Economy
Why more highway spending won’t rev up the economy – Livemint


Economists aren’t so sure. A wide body of research focused on the effects of highway spending suggests that major new investment in U.S. roads would generate little, if any, long-term economic gain.
While the projects would spur hiring and spending temporarily, both when they are announced and under way, they aren’t likely to raise the economy’s productivity and, in turn, its overall growth potential in a lasting way, many researchers find.
That is because the US already has an extensive system of roads, so building more wouldn’t add much to productivity, economists say.
“Highways can generate a boost for the short run, but in the long run that seems to be dubious,” said Gilles Duranton, an economist at the University of Pennsylvania.
New spending for roads accounts for the largest single share—roughly 19%—of the $579 billion in new spending that the White House and a group of lawmakers have agreed to. Both Democrats and Republicans say that money would raise the economy’s productivity, defined as the level of output per hour worked.
President Biden last week touted the agreement as delivering “higher productivity and higher growth for our economy over the long run.”
Sen. Rob Portman, an Ohio Republican who helped craft the deal, said last month that the plan would “increase our productivity as a country.”
Development of the U.S. interstate highway system between the 1950s and 1970s—currently 47,000 miles of multilane highways stretching coast to coast—did make the economy much more productive, John Fernald, an economist at the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco, wrote in a 1999 paper.
The system meant a cross-country trip that used to take months could be accomplished in days. Businesses gained access to new suppliers and new customers. Cities were able to specialize in certain industries. International trade opened up. By one estimate, the U.S. economy would be 3.9% smaller today without the interstate highway system.
But those gains all came about when the highways were built. By now, the gains have been reaped.
“Building the interstate highway system was enormously productive,” Mr. Fernald said. “That does not imply that building a second one would be equally productive.”
Other research has reached similar conclusions.
Charles Hulten, an economist at the University of Maryland, found that infrastructure investment in developing countries like India resulted in increased productivity and higher growth rates. In developed countries with vast road networks, such as the U.S., new investment resulted in no change in overall productivity and growth.
