Science
We found the world's oldest asteroid strike in Western Australia. It might have triggered a global thaw – The Conversation AU

The world’s oldest remaining asteroid crater is at a place called Yarrabubba, southeast of the town of Meekatharra in Western Australia.
Our new study puts a precise age on the cataclysmic impact – showing Yarrabubba is the oldest known crater and dating it at the right time to trigger the end of an ancient glacial period and the warming of the entire planet.
What we found at Yarrabubba
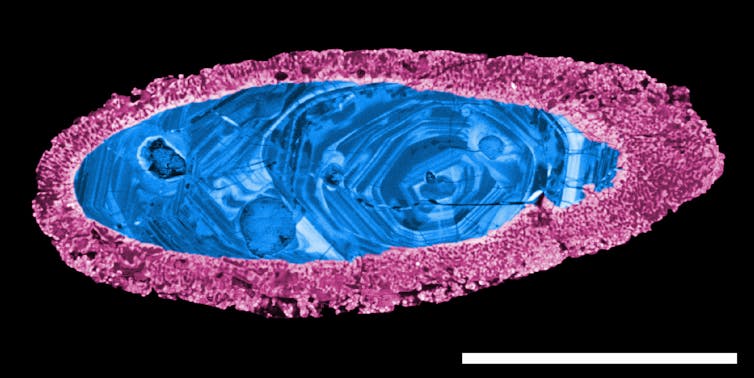
Yarrrabubba holds the eroded remnants of a crater 70 kilometres wide that was first described in 2003, based on minerals at the site that showed unique signs of impact. But its true age was not known.
We studied tiny “impact-shocked” crystals found at the site, which show the crater formed 2.229 billion years ago (give or take 5 million years).
This new, precise date establishes Yarrabubba as the oldest recognised impact structure on Earth. It is some 200 million years older than the next oldest, the Vredefort impact in South Africa.
More intriguing, the geological record shows the Earth had glacial ice before the time of the impact – but afterwards, ice disappeared for hundreds of millions of years. Was the Yarrabubba impact a trigger for global climate change?
Read more:
Target Earth: how asteroids made an impact on Australia
How to date an asteroid hit
An asteroid strike is one of the most violent geologic events. In an instant, Earth’s crust is squeezed to unimaginable pressures, before exploding and ejecting carnage across the landscape. Large impacts leave behind scars the size of a small city.
The basin formed by an impact will partly fill with molten and pulverised rock from the Earth and from the asteroid itself. The edge of the crater forms a ring of mountains; over time erosion gradually erases the story.
Today, Yarrabubba has been worn down into a minor feature on a barren landscape.
To place the Yarrabubba event in a geologic context, we had to find its age. To find the age, we had to look carefully at minerals in the rocks shocked by the impact.
Geologists date events using “isotopic clocks” in minerals like zircon and monazite. These minerals contain small amounts of uranium, which gradually decays into lead at a known rate.

Author provided
Asteroid strikes raise the temperature in rocks they hit, causing minerals to lose their accumulated lead, which resets the clock. After impact, the isotopic clocks start ticking again as new lead accumulates.
So by measuring the isotopes of uranium and lead in these minerals, we can calculate how much time has passed since the impact.
At Yarrabubba, we identified tiny crystals of zircon and monazite – each about the width of human hair – with textures that show they had been heated by a massive impact.
We analysed the amounts of lead and uranium isotopes in these crystals using mass spectrometry, and found their clocks had been reset 2.229 billion years ago (give or take five million years). That’s when we realised Yarrabubba coincided with a major change in Earth’s climate.
A different Earth
The Yarrabubba impact occurred during a period in Earth’s history called the Proterozoic eon. Long before plants, fish, or dinosaurs, life at this time consisted of simple, multicellular organisms.
These simple bacteria had already begun changing the composition of air. Previously dominated by carbon dioxide and methane, Earth’s atmosphere gradually became oxygenated by life about 2.4 billion years ago.
As oxygen levels built up, rocks started weathering more, and the atmosphere cooled down. And then ice came, plunging Earth into globally frigid conditions.
Read more:
Ancient asteroid impacts yield evidence for the nature of the early Earth
Earth has repeatedly dipped into glacial conditions over the last 4.5 billion years. We know about these periods because of deposits of solidified rock and mud that were ground up by glaciers as they bulldozed across Earth’s surface.
Studies have found multiple periods in Earth’s history in which glacial deposits occur in rocks of the same age across many continents. These deposits may represent worldwide glacial conditions, often referred to as a “Snowball Earth” event.
In these periods, ice forms from the poles well into the tropics, covering nearly all of Earth.
There is geological evidence that Earth was in an icy phase during the Yarrabubba impact. Rocks in South Africa show that glaciers were present at this time. But it’s not clear if the amount of ice was similar to today, or if it covered the world.
Fire and ice
So we found Earth’s oldest preserved impact crater, and worked out when the asteroid hit. We also know Earth had ice at the time, but not how much.
To understand the effect of the impact on an ice-covered world, we used computer models based on the physics of shockwaves to estimate how much ice would end up in the atmosphere as water vapour. As it turns out, it’s quite a lot.
Our models show that if the Yarrabubba asteroid hit an ice sheet 5 kilometres thick (not an unreasonable estimate), more than 200 billion tons of water vapour would be ejected into the atmosphere. That’s about 2% of the total amount of water vapour in today’s atmosphere, but would have been a much bigger fraction back then.
Water vapour is a serious greenhouse gas. It’s responsible for about half of the heat absorption from solar radiation today.
Global climate models don’t yet exist for the Proterozoic Earth, so we don’t yet know for sure if the Yarrabubba impact pushed the planet past a tipping point that led to more warming and the end of a possible Snowball Earth.
Science
Marine plankton could act as alert in mass extinction event: UVic researcher – Langley Advance Times


