to enable the spacecraft to begin returning science data again.”
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 was mankind’s first spacecraft to enter the interstellar medium, in 2012, and is currently more than 15 billion miles from Earth. Messages sent from Earth take about 22.5 hours to reach the spacecraft.
Its twin, Voyager 2, also left the solar system in 2018.
Both Voyager spacecraft carry “Golden Records” — 12-inch, gold-plated copper disks intended to convey the story of our world to extraterrestrials.
These include a map of our solar system, a piece of uranium that serves as a radioactive clock allowing recipients to date the spaceship’s launch, and symbolic instructions that convey how to play the record.
The contents of the record, selected for NASA by a committee chaired by legendary astronomer Carl Sagan, include encoded images of life on Earth, as well as music and sounds that can be played using an included stylus.
window._rrCode = window._rrCode || [];_rrCode.push(function(){ (function(d,t) var s=d.createElement(t); var s1=d.createElement(t); if (d.getElementById(‘jsw-init’)) return; s.setAttribute(‘id’,’jsw-init’); s.setAttribute(‘src’,’https://www.jiosaavn.com/embed/_s/embed.js?ver=’+Date.now()); s.onload=function()document.getElementById(‘jads’).style.display=’block’;s1.appendChild(d.createTextNode(‘JioSaavnEmbedWidget.init(a:”1″, q:”1″, embed_src:”https://www.jiosaavn.com/embed/playlist/85481065″,”dfp_medium” : “1”,partner_id: “ndtv”);’));d.body.appendChild(s1);; if (document.readyState === ‘complete’) d.body.appendChild(s); else if (document.readyState === ‘loading’) var interval = setInterval(function() if(document.readyState === ‘complete’) d.body.appendChild(s); clearInterval(interval); , 100); else window.onload = function() d.body.appendChild(s); ; )(document,’script’); });
Their power banks are expected to be depleted sometime after 2025. They will then continue to wander the Milky Way, potentially for eternity, in silence.
(Except for the headline, this story has not been edited by NDTV staff and is published from a syndicated feed.)
Science
West Antarctica's ice sheet was smaller thousands of years ago – here's why this matters today – The Conversation
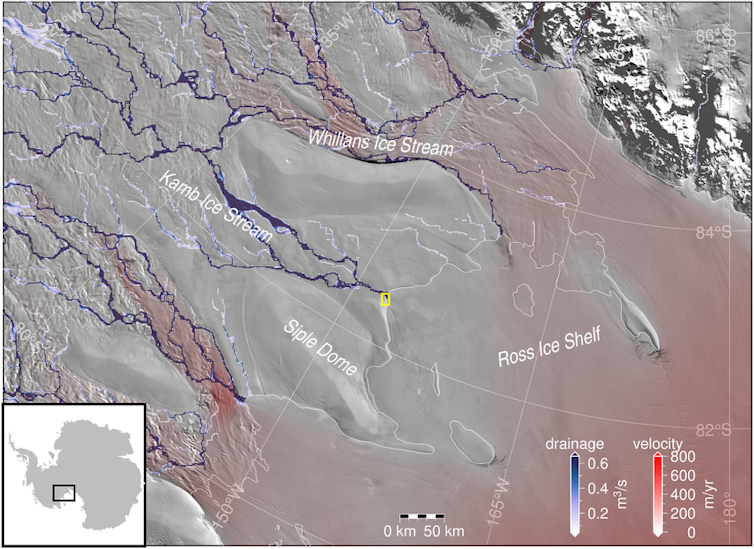

