Economy
Virus' effect on world economy grows after Trump lashes out – CTV News

TOKYO —
The coronavirus outbreak’s impact on the world economy grew more alarming on Saturday, even after U.S. President Donald Trump denounced criticism of his response to the threat as a “hoax” cooked up by his political enemies.
China’s manufacturing plunged in February by an even wider margin than expected after efforts to contain the virus outbreak shut down much of the world’s second-largest economy, an official survey showed Saturday.
The survey, coming as global stock markets fall on fears the virus will spread abroad, adds to mounting evidence of the vast cost of the disease that emerged in central China in December and its economic impact worldwide.
The monthly purchasing managers’ index issued by the Chinese statistics agency and an industry group fell to 35.7 from January’s 50 on a 100-point scale on which numbers below 50 indicate activity contracting.
Iran is preparing for the possibility of “tens of thousands” of people getting tested for the virus as the number of confirmed cases spiked again Saturday, an official said, underscoring the fear both at home and abroad over the outbreak in the Islamic Republic.
The virus and the COVID-19 illness it causes have killed 43 people out of 593 confirmed cases in Iran, Health Ministry spokesman Kianoush Jahanpour said. The new toll represents a jump of 205 cases — a 150% increase from the 388 reported the day before.
But the number of known cases versus deaths would put the virus’ death rate in Iran at over 7%, much higher than other countries. That’s worried experts at the World Health Organization and elsewhere that Iran may be underreporting the number of cases now affecting it.
Earlier Saturday, Bahrain threatened legal prosecution against travellers who came from Iran and hadn’t been tested for the virus, and also barred public gatherings for two weeks.
Saudi Arabia said it would bar citizens of the Gulf Cooperation Council from Islam’s holiest sites in Mecca and Medina over concerns about the virus’ spread. The GCC is a six-nation group including Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates.
On Thursday, Saudi Arabia closed off the holy sites to foreign pilgrims over the coronavirus, disrupting travel for thousands of Muslims already headed to the kingdom and potentially affecting plans later this year for millions more ahead of the fasting month of Ramadan and the annual hajj pilgrimage.
Elsewhere around the world, already slumping financial markets dropped even lower on Friday, while virus fears led to emptied shops and amusement parks, cancelled events, and drastically reduced trade and travel.
Despite anxieties about a wider outbreak in the U.S., Trump has defended measures taken and lashed out Friday at Democrats who have questioned his handling of the threat, calling their criticism a new “hoax” intended to undermine his leadership.
Shortly before Trump began to speak, health officials confirmed a second case of coronavirus in the U.S. in a person who didn’t travel internationally or have close contact with anyone who had the virus.
The list of countries touched by the virus has climbed to nearly 60. More than 85,000 people worldwide have contracted the virus, with deaths topping 2,900.
Even in isolated, sanctions-hit North Korea, leader Kim Jong Un called for stronger anti-virus efforts to guard against COVID-19, saying there will be “serious consequences” if the illness spreads to the country.
China has seen a slowdown in new infections and on Saturday morning reported 427 new cases over the past 24 hours along with 47 additional deaths. The city at the epicenter of the outbreak, Wuhan, accounted for the bulk of both. The ruling party is striving to restore public and business confidence and avert a deeper economic downturn and politically risky job losses after weeks of disruptions due to the viral outbreak.
South Korea, the second hardest hit country, reported 813 new cases on Saturday — the highest daily jump since confirming its first patient in late January and raising its total to 3,150. Emerging clusters in Italy and in Iran have led to infections of people in other countries. France and Germany were also seeing increases, with dozens of infections.
Streets were deserted in the city of Sapporo on Japan’s northernmost main island of Hokkaido, where a state of emergency was issued until mid-March. Seventy cases — the largest from a single prefecture in Japan — have been detected in the island prefecture.
The archbishop of Paris asked all of the French capital’s parish priests to change the way they administer communion to counter the spread of the coronavirus.
Bishop Michel Aupetit instructed that priests no longer put the sacramental bread in the mouths of worshippers celebrating communion and instead place it in their hands. He also asked that worshippers not drink wine directly from a shared chalice, and that sacramental bread instead be dipped in wine.
The bishop’s instructions were listed in a statement Saturday from the Paris diocese. It said a Paris priest tested positive for the virus on Friday after returning from Italy.
The head of the World Health Organization on Friday announced that the risk of the virus spreading worldwide was “very high,” while U.N. Secretary-General Antonio Guterres said the “window of opportunity” for containing the virus was narrowing.
Stock markets around the world plunged again Friday. On Wall Street, the Dow Jones index took yet another hit, closing down nearly 360 points. The index has dropped more than 14% from a recent high, making this the market’s worst week since 2008, during the global financial crisis.
In Asia, Tokyo Disneyland and Universal Studios Japan announced they would close, and events that were expected to attract tens of thousands of people were called off, including a concert series by the K-pop group BTS.
Tourist arrivals in Thailand are down 50% compared with a year ago, and in Italy — which has reported 888 cases, the most of any country outside of Asia — hotel bookings are falling and Premier Giuseppe Conte raised the spectre of recession.
Assuming there are many more cases with no or very mild symptoms, the rate “may be considerably less than 1%,” U.S. health officials wrote in an editorial in the journal. That would make the virus more like a severe seasonal flu than a disease similar to its genetic cousins SARS, severe acute respiratory syndrome, or MERS, Middle East respiratory syndrome.
Given the ease of spread, however, the virus could gain footholds around the world and many could die.
Europe’s economy is already teetering on the edge of recession. A measure of business sentiment in Germany fell sharply last week, suggesting that some companies could postpone investment and expansion plans. China is a huge export market for German manufacturers.
Economists have forecast global growth will slip to 2.4% this year, the slowest since the Great Recession in 2009, and down from earlier expectations closer to 3%. For the United States, estimates are falling to as low as 1.7% growth this year, down from 2.3% in 2019.
But if COVID-19 becomes a global pandemic, economists expect the impact could be much worse, with the U.S. and other global economies falling into recession.
——
Associated Press writers Joe McDonald in Beijing, Jon Gambrell in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, John Leicester in Paris, Deb Riechmann and Darlene Superville in Washington, Adam Geller, Paul Wiseman, Christopher Rugaber, Joseph Pisani and Edith M. Lederer in New York, Hyung-jin Kim and Tong-hyung Kim in Seoul, South Korea, Renata Brito and Giada Zampano in Venice, Italy, Frances D’Emilio in Rome and Frank Jordans in Berlin contributed to this report.
Economy
Poland has EU's second highest emissions in relation to size of economy – Notes From Poland
[unable to retrieve full-text content]
Poland has EU’s second highest emissions in relation to size of economy Notes From Poland





