News
What do people in Canada think about AI – CTV News
New technology involving artificial intelligence (AI) such as ChatGPT and Google Bard are dominating conversations and headlines across Canada.
But what do Canadians really think about AI, and how many have used the technology?
A new survey by Leger, published Feb. 23, dives into what Canadians and Americans think about AI tech and how familiar they are with its uses.
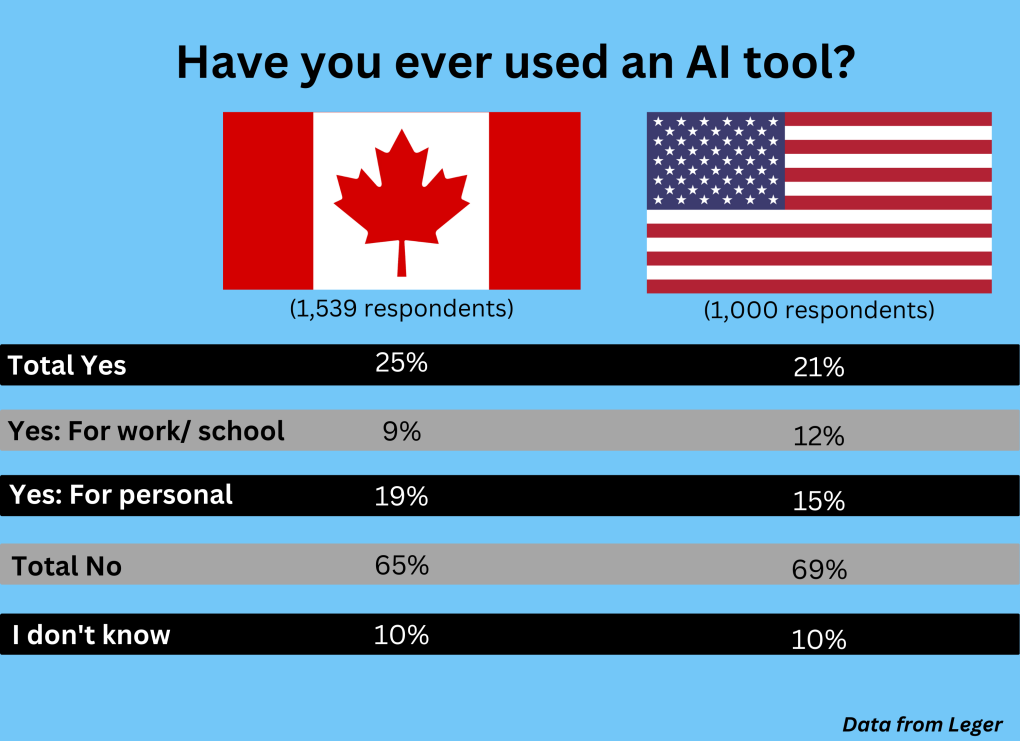
A sample of 1,539 Canadians and 1,000 Americans over the age of 18 were randomly selected for the survey. The questionnaire had 25 questions and was collected between Feb. 10 and Feb. 12.
The survey found the majority (65 per cent) of Canadian respondents had not used an AI tool, with 19 per cent saying they had in a “personal context” only. About nine per cent said they had used AI for work or school.
Broken down by age, about 44 per cent who said they had used AI tools were between the ages of 18 to 34.
According to the data, Alberta had the highest number of people (30 per cent) who had used AI before, followed by 26 per cent of respondents in Ontario and 24 per cent in Manitoba and Saskatchewan.
Overall, 25 per cent of Canadians say they had used AI before, versus 21 per cent of Americans.
‘DO YOU TRUST AI TOOLS?’
Overwhelmingly, many Canadians do not trust AI to be involved in their more personal day-to-day life.
When asked if they would trust AI to teach children, about 48 per cent said “not at all.” Similarly, 43 per cent said they would not trust AI to transport them from one place to another without a driver.
About 41 per cent of Canadians said they wouldn’t trust AI to help find them a life partner.
However, when it comes to completing tasks at home or answering questions about a product online, Canadians are more likely to trust AI. About 46 per cent said they trust the tech to turn down music or adjust the thermostat in their home.
Roughly 41 per cent said they would “somewhat” trust AI to answer questions via a website chat.
According to the survey, younger Canadians tended to trust AI more than older Canadians with many tasks.
The reason Canadians may not trust AI could be linked to people believing “they lack emotion/ empathy required to make good decisions.” About 37 per cent strongly agreed AI can’t make good decisions due to its lack of human emotion.
