Science
The Fastest Things In The Universe – Worldatlas.com
How fast are you moving right now? Maybe you’re reading this while sitting at home, where it seems as though you’re not moving at all. Stand still or sit down, and it feels like you are stationary, yet regardless of what you do, you are constantly in motion. That is because the Earth itself is rotating at a speed of around 1,000 miles per hour. In addition to its rotation, the Earth is also moving around the Sun at a speed of 67,000 miles per hour. Regardless of how stationary we feel, we move tens of thousands of miles every day. That may seem fast, yet the Earth is barely even moving compared to some things in the universe.
The Fastest Thing In The Universe


The universe itself has a cosmic speed limit. That is to say, there is a limit as to how fast objects within space can travel. That speed limit is approximately 186,000 miles per second, and there is only one thing in the cosmos that travels at that speed: light. Light is the fastest known thing in the universe, and thus the cosmic speed limit is called the speed of light. Regardless of how hard you try, you can never exceed the speed of light. Like gravity, the cosmic speed limit is a fixed law of nature that cannot be broken. Whether it’s coming from a star or your cellphone flashlight, every light beam will travel at 186,000 miles per second.
The Fastest Known Planet


Over the last 30 years, scientists have uncovered thousands of planets that orbit stars outside our solar system. Many of these worlds are vastly different from those that orbit our Sun. Regardless of what type of planets orbit a star, one thing they all have in common is how their orbital velocity is related to the distance between them and their star. Planets that orbit close to their star will complete an orbit faster than planets that orbit further away. Mercury is the fastest planet in our solar system, completing one rotation every 88 days. That may seem fast, yet it is nothing compared to some other planets in our galaxy. The fastest planet ever discovered was found in 2013 by NASA’s Kepler Space Telescope. Named Kepler-78b, it orbits its star at a distance of only 900,000 miles. For comparison, Mercury orbits the Sun at a distance of 36 million miles. With very little space between Kepler-78b and its parent star, the planet orbits its Sun at extreme speeds. It takes a mere 8.5 hours for Kepler-78b to complete one orbit around its star. Imagine living on a planet where a year is only 8.5 hours. As of yet, no other planet has been found with a shorter orbital period, making Kepler-78b the fastest known planet in the universe.
The Fastest Known Star


It may not seem like it from our perspective here on Earth, but the Sun is actually speeding through space. Like the planets that orbit the Sun, the Sun is in orbit around the center of the Milky Way Galaxy. At this moment, the entire solar system is moving through space at 448,000 miles per hour. That may seem fast, but it takes the Sun 230-million years to complete one orbit because of how gigantic the Milky Way Galaxy is. Compared to some other stars out there, our Sun is relatively slow. The fastest known star in the universe exists near the very center of the Milky Way. Called US-708, it has been measured moving at a speed of 2.7-million miles per hour. When scientists first uncovered US-708 and measured its velocity, they believed it was in orbit around a black hole. The gravitational pull of the black hole would be so strong that it would have accelerated US-708 to tremendous speeds. However, subsequent observations revealed that US-708 might have actually been propelled to its current speed by an exploding star. US-708 was once part of a binary star system, wherein its companion star eventually exploded in a supernova. The resulting explosion was so energetic that it propelled US-708 to become the fastest known star in the universe.
The Fastest Human-Made Object


We have talked about what some of the fastest things in the universe are, yet how does humanity compare? What’s the fastest thing humans have ever created? As one might expect, the fastest human-made objects are generally spacecraft. Currently, the fastest human-made spacecraft is the Parker Solar Probe, a spacecraft launched by NASA in 2018 to fly closer to the Sun than any spacecraft before it. When NASA launched the Parker Solar Probe, it reached a velocity of 39,500 miles per hour. On its way to the Sun, the Parker Solar Probe conducted repeated flybys of the planet Venus to increase its velocity, using what’s called a gravity assist. As of February 2020, the Parker Solar Probe has become the fastest human-made object in history, reaching a velocity of 330,000 miles per hour. That’s fast enough to circle the Earth 13 times per hour! For humanity, this is truly a remarkable accomplishment. However, even at this speed, the Parker Solar Probe has only achieved 0.05% light speed.
Science
SpaceX launch marks 300th successful booster landing – Phys.org