Source link
Economy
IMF's Georgieva warns "there's plenty to worry about'' in world economy — including inflation, debt – Yahoo Canada Finance

WASHINGTON (AP) — The head of the International Monetary Fund said Thursday that the world economy has proven surprisingly resilient in the face of higher interest rates and the shock of war in Ukraine and Gaza, but “there is plenty to worry about,” including stubborn inflation and rising levels of government debt.
“ Inflation is down but not gone,” Kristalina Georgieva told reporters at the spring meeting of the IMF and its sister organization, the World Bank. In the United States, she said, “the flipside” of unexpectedly strong economic growth is that it ”taking longer than expected” to bring inflation down.
Georgieva also warned that government debts are growing around the world. Last year, they ticked up to 93% of global economic output — up from 84% in 2019 before the response to the COVID-19 pandemic pushed governments to spend more to provide healthcare and economic assistance. She urged countries to more efficiently collect taxes and spend public money. “In a world where the crises keep coming, countries must urgently build fiscal resilience to be prepared for the next shock,” she said.
On Tuesday, the IMF said it expects to the global economy to grow 3.2% this year, a modest upgrade from the forecast it made in January and unchanged from 2023. It also expects a third straight year of 3.2% growth in 2025.
ADVERTISEMENT
The world economy has proven unexpectedly sturdy, but it remains weak by historical standards: Global growth averaged 3.8% from 2000 to 2019.
One reason for sluggish global growth, Georgieva said, is disappointing improvement in productivity. She said that countries had not found ways to most efficiently match workers and technology and that years of low interest rates — that only ended after inflation picked up in 2021 — had allowed “firms that were not competitive to stay afloat.”
She also cited in many countries an aging “labor force that doesn’t bring the dynamism” needed for faster economic growth.
The United States has been an exception to the weak productivity gains over the past year. Compared to Europe, Georgieva said, America makes it easier for businesses to bring innovations to the marketplace and has lower energy costs.
She said countries could help their economies by slashing bureaucratic red tape and getting more women into the job market.
Paul Wiseman, The Associated Press
Economy
Nigeria’s Economy, Once Africa’s Biggest, Slips to Fourth Place – BNN Bloomberg
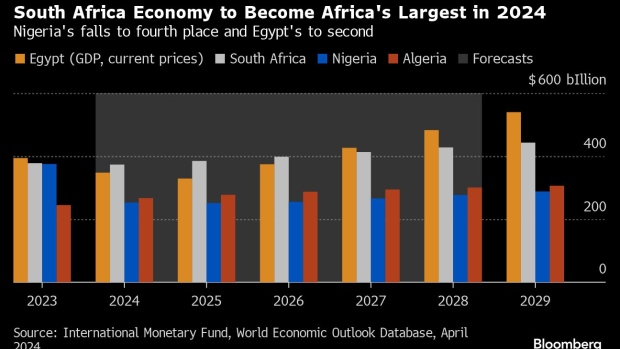