Canadians also said they believe AI is susceptible to fraud or hacking.
‘HOW FAMILIAR ARE YOU WITH AI TOOLS?’
AI can come in many forms, such as smart home features or facial recognition detection technology. The majority of Canadians (41 per cent) are “somewhat familiar” the survey says, with home-based AI tools like robot vacuums.
Canadians were second-most familiar with facial detection software AI tools, with 38 per cent saying they were somewhat familiar.
Tools like ChatGPT and Synthesia which create content such as text, images and voices are the most unfamiliar to Canadians, according to the survey. About 43 per cent of respondents said they were “not at all familiar” with the AI tools.
Younger Canadians, aged 18 to 34, were more familiar with AI tools than older Canadians above the age of 35.
Canadians aged 18 to 34 were most familiar (65 per cent) with home-based AI tools and least familiar (43 per cent) with content creation AI like ChatGPT. Older Canadians were least likely to be familiar with any AI tools.
Between Canada and the U.S., Americans were more familiar across the board with all AI tools, despite not using them as much as Canadians.

‘DO YOU BELIEVE AI IS GOOD FOR SOCIETY?’
With somewhat of an understanding of how AI works and what it is used for, about 36 per cent of Canadians believed the tech is good for society. The positive opinion increased to 52 percent for younger Canadians and decreased for those aged 55 and older to 25 per cent, the survey shows.
Manitoba and Saskatchewan residents were most likely (39 per cent) to believe AI is bad for society compared to the second-highest (31 per cent) negative response from B.C. respondents.
Compared to the U.S., Canadians had better positive attitudes towards AI than Americans, with 36 per cent of respondents from Canada saying the tech is good for society compared to 32 per cent of respondents from the States.
————–
A margin of error cannot be associated with a non-probability sample in a panel survey. For comparison purposes, a probability sample of this size would have a margin of error ±2.50%, 19 times out of 20 for the Canadian sample and of ±3.09%, 19 times out of 20 for the American sample. The results presented in this study comply with the public opinion research standards and disclosure requirements of CRIC (the Canadian Research and Insights Council) and the global ESOMAR network.
News
Freeland tables her fourth federal budget — this time with a tight focus on housing – CBC.ca
Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland will table her fourth federal budget today, laying out the government’s plan to spend billions of dollars on housing to improve supply — a plan the Liberals also hope will boost their prospects with a crucial group of voters.
Unlike past budgets, which mostly saved their announcements for budget day itself, this one has been publicized piecemeal. Freeland, Prime Minister Justin Trudeau, Housing Minister Sean Fraser and other cabinet ministers have been touring the country for weeks, releasing details of key budget measures.
It’s part of a plan to pitch voters on new programs that otherwise might have been buried in today’s news coverage of a budget document that’s expected to be physically bigger than in years’ past.
Freeland will table the budget around 4 p.m. ET. CBCNews.ca will carry her remarks in the House of Commons live.
Ottawa has announced roughly $38 billion in new financial commitments — including $17 billion in loan-based programs — before the budget’s release.
How the federal government intends to pay for all that new spending isn’t clear yet. Sources have told Radio-Canada that the budget will impose a tax increase on the richest taxpayers — one that senior Liberal sources say will affect less than 1 per cent of Canadians.
Some of the planned new spending is earmarked for future fiscal years — a manoeuvre that will give Ottawa some fiscal breathing room.
The economy is also marginally stronger than Ottawa initially projected, which could mean higher revenue to offset some of the planned new spending.
Polls continue to suggest the government is polling underwater with house-hunting voters — particularly those in the millennial and Generation Z cohorts.
In response, Freeland has freed up money to send more cash to municipalities through the housing accelerator fund, build more homes on underused public lands, cut cheques for new water and solid waste infrastructure in growing communities, offer tens of billions of dollars in loans to spur new rental construction and secondary suites, and help non-profits acquire existing rental homes and keep them affordable.
- What do you want to see included in today’s federal budget announcement? Let us know in an email to ask@cbc.ca.
The government’s 28-page housing plan, unveiled last week, promises to maintain the already well-subscribed tax-free savings account, extend mortgage amortization terms and increase the RRSP withdrawal limit for some first-home buyers, among other measures.
It’s a dizzying array of new commitments meant to blunt the attacks of critics like Conservative Leader Pierre Poilievre, who has made housing the centrepiece of his policy playbook.