SpaceX sent up the 30th launch from the Space Coast for the year on the evening of April 23, a mission that also featured the company’s 300th successful booster recovery.
A Falcon 9 rocket carrying 23 of SpaceX’s Starlink internet satellites blasted off at 6:17 p.m. Eastern time from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 40.
The first-stage booster set a milestone of the 300th time a Falcon 9 or Falcon Heavy booster made a successful recovery landing, and the 270th time SpaceX has reflown a booster.
This particular booster made its ninth trip to space, a resume that includes one human spaceflight, Crew-6. It made its latest recovery landing downrange on the droneship Just Read the Instructions in the Atlantic Ocean.
The company’s first successful booster recovery came in December 2015, and it has not had a failed booster landing since February 2021.
The current record holder for flights flew 11 days ago making its 20th trip off the launch pad.
SpaceX has been responsible for all but two of the launches this year from either Kennedy Space Center or Cape Canaveral with United Launch Alliance having launched the other two.
SpaceX could knock out more launches before the end of the month, putting the Space Coast on pace to hit more than 90 by the end of the year, but the rate of launches by SpaceX is also set to pick up for the remainder of the year with some turnaround times at the Cape’s SLC-40 coming in less than three days.
That could amp up frequency so the Space Coast could surpass 100 launches before the end of the year, with the majority coming from SpaceX. It hosted 72 launches in 2023.
More launches from ULA are on tap as well, though, including the May 6 launch atop an Atlas V rocket of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner with a pair of NASA astronauts to the International Space Station.
ULA is also preparing for the second launch ever of its new Vulcan Centaur rocket, which recently received its second Blue Origin BE-4 engine and is just waiting on the payload, Sierra Space’s Dream Chaser spacecraft, to make its way to the Space Coast.
Blue Origin has its own rocket it wants to launch this year as well, with New Glenn making its debut as early as September, according to SLD 45’s range manifest.
2024 Orlando Sentinel. Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.
Citation:
SpaceX launch marks 300th successful booster landing (2024, April 24)
retrieved 24 April 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-04-spacex-300th-successful-booster.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
Science
Wildlife Wednesday: loons are suffering as water clarity diminishes – Canadian Geographic
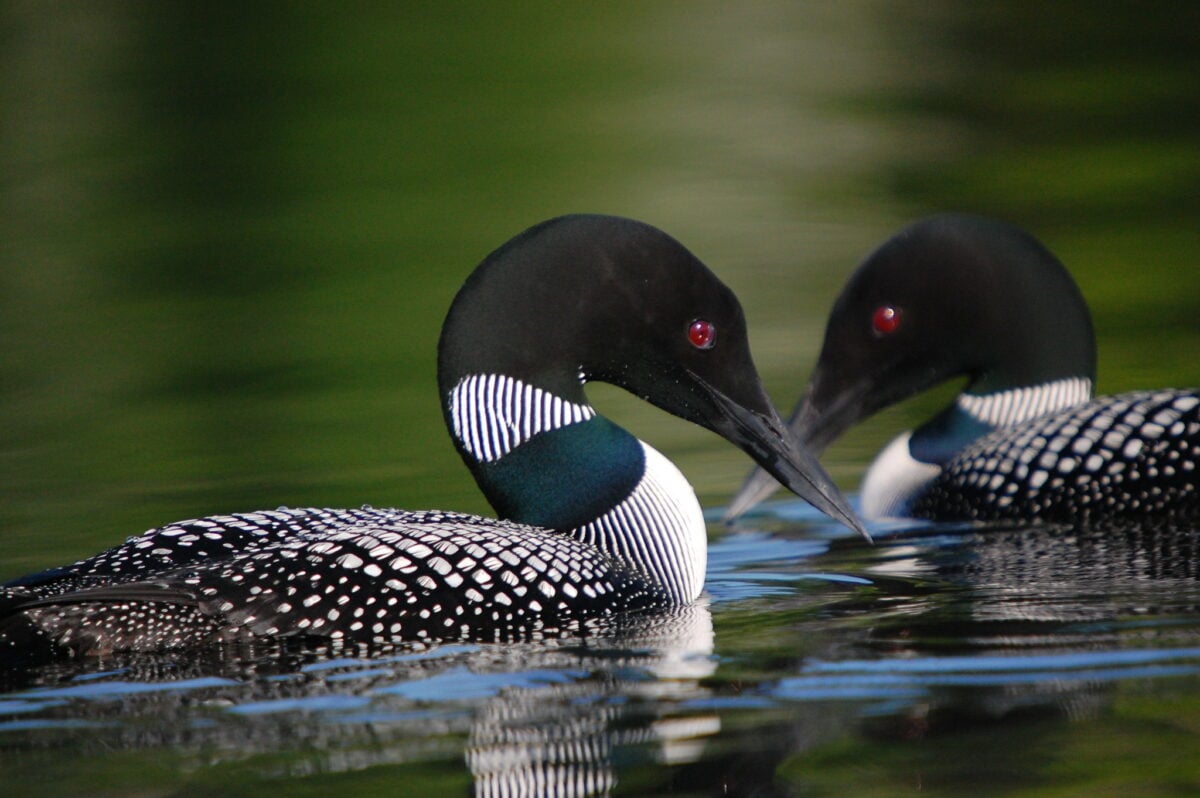


