Economy
Wall Street Tumbles on Fears for Economy as More Rates Rise – Voice of America – VOA News
NEW YORK —
Fear swept through financial markets Thursday, and Wall Street tumbled as worries roared back to the fore that the world’s fragile economy may buckle under higher interest rates.
The S&P 500 fell 3.3% in a widespread wipeout to more than reverse its blip of a 1.5% rally from a day before. Analysts had warned of more big swings given deep uncertainties about whether the Federal Reserve and other central banks can tiptoe the narrow path of hiking interest rates enough to get inflation under control but not so much that they cause a recession.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average lost 2.4% and was briefly down more than 900 points, while the Nasdaq composite sank 4.1%. It was the sixth loss for the S&P 500 in its last seven tries, and all but 3% of the stocks in the index dropped.
Wall Street fell with stocks across Europe after central banks there followed up on the Federal Reserve’s big interest-rate hike on Wednesday. The Bank of England raised its key rate for the fifth time since December, though it opted for a more modest increase of 0.25 percentage points than the 0.75-point hammer brought by the Fed.
Switzerland’s central bank, meanwhile, raised rates for the first time in years, a half-point hike. Taiwan’s central bank raised its key rate by an eighth of a point. Japan’s central bank began a two-day meeting, though it has held out on raising rates and making other economy-slowing moves that investors call “hawkish.”
Such moves and expectations for plenty more have sent investments tumbling this year, from bonds to bitcoin. Higher interest rates slow the economy by design, in hopes of stamping out inflation. But they’re a blunt tool that can choke off the economy if used too aggressively.
“Another concern is that with the change in policy, there’s been weakening economic data already,” said Bill Northey, senior investment director at U.S. Bank Wealth Management. “That raises the odds of a recession in the latter part of 2022 into 2023.”
The worries dragged the S&P 500 into a bear market earlier this week, meaning it had dropped more than 20% from its peak. It’s now 23.6% below its record set early this year and back to where it was in late 2020. That effectively erases 2021, which was one of the best years for Wall Street since the turn of the millennium.
The S&P 500 fell 123.22 points to 3,666.77. The Dow lost 741.46 to 29,927.07, and the Nasdaq dropped 453.06 to 10,646.10. Thursday’s biggest losses hit the stocks of the smallest companies, a signal of pessimism about the economy’s strength. The Russell 2000 index of smaller stocks sank 81.30, or 4.7%, to 1,649.84.