Speaking to the Canadian Chamber of Commerce on Monday, Trudeau said millennials and members of Generation Z, the people who now make up a majority of the country’s workforce, need a hand up as they grapple with “a cost of living crisis.”
“This is a resilient group but … they now feel like middle class stability is out of reach,” he said. “We need to meet this moment. Our country cannot succeed unless young people succeed.”
Deputy Prime Minister Chrystia Freeland announced new measures on Thursday aimed at lessening the financial strain on first-time homebuyers, including 30-year amortization rates on insured mortgages for newly built homes.
Freeland also has announced a $500-million fund for youth mental health, $2.4 billion for artificial intelligence, $8.1 billion in new defence spending and $1 billion to expand school lunch programs.
“We recognize that there is an urgent need today to invest in Canada and Canadians, and we recognize in particular that we’re at really a pivotal moment for young Canadians, for millennials, for Gen Z,” Freeland said last week.
It’s a longstanding Canadian tradition for the finance minister to purchase a new pair of shoes before budget day.
On Monday, Freeland chose a pair of black pumps from Maguire, a Montreal-based firm owned by millennial women — a nod to the people the government is hoping to reach with its latest spending plan.
While the budget is expected to boost spending, Freeland has said it won’t increase the $40 billion deficit forecast last year. Today, the public will learn what the government’s projected deficit and debt levels are and how it plans to keep the country on a sustainable fiscal track.
The Trudeau government has run a deficit every year since it was elected.
It posted even bigger deficits during the COVID-19 pandemic as it scrambled to shore up an economy on the ropes during an unprecedented global health crisis.
On the Liberal government’s watch, the national debt has more than doubled to $1.2 trillion.
Now, with interest rates at a 20-year high, the cost to carry that debt has spiked from $20.3 billion in 2020-21 to $46.5 billion, according to Freeland’s fall economic statement.
That’s nearly double the amount Ottawa spends on the military. And debt service charges can be expected to march even higher in the years ahead.
Political watchers say Ottawa has no choice but to raise taxes in the upcoming federal budget to offset billions of dollars of new spending, but who will be getting the increase remains to be seen.
As economic growth stagnates and high inflation adds to the government’s spending pressures, Ottawa faces some tough choices.
Freeland’s preferred fiscal “guardrail” has changed over the years.
In the fall economic statement, Freeland said Ottawa would keep the deficit at about one per cent of gross domestic product (GDP) — essentially one per cent of the size of the national economy — and lower the debt-to-GDP ratio.
Tuesday’s document will reveal if Ottawa has kept that promise. The government’s decision to cut or “reprofile” some spending — with estimated savings of about $2.25 billion a year — has helped, but there may be more to do.
Canada flirting with a rating downgrade, RBC warns
In a recent report, RBC Royal Bank warned that Canada faces a possible ratings agency downgrade — which would be a bad development for the government and everyone else who borrows money in this country.
Canada is one of the select few countries with a AAA credit rating on its sovereign debt.
RBC said “Canada is at a greater risk of a downgrade than other top-rated peers” as Ottawa piles on more spending to tackle the housing crisis.
“Even though deeper deficits and higher associated sovereign borrowing costs may feel like a distant problem for many Canadians, the impact has the potential to trickle down to most households and businesses,” economist Rachel Battaglia said in the RBC report.
Experts are expecting the government to increase taxes.
Freeland last week ruled out a middle-class tax hike — but this government’s definition of “middle class” has never been clear.
“I’m pretty confident they will raise revenues because they’ve squeezed themselves on their fiscal situation and they continue to commit to spending that is not sustainable,” said Robert Asselin, senior vice president of policy at the Business Council of Canada and an adviser to Bill Morneau when he was finance minister.
Budget expected to target wealthy Canadians
Many experts have been predicting tax measures targeting wealthy Canadians or large corporations, or both.
“The problem for [the government] is either a surtax on big corporations or a wealth tax sounds very good, but in practice they’re terrible. They don’t work,” said Asselin.
“Let’s be honest. They have to raise taxes. I don’t think that’s a big secret. But can they do it in a thoughtful, provocative way?” said James Thorne, chief capital market strategist for Wellington Altus Private Wealth.
“If you do it on the high-income people, they’re just going to move their money offshore.”
Speaking to reporters on Parliament Hill Monday, NDP Leader Jagmeet Singh said he expects the government — his party’s partner in the confidence-and-supply agreement — to “take on corporate greed.”


“The wealthy should pay,” he said, adding that big business should also shoulder the burden.