The common loon, that icon of northern wilderness, is under threat from climate change due to declining water clarity. Published earlier this month in the journal Ecology, a study conducted by biologists from Chapman University and Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in the U.S. has demonstrated the first clear evidence of an effect of climate change on this species whose distinct call is so tied to the soundscape of Canada’s lakes and wetlands.
Through the course of their research, the scientists found that July rainfall results in reduced July water clarify in loon territories in Northern Wisconsin. In turn, this makes it difficult for adult loons to find and capture their prey — mainly small fish — underwater, meaning they are unable to meet their chicks’ metabolic needs. Undernourished, the chicks face higher mortality rates. The consistent foraging techniques used by loons across their range means this impact is likely echoed wherever they are found — from Alaska to Canada to Iceland.
The researchers used Landsat imagery to find that there has been a 25-year consistent decline in water clarity, and during this period, body weights of adult loon and chicks alike have also declined. With July being the month of most rapid growth in young loons, the study also pinpointed water clarity in July as being the greatest predictor of loon body weight.
One explanation for why heavier rainfall leads to reduced water clarity is the rain might carry dissolved organic matter into lakes from adjacent streams and shoreline areas. Lawn fertilizers, pet waste and septic system leaks may also be to blame.
The researchers, led by Chapman University professor Walter Piper, hope to use these insights to further conservation efforts for this bird Piper describes as both “so beloved and so poorly understood.”
Return of the king
Science
Giant prehistoric salmon had tusk-like teeth for defence, building nests


|
|
The artwork and publicity materials showcasing a giant salmon that lived five million years ago were ready to go to promote a new exhibit, when the discovery of two fossilized skulls immediately changed what researchers knew about the fish.
Initial fossil discoveries of the 2.7-metre-long salmon in Oregon in the 1970s were incomplete and had led researchers to mistakenly suggest the fish had fang-like teeth.
It was dubbed the “sabre-toothed salmon” and became a kind of mascot for the Museum of Natural and Cultural History at the University of Oregon, says researcher Edward Davis.
But then came discovery of two skulls in 2014.
Davis, a member of the team that found the skulls, says it wasn’t until they got back to the lab that he realized the significance of the discovery that has led to the renaming of the fish in a new, peer-reviewed study.
“There were these two skulls staring at me with sideways teeth,” says Davis, an associate professor in the department of earth sciences at the university.
In that position, the tusk-like teeth could not have been used for biting, he says.
“That was definitely a surprising moment,” says Davis, who serves as director of the Condon Fossil Collection at the university’s Museum of Natural and Cultural History.
“I realized that all of the artwork and all of the publicity materials and bumper stickers and buttons and T-shirts we had just made two months prior, for the new exhibit, were all out of date,” he says with a laugh.
Davis is co-author of the new study in the journal PLOS One, which renames the giant fish the “spike-toothed salmon.”
It says the salmon used the tusk-like spikes for building nests to spawn, and as defence mechanisms against predators and other salmon.
The salmon lived about five million years ago at a time when Earth was transitioning from warmer to relatively cooler conditions, Davis says.
It’s hard to know exactly why the relatives of today’s sockeye went extinct, but Davis says the cooler conditions would have affected the productivity of the Pacific Ocean and the amount of rain feeding rivers that served as their spawning areas.
Another co-author, Brian Sidlauskas, says a fish the size of the spike-toothed salmon must have been targeted by predators such as killer whales or sharks.
“I like to think … it’s almost like a sledgehammer, these salmon swinging their head back and forth in order to fend off things that might want to feast on them,” he says.
Sidlauskas says analysis by the lead author of the paper, Kerin Claeson, found both male and female salmon had the “multi-functional” spike-tooth feature.
“That’s part of our reason for hypothesizing that this tooth is multi-functional … It could easily be for digging out nests,” he says.
“Think about how big the (nest) would have to be for an animal of this size, and then carving it out in what’s probably pretty shallow water; and so having an extra digging tool attached to your head could be really useful.”
Sidlauskas says the giant salmon help researchers understand the boundaries of what’s possible with the evolution of salmon, but they also capture the human imagination and a sense of wonder about what’s possible on Earth.
“I think it helps us value a little more what we do still have, or I hope that it does. That animal is no longer with us, but it is a product of the same biosphere that sustains us.”
This report by The Canadian Press was first published April 24, 2024.
Brenna Owen, The Canadian Press





-



 Politics20 hours ago
Politics20 hours agoOpinion: Fear the politicization of pensions, no matter the politician
-



 Science19 hours ago
Science19 hours agoNASA Celebrates As 1977’s Voyager 1 Phones Home At Last
-



 Politics19 hours ago
Politics19 hours agoPecker’s Trump Trial Testimony Is a Lesson in Power Politics
-
Media18 hours ago
B.C. puts online harms bill on hold after agreement with social media companies
-
Business18 hours ago
Oil Firms Doubtful Trans Mountain Pipeline Will Start Full Service by May 1st
-
Art20 hours ago
Turner Prize: Shortlisted artist showcases Scottish Sikh community
-
Media12 hours ago
B.C. online harms bill on hold after deal with social media firms
-
Investment20 hours ago
FLAGSHIP COMMUNITIES REAL ESTATE INVESTMENT TRUST ANNOUNCES CLOSING OF APPROXIMATELY US