A group of economists in Spain studying that country’s infrastructure spending between 1964 and 1991 concluded that the investment earlier in the period produced greater economic gains than investments later, when much of the infrastructure was already in place.
Researchers have also found that in developed countries, whatever local benefits come from highway improvements come at the expense of other locations. In other words, road spending reallocates the pie but doesn’t make it bigger.
Mr. Duranton and two co-authors, Geetika Nagpal and Matthew Turner, both of Brown University, suggested in a paper last year that new investments “lead to a displacement of economic activity while net growth effects are limited.”
That’s not to say that billions of dollars in new government road spending wouldn’t boost growth in the short term. But the gains would come about as the result of the construction, and would dissipate once all the projects are completed.
In a 2012 paper, San Francisco Fed economists Sylvain Leduc and Daniel Wilson found that new spending on roads can boost an area’s economy at two specific times: immediately after the new spending has been announced, and six to eight years later, when construction is under way. Beyond 10 years, there were no economic benefits to infrastructure spending, they found.
Moreover, the immediate effect applies only during recessions, they wrote. It’s unclear whether the U.S. would see that short-term boost now that the economy is expanding rapidly.
Some of the spending lawmakers are considering could ease congestion. But those improvements would also be temporary. Adding more highway lanes to ease congestion tends to encourage more people to use those lanes, making them congested once more, a phenomenon known as “induced demand.”
A 2011 paper by Mr. Duranton and Mr. Turner found that areas that added road miles saw a proportional increase in driving, resulting in the same overall traffic levels.
Even if long-term benefits are limited, there is still a case to be made for spending money on roads, economists say. Filling potholes could provide a more comfortable driving experience, for instance.
“The more comfortable ride is getting you the improved quality of life but it’s not necessarily adding tons of private sector productivity,” Mr. Fernald said.
Never miss a story! Stay connected and informed with Mint.
Download
our App Now!!
Economy
China Wants Everyone to Trade In Their Old Cars, Fridges to Help Save Its Economy – Bloomberg
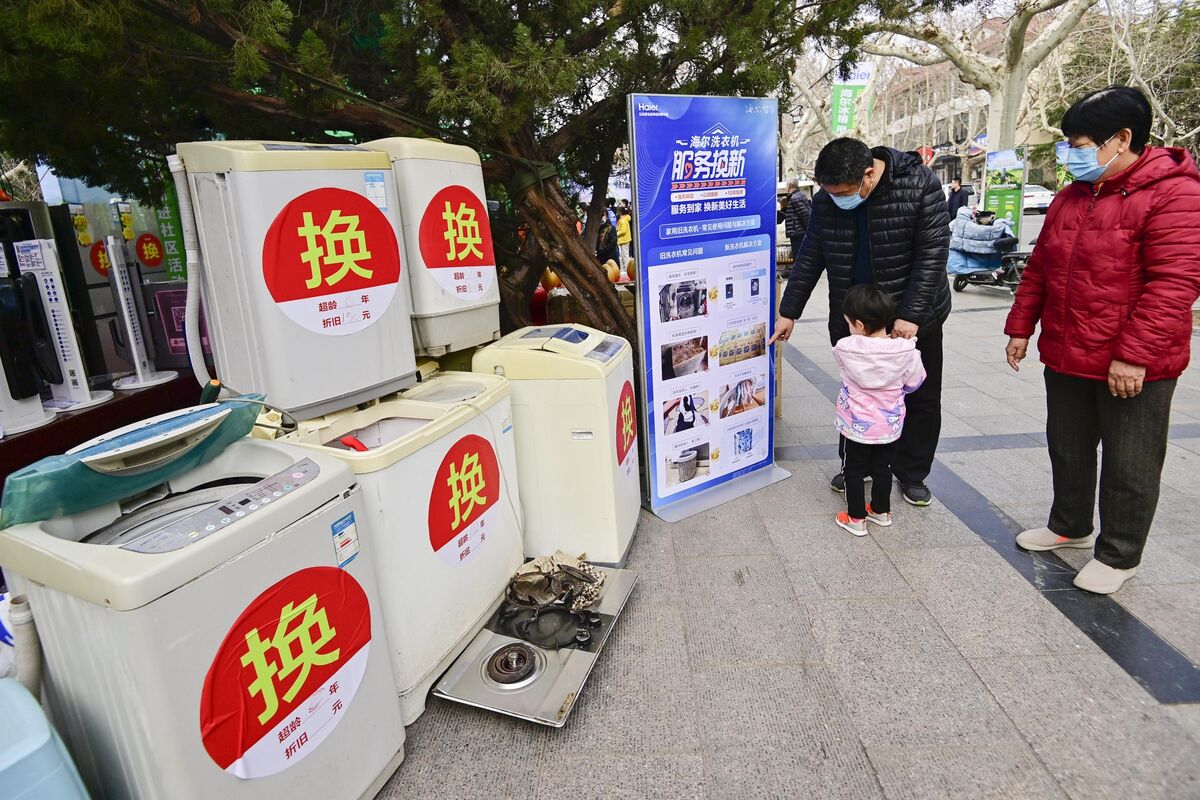