“We do not want to see any pressure put on working people. We don’t want tax increases on working class people. We want to see big corporations start paying their fair share.”
At a conference in Ottawa last week, Poilievre — who has mocked Trudeau and his government as “not worth the cost” — said his party will fight tooth and nail against any tax increases.
“We believe that a dollar in the hands of a person who earned it is always more powerful than in the hands of a politician who taxed it,” he said.
News
Peel police to announce arrests in Pearson Airport gold heist
|
|
Peel Regional Police and the U.S. Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms Bureau say they plan to announce arrests on Wednesday in the theft of roughly $20 million in gold and nearly $2 million US in cash from Toronto’s Pearson International Airport.
The announcement, to be made at 8:30 a.m. ET in Brampton, will come exactly one year after the incident.
CBC News will carry the announcement live.
In a news advisory, the law enforcement services said they would reveal “details and arrests made concerning the theft of gold and cash from Pearson International Airport” as part of Project 24K, a joint-task investigation into the high-value theft.
Peel Police Chief Nishan Duraiappah, Det-Sgt. Mike Mavity and Eric DeGree, special agent in charge of the Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms Bureau, are scheduled to speak.
Police have said little about the case in the last 12 months.
In response to recent questions from CBC News, police have said investigators are “working around the clock in order to locate, arrest and charge those responsible for this crime.”
Brink’s suing Air Canada over theft
Brink’s, a Miami-based security company, meanwhile, is suing Air Canada for allegedly letting a thief walk into an Air Canada facility at the airport and walk out with the gold bars and cash.
In an email on Tuesday, Brink’s spokesperson Kaye Faris said: “We were alerted of the news of the announcement today, as well, and look forward to learning more from the Peel Police Department at their news conference tomorrow.”
According to court documents obtained by CBC News, on April 14, 2023, Brink’s was commissioned by two Swiss banks — Raiffeisen and Valcambi — to move more than 400 kilograms of gold, and $1,945,843 in US bills, from Zurich to Toronto.
At the time, the value of the gold was just over 13.2 million Swiss francs, or almost $20 million Canadian at current exchange rates.
The cargo was loaded on to flight AC881, which departed Zurich at 1:25 p.m. local time on April 17 and arrived safely at Pearson at 3:56 p.m., without incident.
The two cargo shipments — emblazoned with the words BANKNOTES and GOLDBARS — were offloaded from the plane about 20 minutes later and deposited at an Air Canada storage facility about an hour and a half after that.
That’s when things went awry, the lawsuit alleges.
“At approximately 18:32,” Brink’s alleges in the documents, “an unidentified individual gained access to AC’s cargo storage facilities. No security protocols or features were in place to monitor, restrict or otherwise regulate the unidentified individual’s access to the facilities.”
The unnamed individual handed over a waybill to Air Canada personnel. A waybill is a document that has all the details of the cargo including instructions as to what it contains and where it should go.
Brink’s says the waybill was a copy of one tied to an unrelated shipment. Brink’s says the airline took the waybill “without verifying its authenticity in any way.”
“Upon receipt of the fraudulent waybill, AC personnel released the shipments to the unidentified individual, following which the unidentified individual absconded with the cargo.”
Brink’s says Air Canada handled the cargo “negligently and carelessly” and was “reckless” for failing to follow through on appropriate security measures, despite charging higher shipping rates for its “secure service.” It says the airline failed to provide “storing facilities equipped with effective vaults and cages, constant CCTV surveillance and active human surveillance patrols.”
Brink’s says it reached out to Air Canada on April 27, 2023 to let the airline know it was demanding a full reimbursement of the costs it has sustained. Brink’s is pursuing the matter in Federal Court.


Air Canada has rejected allegations
In a Nov. 8, 2023 statement of defence, Air Canada rejected “each and every allegation” in the Brink’s suit, saying it fulfilled its carriage contracts and denying any improper or “careless” conduct.
The country’s largest airline says that Brink’s failed to note the value of the haul on the waybill — a document typically issued by a carrier with details of the shipment — and that if Brink’s did suffer losses, a multilateral treaty known as the Montreal Convention would cap Air Canada’s liability.
“Brink’s Switzerland Ltd. elected for its own reasons not to declare a value for carriage and to pay the standard rate for the AC Secure services product and, to Air Canada’s knowledge, elected not to insure these shipments,” the Air Canada filing reads, adding that Brink’s was “fully aware of the consequences.”