(Bloomberg) — Nigeria’s economy, which ranked as Africa’s largest in 2022, is set to slip to fourth place this year and Egypt, which held the top position in 2023, is projected to fall to second behind South Africa after a series of currency devaluations, International Monetary Fund forecasts show.
The IMF’s World Economic Outlook estimates Nigeria’s gross domestic product at $253 billion based on current prices this year, lagging energy-rich Algeria at $267 billion, Egypt at $348 billion and South Africa at $373 billion.
Africa’s most industrialized nation will remain the continent’s largest economy until Egypt reclaims the mantle in 2027, while Nigeria is expected to remain in fourth place for years to come, the data released this week shows.
Nigeria and Egypt’s fortunes have dimmed as they deal with high inflation and a plunge in their currencies.
Bola Tinubu has announced significant policy reforms since he became Nigeria’s president at the end of May 2023, including allowing the currency to float more freely, scrapping costly energy and gasoline subsidies and taking steps to address dollar shortages. Despite a recent rebound, the naira is still 50% weaker against the greenback than what it was prior to him taking office after two currency devaluations.
Read More: Why Nigeria’s Currency Rebounded and What It Means: QuickTake
Egypt, one of the emerging world’s most-indebted countries and the IMF’s second-biggest borrower after Argentina, has also allowed its currency to float, triggering an almost 40% plunge in the pound’s value against the dollar last month to attract investment.
The IMF had been calling for a flexible currency regime for many months and the multilateral lender rewarded Egypt’s government by almost tripling the size of a loan program first approved in 2022 to $8 billion. This was a catalyst for a further influx of around $14 billion in financial support from the European Union and the World Bank.
Read More: Egypt Avoided an Economic Meltdown. What Next?: QuickTake
Unlike Nigeria’s naira and Egypt’s pound, the value of South Africa’s rand has long been set in the financial markets and it has lost about 4% of its value against the dollar this year. Its economy is expected to benefit from improvements to its energy supply and plans to tackle logistic bottlenecks.
Algeria, an OPEC+ member has been benefiting from high oil and gas prices caused first by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and now tensions in the Middle East. It stepped in to ease some of Europe’s gas woes after Russia curtailed supplies amid its war in Ukraine.
©2024 Bloomberg L.P.
-



 Tech23 hours ago
Tech23 hours agoCytiva Showcases Single-Use Mixing System at INTERPHEX 2024 – BioPharm International
-



 Health19 hours ago
Health19 hours agoSupervised consumption sites urgently needed, says study – Sudbury.com
-



 Science5 hours ago
Science5 hours agoJeremy Hansen – The Canadian Encyclopedia
-
News18 hours ago
Canada's 2024 budget announces 'halal mortgages'. Here's what to know – National Post
-
News17 hours ago
2024 federal budget's key takeaways: Housing and carbon rebates, students and sin taxes – CBC News
-



 Tech21 hours ago
Tech21 hours agoNew EV features for Google Maps have arrived. Here’s how to use them. – The Washington Post
-



 Science18 hours ago
Science18 hours agoGiant, 82-foot lizard fish discovered on UK beach could be largest marine reptile ever found – Livescience.com
-
Tech24 hours ago
Nintendo Indie World Showcase April 2024 – Every Announcement, Game Reveal & Trailer – Nintendo Life