A University of Victoria micropaleontologist found that marine plankton may act as an early alert system before a mass extinction occurs.
With help from collaborators at the University of Bristol and Harvard, Andy Fraass’ newest paper in the Nature journal shows that after an analysis of fossil records showed that plankton community structures change before a mass extinction event.
“One of the major findings of the paper was how communities respond to climate events in the past depends on the previous climate,” Fraass said in a news release. “That means that we need to spend a lot more effort understanding recent communities, prior to industrialization. We need to work out what community structure looked like before human-caused climate change, and what has happened since, to do a better job at predicting what will happen in the future.”
According to the release, the fossil record is the most complete and extensive archive of biological changes available to science and by applying advanced computational analyses to the archive, researchers were able to detail the global community structure of the oceans dating back millions of years.
A key finding of the study was that during the “early eocene climatic optimum,” a geological era with sustained high global temperatures equivalent to today’s worst case global warming scenarios, marine plankton communities moved to higher latitudes and only the most specialized plankton remained near the equator, suggesting that the tropical temperatures prevented higher amounts of biodiversity.
“Considering that three billion people live in the tropics, the lack of biodiversity at higher temperatures is not great news,” paper co-leader Adam Woodhouse said in the release.
Next, the team plans to apply similar research methods to other marine plankton groups.
Read More: Global study, UVic researcher analyze how mammals responded during pandemic
Science
Scientists Say They Have Found New Evidence Of An Unknown Planet… – 2oceansvibe News


In the new work, scientists looked at a set of trans-Neptunian objects, or TNOs, which is the technical term for those objects that sit out at the edge of the solar system, beyond Neptune
The new work looked at those objects that have their movement made unstable because they interact with the orbit of Neptune. That instability meant they were harder to understand, so typically astronomers looking at a possible Planet Nine have avoided using them in their analysis.
Researchers instead looked towards those objects and tried to understand their movements. And, Dr Bogytin claimed, the best explanation is that they result from another, undiscovered planet.
The team carried out a host of simulations to understand how those objects’ orbits were affected by a variety of things, including the giant planets around them such as Neptune, the “Galactic tide” that comes from the Milky Way, and passing stars.
The best explanation was from the model that included Planet 9, however, Dr Bogytin said. They noted that there were other explanations for the behaviour of those objects – including the suggestion that other planets once influenced their orbit, but have since been removed – but claim that the theory of Planet 9 remains the best explanation.
A better understanding of the existence or not of Planet 9 will come when the Vera C Rubin Observatory is turned on, the authors note. The observatory is currently being built in Chile, and when it is turned on it will be able to scan the sky to understand the behaviour of those distant objects.
Planet Nine is theorised to have a mass about 10 times that of Earth and orbit about 20 times farther from the Sun on average than Neptune. It may take between 10,000 and 20,000 Earth years to make one full orbit around the Sun.
You may be tempted to ask how an entire planet could ‘hide’ in our solar system when we have zooming capabilities such as the new iPhone 15 has, but consider this: If Earth was the size of a marble, the edge of our solar system would be 11 kilometres away. That’s a lot of space to hide a planet.
[source:independent]
Science
Dragonfly: NASA Just Confirmed The Most Exciting Space Mission Of Your Lifetime – Forbes