News
Ironman Canada: Ottawa to host 2025 triathlon – CTV News Ottawa
The city of Ottawa will be hosting the Ironman Canada Triathlon in 2025.
It will be the first full-distance Ironman event to be held in Ottawa. The event is scheduled to take place Aug. 3, 2025.
“We are thrilled to announce this new partnership with Ottawa and bring Ironman Canada-Ottawa, one of our most historic race franchises, to the Canadian capital,” said Ironman VP of North American operations Keats McGonigal in a news release. “Ottawa offers the quintessential Canadian race environment with a plethora of outdoor activities, great weather and a mosaic of culture all nestled at the very seat of government. Ironman Canada has played a prominent role in the history of Ironman and will continue with the expansion to Ottawa. We are enthusiastic and excited to see what futures hold here in Ottawa, Ontario.”
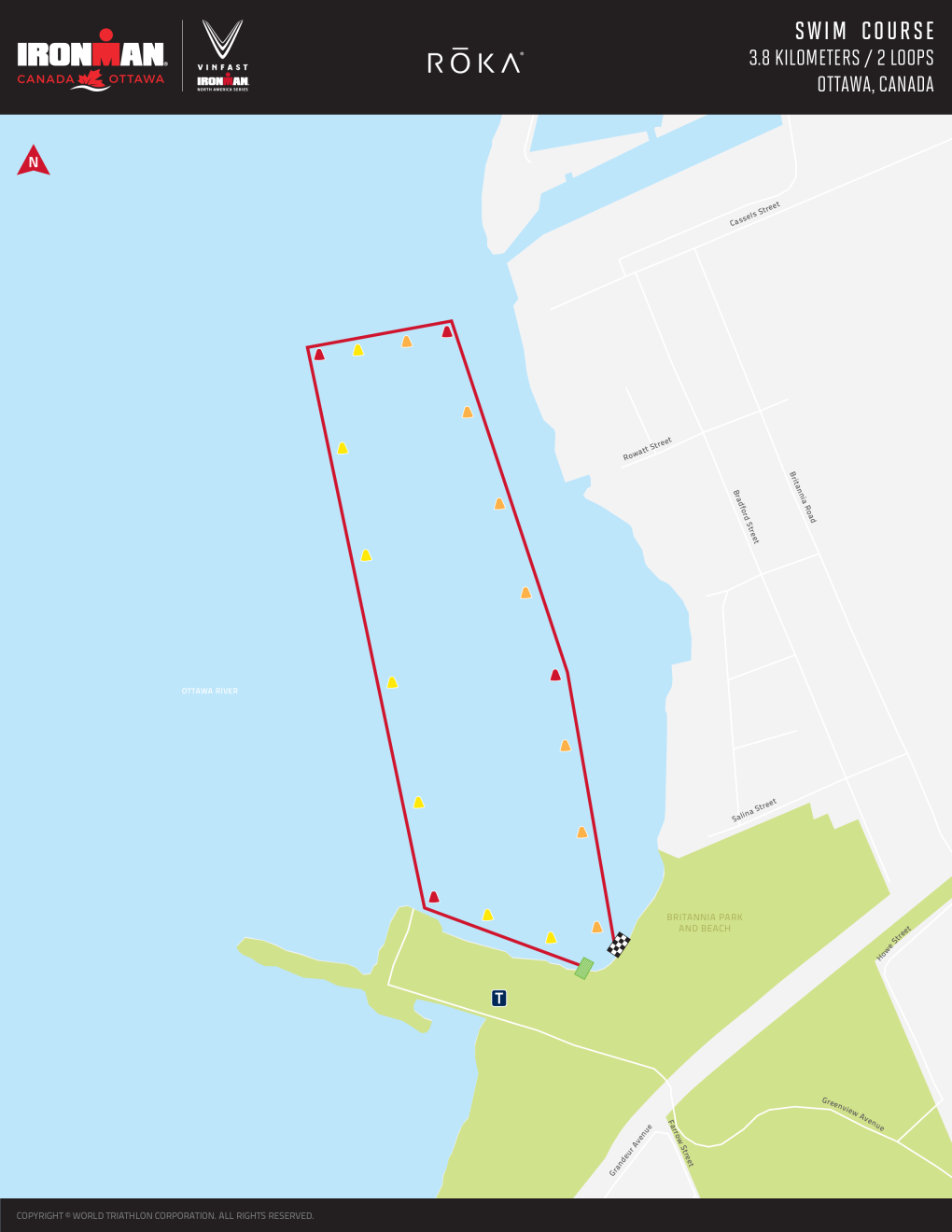
The triathlon will begin at Britannia Beach, with a 3.8-kilometre two-loop swim in the Ottawa River.