China’s world-beating electric vehicle industry, at the heart of growing trade tensions with the US and Europe, is set to receive a big boost from the government’s latest effort to accelerate growth.
That’s one takeaway from what Beijing has revealed about its plan for incentives that will encourage Chinese businesses and households to adopt cleaner technologies. It’s widely expected to be one of this year’s main stimulus programs, though question-marks remain — including how much the government will spend.
Economy
German Business Outlook Hits One-Year High as Economy Heals – BNN Bloomberg
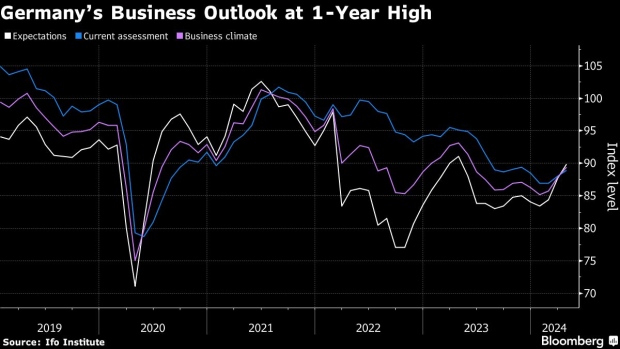

(Bloomberg) — German business sentiment improved to its highest level in a year — reinforcing recent signs that Europe’s largest economy is exiting two years of struggles.
An expectations gauge by the Ifo institute rose to 89.9. in April from a revised 87.7 the previous month. That exceeds the 88.9 median forecast in a Bloomberg survey. A measure of current conditions also advanced.
“Sentiment has improved at companies in Germany,” Ifo President Clemens Fuest said. “Companies were more satisfied with their current business. Their expectations also brightened. The economy is stabilizing, especially thanks to service providers.”
A stronger global economy and the prospect of looser monetary policy in the euro zone are helping drag Germany out of the malaise that set in following Russia’s attack on Ukraine. European Central Bank President Christine Lagarde said last week that the country may have “turned the corner,” while Chancellor Olaf Scholz has also expressed optimism, citing record employment and retreating inflation.
There’s been a particular shift in the data in recent weeks, with the Bundesbank now estimating that output rose in the first quarter, having only a month ago foreseen a contraction that would have ushered in a first recession since the pandemic.
Even so, the start of the year “didn’t go great,” according to Fuest.
“What we’re seeing at the moment confirms the forecasts, which are saying that growth will be weak in Germany, but at least it won’t be negative,” he told Bloomberg Television. “So this is the stabilization we expected. It’s not a complete recovery. But at least it’s a start.”
Monthly purchasing managers’ surveys for April brought more cheer this week as Germany returned to expansion for the first time since June 2023. Weak spots remain, however — notably in industry, which is still mired in a slump that’s being offset by a surge in services activity.
“We see an improving worldwide economy,” Fuest said. “But this doesn’t seem to reach German manufacturing, which is puzzling in a way.”
Germany, which was the only Group of Seven economy to shrink last year and has been weighing on the wider region, helped private-sector output in the 20-nation euro area strengthen this month, S&P Global said.
–With assistance from Joel Rinneby, Kristian Siedenburg and Francine Lacqua.
(Updates with more comments from Fuest starting in sixth paragraph.)
©2024 Bloomberg L.P.
Economy
Parallel economy: How Russia is defying the West’s boycott
|
|


When Moscow resident Zoya, 62, was planning a trip to Italy to visit her daughter last August, she saw the perfect opportunity to buy the Apple Watch she had long dreamed of owning.
Officially, Apple does not sell its products in Russia.
The California-based tech giant was one of the first companies to announce it would exit the country in response to Russian President Vladimir Putin’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine on February 24, 2022.
But the week before her trip, Zoya made a surprise discovery while browsing Yandex.Market, one of several Russian answers to Amazon, where she regularly shops.
Not only was the Apple Watch available for sale on the website, it was cheaper than in Italy.
Zoya bought the watch without a moment’s delay.
The serial code on the watch that was delivered to her home confirmed that it was manufactured by Apple in 2022 and intended for sale in the United States.
“In the store, they explained to me that these are genuine Apple products entering Russia through parallel imports,” Zoya, who asked to be only referred to by her first name, told Al Jazeera.
“I thought it was much easier to buy online than searching for a store in an unfamiliar country.”
Nearly 1,400 companies, including many of the most internationally recognisable brands, have since February 2022 announced that they would cease or dial back their operations in Russia in protest of Moscow’s military aggression against Ukraine.
But two years after the invasion, many of these companies’ products are still widely sold in Russia, in many cases in violation of Western-led sanctions, a months-long investigation by Al Jazeera has found.
Aided by the Russian government’s legalisation of parallel imports, Russian businesses have established a network of alternative supply chains to import restricted goods through third countries.
The companies that make the products have been either unwilling or unable to clamp down on these unofficial distribution networks.





-



 Health14 hours ago
Health14 hours agoRemnants of bird flu virus found in pasteurized milk, FDA says
-
Art20 hours ago
Mayor's youth advisory council seeks submissions for art gala – SooToday
-



 Health18 hours ago
Health18 hours agoBird flu virus found in grocery milk as officials say supply still safe
-



 Investment19 hours ago
Investment19 hours agoTaxes should not wag the tail of the investment dog, but that’s what Trudeau wants
-
News19 hours ago
Peel police chief met Sri Lankan officer a court says ‘participated’ in torture – Global News
-



 Science23 hours ago
Science23 hours agoiN PHOTOS: Nature lovers celebrate flora, fauna for Earth Day in Kamloops, Okanagan | iNFOnews | Thompson-Okanagan's News Source – iNFOnews
-
Art20 hours ago
An exhibition with a cause: Montreal's 'Art by the Water' celebrates 15 years – CityNews Montreal
-
Media14 hours ago
Vaughn Palmer: B.C. premier gives social media giants another chance