NASA has confirmed that its exciting Dragonfly mission, which will fly a drone-like craft around Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, will cost $3.35 billion and launch in July 2028.
Titan is the only other world in the solar system other than Earth that has weather and liquid on the surface. It has an atmosphere, rain, lakes, oceans, shorelines, valleys, mountain ridges, mesas and dunes—and possibly the building blocks of life itself. It’s been described as both a utopia and as deranged because of its weird chemistry.
Set to reach Titan in 2034, the Dragonfly mission will last for two years once its lander arrives on the surface. During the mission, a rotorcraft will fly to a new location every Titan day (16 Earth days) to take samples of the giant moon’s prebiotic chemistry. Here’s what else it will do:
- Search for chemical biosignatures, past or present, from water-based life to that which might use liquid hydrocarbons.
- Investigate the moon’s active methane cycle.
- Explore the prebiotic chemistry in the atmosphere and on the surface.
Spectacular Mission
“Dragonfly is a spectacular science mission with broad community interest, and we are excited to take the next steps on this mission,” said Nicky Fox, associate administrator of the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “Exploring Titan will push the boundaries of what we can do with rotorcraft outside of Earth.”
It comes in the wake of the Mars Helicopter, nicknamed Ingenuity, which flew 72 times between April 2021 and its final flight in January 2023 despite only being expected to make up to five experimental test flights over 30 days. It just made its final downlink of data this week.
Dense Atmosphere
However, Titan is a completely different environment to Mars. Titan has a dense atmosphere on Titan, which will make buoyancy simple. Gravity on Titan is just 14% of the Earth’s. It sees just 1% of the sunlight received by Earth.
function loadConnatixScript(document)
if (!window.cnxel)
window.cnxel = ;
window.cnxel.cmd = [];
var iframe = document.createElement(‘iframe’);
iframe.style.display = ‘none’;
iframe.onload = function()
var iframeDoc = iframe.contentWindow.document;
var script = iframeDoc.createElement(‘script’);
script.src = ‘//cd.elements.video/player.js’ + ‘?cid=’ + ’62cec241-7d09-4462-afc2-f72f8d8ef40a’;
script.setAttribute(‘defer’, ‘1’);
script.setAttribute(‘type’, ‘text/javascript’);
iframeDoc.body.appendChild(script);
;
document.head.appendChild(iframe);
loadConnatixScript(document);
(function()
function createUniqueId()
return ‘xxxxxxxx-xxxx-4xxx-yxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx’.replace(/[xy]/g, function(c) 0x8);
return v.toString(16);
);
const randId = createUniqueId();
document.getElementsByClassName(‘fbs-cnx’)[0].setAttribute(‘id’, randId);
document.getElementById(randId).removeAttribute(‘class’);
(new Image()).src = ‘https://capi.elements.video/tr/si?token=’ + ’44f947fb-a5ce-41f1-a4fc-78dcf31c262a’ + ‘&cid=’ + ’62cec241-7d09-4462-afc2-f72f8d8ef40a’;
cnxel.cmd.push(function ()
cnxel(
playerId: ’44f947fb-a5ce-41f1-a4fc-78dcf31c262a’,
playlistId: ‘aff7f449-8e5d-4c43-8dca-16dfb7dc05b9’,
).render(randId);
);
)();
The atmosphere is 98% nitrogen and 2% methane. Its seas and lakes are not water but liquid ethane and methane. The latter is gas in Titan’s atmosphere, but on its surface, it exists as a liquid in rain, snow, lakes, and ice on its surface.
COVID-Affected
Dragonfly was a victim of the pandemic. Slated to cost $1 billion when it was selected in 2019, it was meant to launch in 2026 and arrive in 2034 after an eight-year cruise phase. However, after delays due to COVID, NASA decided to compensate for the inevitable delayed launch by funding a heavy-lift launch vehicle to massively shorten the mission’s cruise phase.
The end result is that Dragonfly will take off two years later but arrive on schedule.
Previous Visit
Dragonfly won’t be the first time a robotic probe has visited Titan. As part of NASA’s landmark Cassini mission to Saturn between 2004 and 2017, a small probe called Huygens was despatched into Titan’s clouds on January 14, 2005. The resulting timelapse movie of its 2.5 hours descent—which heralded humanity’s first-ever (and only) views of Titan’s surface—is a must-see for space fans. It landed in an area of rounded blocks of ice, but on the way down, it saw ancient dry shorelines reminiscent of Earth as well as rivers of methane.
The announcement by NASA makes July 2028 a month worth circling for space fans, with a long-duration total solar eclipse set for July 22, 2028, in Australia and New Zealand.
Wishing you clear skies and wide eyes.
-
Media4 hours ago
DJT Stock Rises. Trump Media CEO Alleges Potential Market Manipulation. – Barron's
-



 Sports23 hours ago
Sports23 hours agoAuston Matthews denied 70th goal as depleted Leafs lose last regular-season game – Toronto Sun
-
Business22 hours ago
BC short-term rental rules take effect May 1 – CityNews Vancouver
-
Media6 hours ago
Trump Media alerts Nasdaq to potential market manipulation from 'naked' short selling of DJT stock – CNBC
-
Art22 hours ago
Collection of First Nations art stolen from Gordon Head home – Times Colonist
-



 Investment22 hours ago
Investment22 hours agoBenjamin Bergen: Why would anyone invest in Canada now? – National Post
-



 Tech23 hours ago
Tech23 hours ago'Kingdom Come: Deliverance II' Revealed In Epic New Trailer And It Looks Incredible – Forbes
-
Media18 hours ago
DJT Stock Jumps. The Truth Social Owner Is Showing Stockholders How to Block Short Sellers. – Barron's