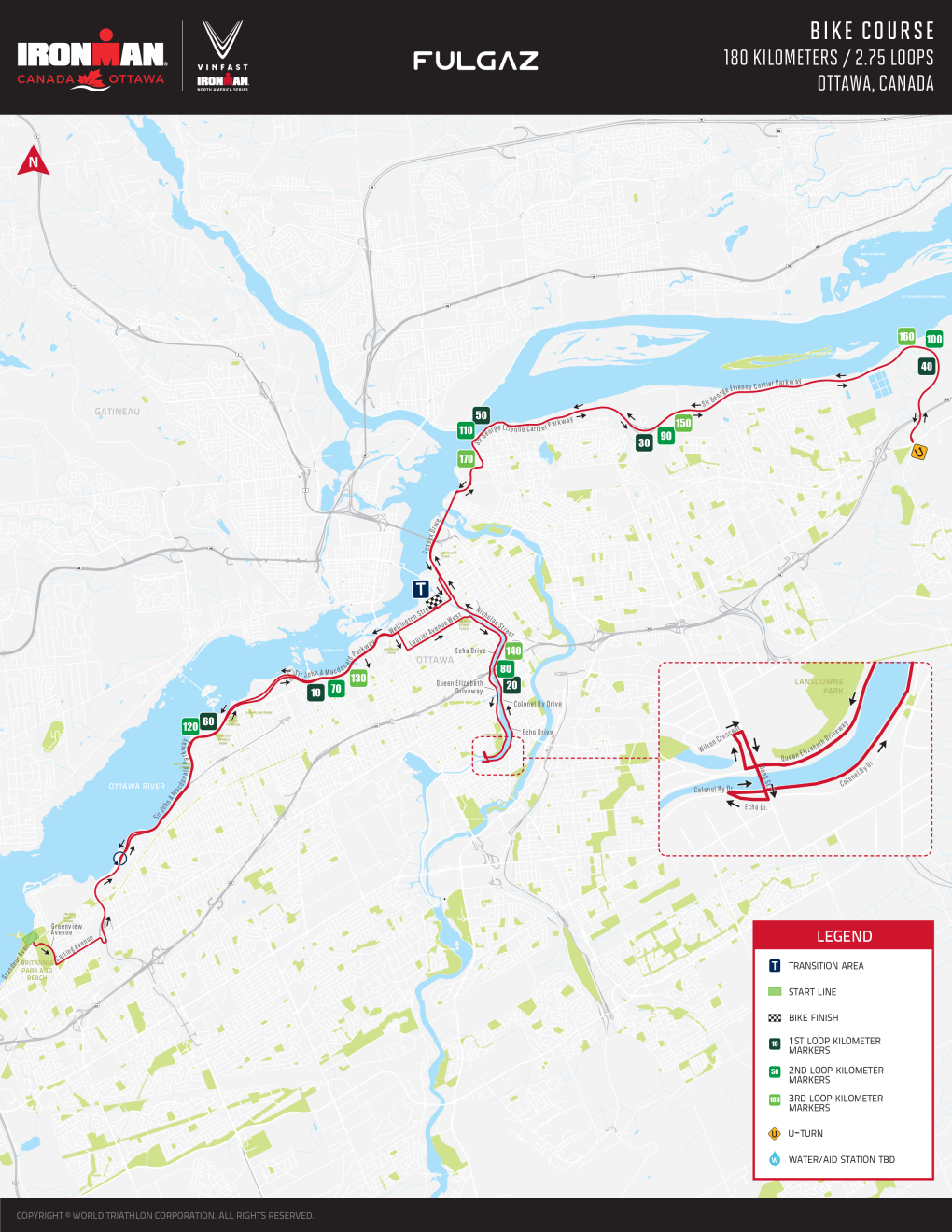
From there, the 180-km bike portion will run along NCC and city roads, including the Kichi Zibi Mikan, the Queen Elizabeth Driveway, Laurier Avenue, Nicholas Street, Sussex Drive, and the Sir George-Étienne Cartier Parkway. Roads will be closed to traffic for the event.