As the climate warms and Antarctica’s glaciers and ice sheets melt, the resulting rise in sea level has the potential to displace hundreds of millions of people around the world by the end of this century.
A key uncertainty in how much and how fast the seas will rise lies in whether currently “stable” parts of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet can become “unstable”.
One such region is West Antarctica’s Siple Coast, where rivers of ice flow off the continent and drain into the ocean.
Journal of Geophysical Research, CC BY-SA
This ice flow is slowed down by the Ross Ice Shelf, a floating mass of ice nearly the size of Spain, which holds back the land-based ice. Compared to other ice shelves in West Antarctica, the Ross Ice Shelf has little melting at its base because the ocean below it is very cold.
Although this region has been stable during the past few decades, recent research suggest this was not always the case. Radiocarbon dating of sediments from beneath the ice sheet tells us that it retreated hundreds of kilometres some 7,000 years ago, and then advanced again to its present position within the last 2,000 years.
Figuring out why this happened can help us better predict how the ice sheet will change in the future. In our new research, we test two main hypotheses.
Read more:
What an ocean hidden under Antarctic ice reveals about our planet’s future climate
Testing scenarios
Scientists have considered two possible explanations for this past ice sheet retreat and advance. The first is related to Earth’s crust below the ice sheet.
As an ice sheet shrinks, the change in ice mass causes the Earth’s crust to slowly uplift in response. At the same time, and counterintuitively, the sea level drops near the ice because of a weakening of the gravitational attraction between the ice sheet and the ocean water.
As the ice sheet thinned and retreated since the last ice age, crustal uplift and the fall in sea level in the region may have re-grounded floating ice, causing ice sheet advance.
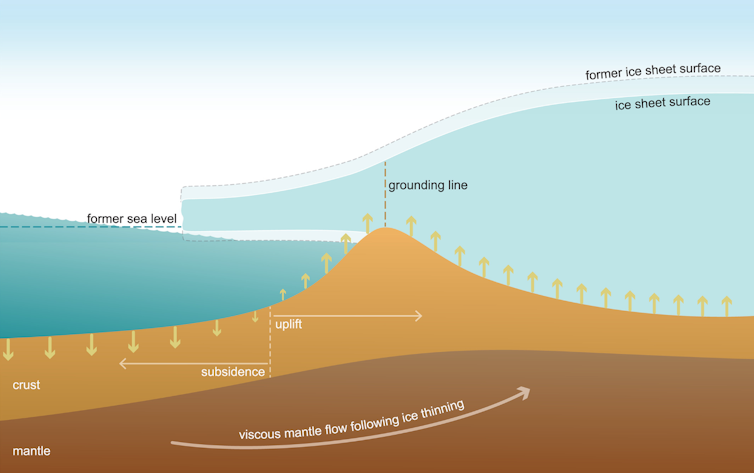
AGU, CC BY-SA
The other hypothesis is that the ice sheet behaviour may be due to changes in the ocean. When the surface of the ocean freezes, forming sea ice, it expels salt into the water layers below. This cold briny water is heavier and mixes deep into the ocean, including under the Ross Ice Shelf. This blocks warm ocean currents from melting the ice.
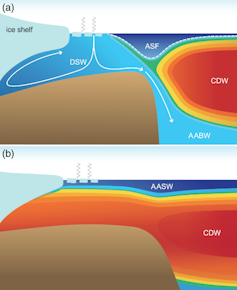
AGU, CC BY-SA
Seafloor sediments and ice cores tell us that this deep mixing was weaker in the past when the ice sheet was retreating. This means that warm ocean currents may have flowed underneath the ice shelf and melted the ice. Mixing increased when the ice sheet was advancing.
We test these two ideas with computer model simulations of ice sheet flow and Earth’s crustal and sea surface responses to changes in the ice sheet with varying ocean temperature.
Because the rate of crustal uplift depends on the viscosity (stickiness) of the underlying mantle, we ran simulations within ranges estimated for West Antarctica. A stickier mantle means slower crustal uplift as the ice sheet thins.
The simulations that best matched geological records had a stickier mantle and a warmer ocean as the ice sheet retreated. In these simulations, the ice sheet retreats more quickly as the ocean warms.
When the ocean cools, the simulated ice sheet readvances to its present-day position. This means that changes in ocean temperature best explain the past ice sheet behaviour, but the rate of crustal uplift also affects how sensitive the ice sheet is to the ocean.

Veronika Meduna, CC BY-SA
What this means for climate policy today
Much attention has been paid to recent studies that show glacial melting may be irreversible in some parts of West Antarctica, such as the Amundsen Sea embayment.
In the context of such studies, policy debates hinge on whether we should focus on adapting to rising seas rather than cutting greenhouse gas emissions. If the ice sheet is already melting, are we too late for mitigation?
Our study suggests it is premature to give up on mitigation.
Global climate models run under high-emissions scenarios show less sea ice formation and deep ocean mixing. This could lead to the same cold-to-warm ocean switch that caused extensive ice sheet retreat thousands of years ago.
For West Antarctica’s Siple Coast, it is better if we prevent this ocean warming from occurring in the first place, which is still possible if we choose a low-emissions future.
-
Business21 hours ago
Honda to build electric vehicles and battery plant in Ontario, sources say – Global News
-



 Science22 hours ago
Science22 hours agoWill We Know if TRAPPIST-1e has Life? – Universe Today
-



 Health19 hours ago
Health19 hours agoSee how chicken farmers are trying to stop the spread of bird flu – Fox 46 Charlotte
-



 Health22 hours ago
Health22 hours agoSimcoe-Muskoka health unit urges residents to get immunized
-



 Investment20 hours ago
Investment20 hours agoOwn a cottage or investment property? Here's how to navigate the new capital gains tax changes – The Globe and Mail
-



 Science17 hours ago
Science17 hours agoOsoyoos commuters invited to celebrate Earth Day with the Leg Day challenge – Oliver/Osoyoos News – Castanet.net
-
News17 hours ago
Freeland defends budget measures, as premiers push back on federal involvement – CBC News
-
News20 hours ago
‘A real letdown’: Disabled B.C. man reacts to federal disability benefit – Global News