Not only is the Federal Reserve hiking short-term rates, it also this month began allowing some of the trillions of dollars of bonds it purchased through the pandemic to roll off its balance sheet. That should put upward pressure on longer-term interest rates. It’s another way central banks have been ripping away supports they earlier propped underneath markets to juice the economy.
The U.S. economy is still holding up, driven in particular by a strong jobs market. Fewer workers filed for unemployment benefits last week than a week before, a report showed on Thursday. But more signs of trouble have been emerging.
On Thursday, one report showed homebuilders broke ground on fewer homes last month. Rising mortgage rates resulting directly from the Fed’s moves are digging into the industry. A separate reading on manufacturing in the mid-Atlantic region also unexpectedly fell.
“Corporate earnings estimates have not yet changed to reflect some of the softening economic data and that could lead to the second leg of this repricing,” Northey said.
Treasury yields swung sharply on Thursday, with the 10-year yield down to 3.23% from 3.39% late Wednesday. It had climbed as high as 3.48% in the morning, near its highest level since 2011.
Higher rates have been delivering the hardest hits this year to the investments that soared the most through the easy, ultralow rates of earlier in the pandemic, which now look to be among the most expensive and risky investments. That includes bitcoin and high-growth technology stocks.
Big Tech stocks were among the heaviest weights on the market Thursday, but the sharpest losses hit stocks whose profits depend more on the strength of the economy and whether customers can keep up their purchases amid the highest inflation in decades.
Cruise operators Norwegian Cruise Line Holdings, Royal Caribbean Group and Carnival all lost more than 11%.
It’s all a sharp turnaround from a day earlier, when stocks rallied immediately after the Fed’s biggest hike to rates since 1994. Analysts said investors seemed to latch onto a comment from Fed Chair Jerome Powell, who said mega-hikes of three-quarters of a percentage point would not be common.
Powell said Wednesday the Fed is moving “expeditiously” to get rates closer to normal levels after last week’s stunning report that showed inflation at the consumer level unexpectedly accelerated last month, which dashed hopes that inflation may have already peaked.
The Fed is “not trying to induce a recession now, let’s be clear about that,” Powell said. He called Wednesday’s big increase “front-end loading.”
Economy
China Wants Everyone to Trade In Their Old Cars, Fridges to Help Save Its Economy – Bloomberg
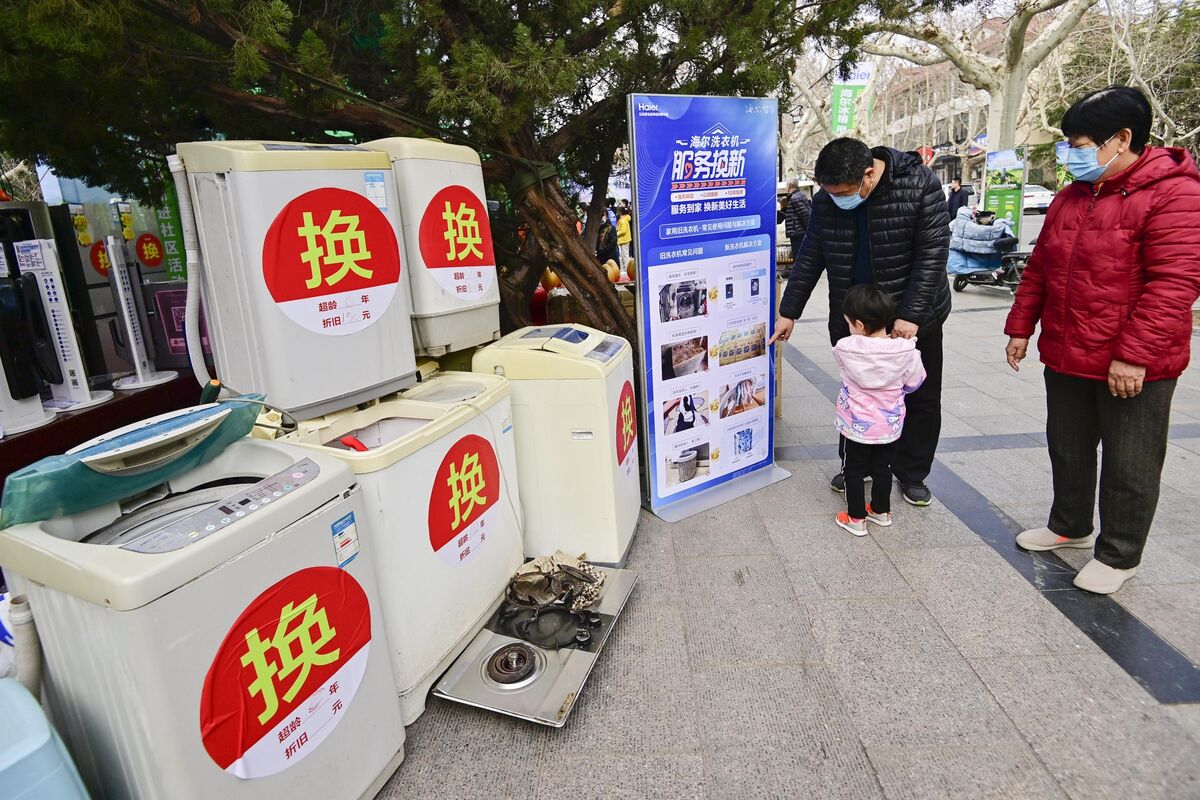