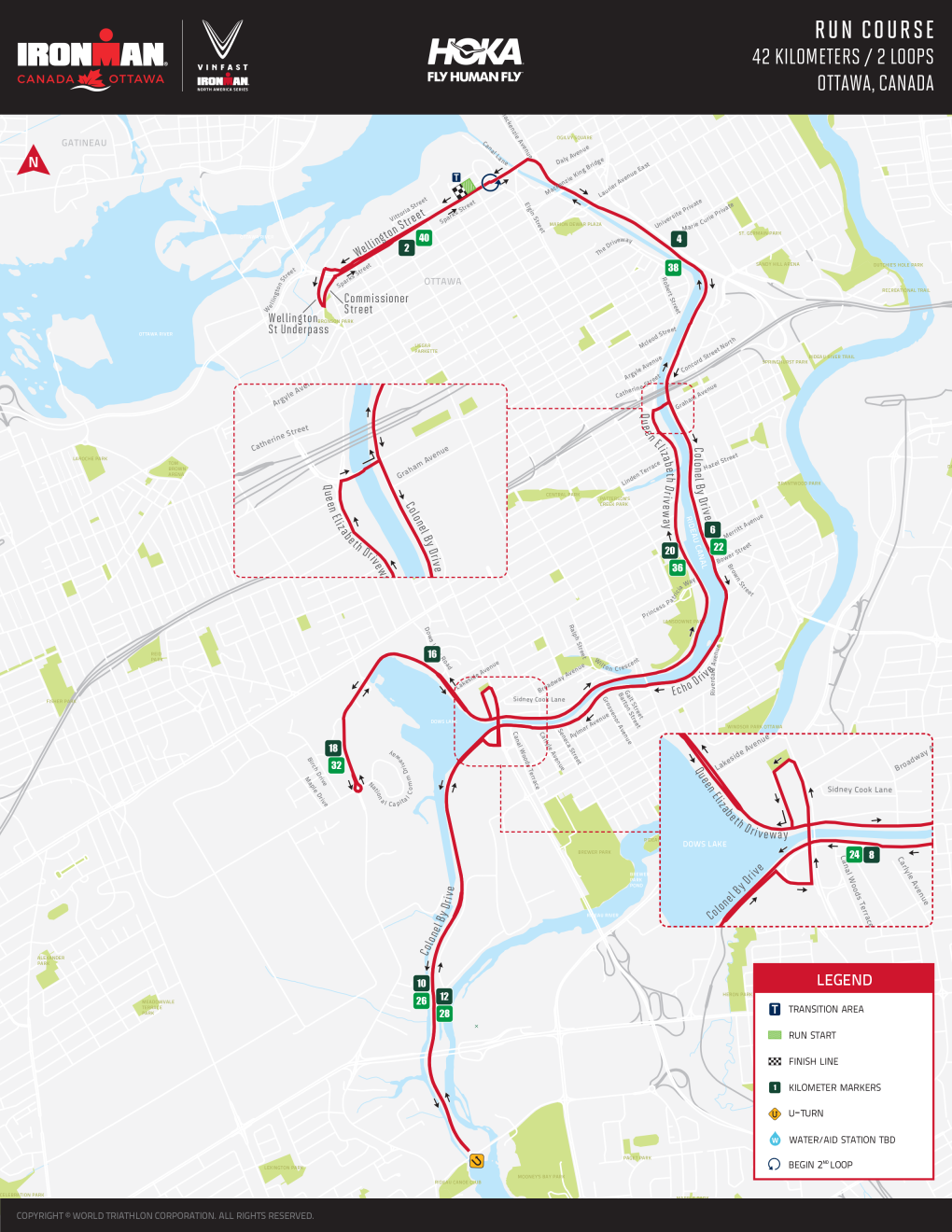
Finally, the marathon run will begin at Parliament Hill, run along Wellington Street before looping to head south on Colonel By Drive alongside the Rideau Canal to Hog’s Back and then back up the Queen Elizabeth Driveway to Parliament Hill.
“I am thrilled to welcome the Ironman Canada competition to Ottawa,” said Ottawa Mayor Mark Sutcliffe. “I love this city and so will you. There are so many triathletes in Ottawa. And it’s an absolutely stunning and beautiful place to swim, bike and run. It’s also the perfect location for outdoor adventures and world class events, especially an event as prestigious as Ironman Canada. Ottawa is a great place for this amazing competition. Everyone from athletes to families, friends and fans will have an amazing race experience here. I look forward to seeing everyone here in August 2025.”
General registration opens April 22 on the Ironman website. The Ironman Canada-Ottawa triathlon, part of the VinFast Ironman North America Series, will offer qualifying slots to the 2026 VinFast Ironman World Championship.
“This event showcases the resilience and determination of athletes from far and wide, leaving a legacy of excellence in our city,” said Ottawa Tourism president and CEO Michael Crockatt. “We’re confident about this partnership and believe this will significantly contribute to our local economy, grow our sports tourism market, inspire our community, and further showcase our ability to host world-class events. Ottawa’s scenic landscapes and vibrant communities are ready to welcome participants and spectators alike for an unforgettable experience.”
[embedded content]
Turn by turn directions
Bike course
- Head southeast on Greenview Ave
- Turn left onto Carling Ave
- Take the ramp onto Kichi Zibi Mikan East
- Stay on parkway until it turns into Wellington St
- Turn Right onto Lyon St
- Turn Left onto Laurier Ave W
- Take Ramp onto Queen Elizabeth Driveway and head south
- Turn Right onto Queen Elizabeth Pl towards Wilton Crescent and Bank St
- Turn Right onto Wilton Crescent
- Turn Right onto Bank St
- Turn Right onto Echo Dr
- Turn Right onto Colonel By Dr and head north
- Colonel By Dr ends and becomes Sussex Dr – Continue North on Sussex Dr
- Sussex Dr continues along the Ottawa River and turns into Princess Ave
- Princess Ave becomes Sir-George-Étienne-Cartier Pkwy
- Stay on Sir-George-Étienne-Cartier Pkwy until it ends at Regional Rd 48/St Joseph Blvd where you will U-Turn prior to the intersection.
- Stay on Sir-George-Étienne-Cartier Pkwy west until its Princess Ave, and then Sussex Dr again into Ottawa
- Right onto Wellington St
- Continue on Wellington St until it turns back into Kichi Zibi Mikan West
- Stay on Kichi Zibi Mikan until the yet to be determined exact turn around point approx. near Deschênes Rapids Lookout and begin your second or final loop.
- Repeat these steps above until you return to our transition area for the final time and dismount.
Exact transition area is still being determined and right now it shows on Wellington St. This remains to be determined but it will be in and around this general area within 800 meters.

Run course
- Head west on Wellington St
- Use the Wellington St Underpass to access Commissioner St
- Turn left onto Commissioner St
- Right onto Wellington St
- Right on Colonel By Dr- Stay on Colonel By Dr all the way down to Hogs Back Rd
- Turn around just before Hogs Back Rd and head North
- Turn Right onto the ramp up to Bronson Ave
- Turn Left onto Bronson Ave
- Turn Left onto Lakeview Terrace
- Turn Right onto Queen Elizabeth Driveway
- Queen Elizabeth Driveway turns into Prince of Wales Dr
- Turn around at Prince of Wales Dr and NCC Scenic Driveway (exact turn around will be adjusted here to make the exact distance and may be before or after the roundabout)
- Head North on Prince of Wales Dr
- Prince of Wales Dr turns into Queen Elizabeth Driveway
- Stay on Queen Elizabeth Driveway until Hawthorne Ave
- Turn right onto Hawthorne Ave
- Turn left onto Colonel By Dr
- Turn left onto Wellington St
- Continue on Wellington until turn around to start second loop
- Follow steps above to complete second loop
- Finish line is currently planned on the beautiful and historic Wellington St.
Athletes will notice the bike, run and finish are all planned for Wellington St. Ironman has different versions of the plan still being vetted out and will have updates as it completes those discussions.

-
Tech4 hours ago
Motorola's Edge 50 Phone Line Has Moto AI, 125-Watt Charging – CNET
-
Real eState5 hours ago
Search platform ranks Moncton real estate high | CTV News – CTV News Atlantic
-
Media24 hours ago
Trump Media plunges amid plan to issue more shares. It's lost $7 billion in value since its peak. – CBS News
-



 Investment23 hours ago
Investment23 hours agoInvestors are growing increasingly weary of AI – TechCrunch
-
News18 hours ago
Budget 2024 sets up a ‘hard year’ for the Liberals. Here’s what to expect – Global News
-
Media18 hours ago
Psychology group says infinite scrolling and other social media features are ‘particularly risky’ to youth mental health – NBC News
-
News20 hours ago
Freeland 2024 budget 'likely to be the worst' in years: Dodge – CTV News
-



 Investment13 hours ago
Investment13 hours agoSo You Own Algonquin Stock: Is It Still a Good Investment? – The Motley Fool Canada



.jpg?crop=1.777xh:h;*,*&downsize=510px:*510w)