China’s world-beating electric vehicle industry, at the heart of growing trade tensions with the US and Europe, is set to receive a big boost from the government’s latest effort to accelerate growth.
That’s one takeaway from what Beijing has revealed about its plan for incentives that will encourage Chinese businesses and households to adopt cleaner technologies. It’s widely expected to be one of this year’s main stimulus programs, though question-marks remain — including how much the government will spend.
Economy
German Business Outlook Hits One-Year High as Economy Heals – BNN Bloomberg
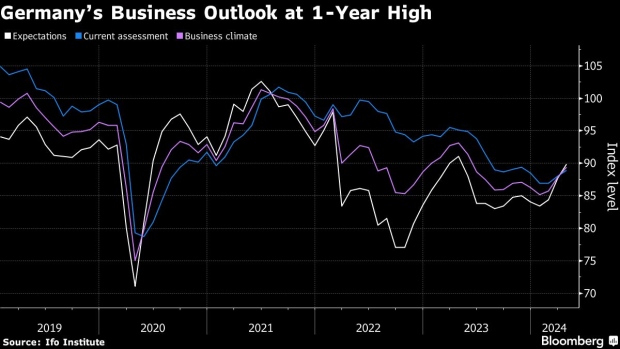

(Bloomberg) — German business sentiment improved to its highest level in a year — reinforcing recent signs that Europe’s largest economy is exiting two years of struggles.
An expectations gauge by the Ifo institute rose to 89.9. in April from a revised 87.7 the previous month. That exceeds the 88.9 median forecast in a Bloomberg survey. A measure of current conditions also advanced.
“Sentiment has improved at companies in Germany,” Ifo President Clemens Fuest said. “Companies were more satisfied with their current business. Their expectations also brightened. The economy is stabilizing, especially thanks to service providers.”
A stronger global economy and the prospect of looser monetary policy in the euro zone are helping drag Germany out of the malaise that set in following Russia’s attack on Ukraine. European Central Bank President Christine Lagarde said last week that the country may have “turned the corner,” while Chancellor Olaf Scholz has also expressed optimism, citing record employment and retreating inflation.
There’s been a particular shift in the data in recent weeks, with the Bundesbank now estimating that output rose in the first quarter, having only a month ago foreseen a contraction that would have ushered in a first recession since the pandemic.
Even so, the start of the year “didn’t go great,” according to Fuest.
“What we’re seeing at the moment confirms the forecasts, which are saying that growth will be weak in Germany, but at least it won’t be negative,” he told Bloomberg Television. “So this is the stabilization we expected. It’s not a complete recovery. But at least it’s a start.”
Monthly purchasing managers’ surveys for April brought more cheer this week as Germany returned to expansion for the first time since June 2023. Weak spots remain, however — notably in industry, which is still mired in a slump that’s being offset by a surge in services activity.
“We see an improving worldwide economy,” Fuest said. “But this doesn’t seem to reach German manufacturing, which is puzzling in a way.”
Germany, which was the only Group of Seven economy to shrink last year and has been weighing on the wider region, helped private-sector output in the 20-nation euro area strengthen this month, S&P Global said.
–With assistance from Joel Rinneby, Kristian Siedenburg and Francine Lacqua.
(Updates with more comments from Fuest starting in sixth paragraph.)
©2024 Bloomberg L.P.
Economy
Parallel economy: How Russia is defying the West’s boycott
|
|


When Moscow resident Zoya, 62, was planning a trip to Italy to visit her daughter last August, she saw the perfect opportunity to buy the Apple Watch she had long dreamed of owning.
Officially, Apple does not sell its products in Russia.
The California-based tech giant was one of the first companies to announce it would exit the country in response to Russian President Vladimir Putin’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine on February 24, 2022.
But the week before her trip, Zoya made a surprise discovery while browsing Yandex.Market, one of several Russian answers to Amazon, where she regularly shops.
Not only was the Apple Watch available for sale on the website, it was cheaper than in Italy.
Zoya bought the watch without a moment’s delay.
The serial code on the watch that was delivered to her home confirmed that it was manufactured by Apple in 2022 and intended for sale in the United States.
“In the store, they explained to me that these are genuine Apple products entering Russia through parallel imports,” Zoya, who asked to be only referred to by her first name, told Al Jazeera.
“I thought it was much easier to buy online than searching for a store in an unfamiliar country.”
Nearly 1,400 companies, including many of the most internationally recognisable brands, have since February 2022 announced that they would cease or dial back their operations in Russia in protest of Moscow’s military aggression against Ukraine.
But two years after the invasion, many of these companies’ products are still widely sold in Russia, in many cases in violation of Western-led sanctions, a months-long investigation by Al Jazeera has found.
Aided by the Russian government’s legalisation of parallel imports, Russian businesses have established a network of alternative supply chains to import restricted goods through third countries.
The companies that make the products have been either unwilling or unable to clamp down on these unofficial distribution networks.





-



 Health7 hours ago
Health7 hours agoRemnants of bird flu virus found in pasteurized milk, FDA says
-
Art13 hours ago
Mayor's youth advisory council seeks submissions for art gala – SooToday
-



 Science21 hours ago
Science21 hours ago"Hi, It's Me": NASA's Voyager 1 Phones Home From 15 Billion Miles Away – NDTV
-
News19 hours ago
Some Canadians will be digging out of 25+ cm of snow by Friday – The Weather Network
-



 Health11 hours ago
Health11 hours agoBird flu virus found in grocery milk as officials say supply still safe
-
Media18 hours ago
Jon Stewart Slams the Media for Coverage of Trump Trial – The New York Times
-



 Investment12 hours ago
Investment12 hours agoTaxes should not wag the tail of the investment dog, but that’s what Trudeau wants
-



 Sports22 hours ago
Sports22 hours agoAuston Matthews turns it up with three-point night as Maple Leafs slay Bruins in Game 2 – Toronto Sun




