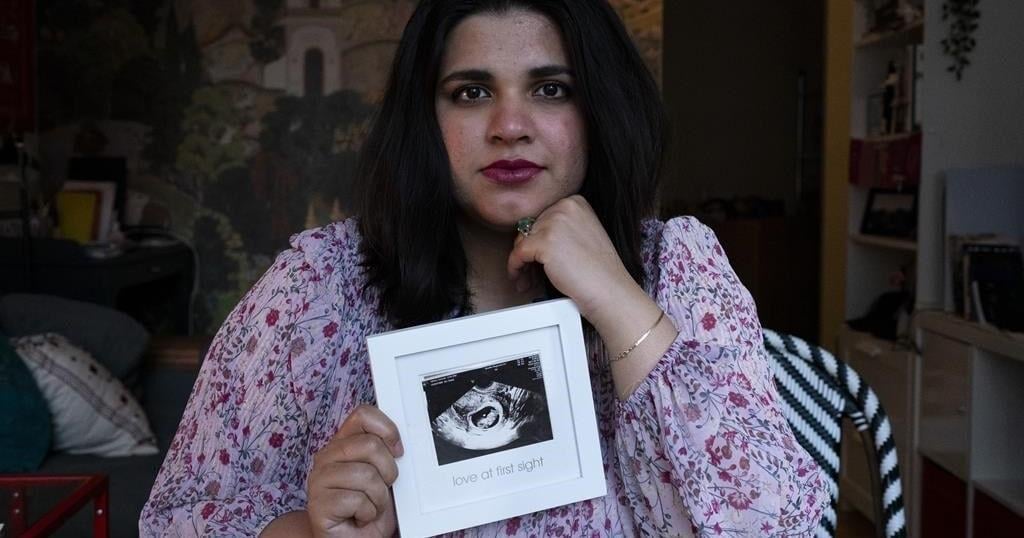
TORONTO – Sanniah Jabeen holds a sonogram of the unborn baby she lost after contracting listeria last December. Beneath, it says “love at first sight.”
Jabeen says she believes she and her baby were poisoned by a listeria outbreak linked to some plant-based milks and wants answers. An investigation continues into the recall declared July 8 of several Silk and Great Value plant-based beverages.
“I don’t even have the words. I’m still processing that,” Jabeen says of her loss. She was 18 weeks pregnant when she went into preterm labour.
The first infection linked to the recall was traced back to August 2023. One year later on Aug. 12, 2024, the Public Health Agency of Canada said three people had died and 20 were infected.
The number of cases is likely much higher, says Lawrence Goodridge, Canada Research Chair in foodborne pathogen dynamics at the University of Guelph: “For every person known, generally speaking, there’s typically 20 to 25 or maybe 30 people that are unknown.”
The case count has remained unchanged over the last month, but the Public Health Agency of Canada says it won’t declare the outbreak over until early October because of listeria’s 70-day incubation period and the reporting delays that accompany it.
Danone Canada’s head of communications said in an email Wednesday that the company is still investigating the “root cause” of the outbreak, which has been linked to a production line at a Pickering, Ont., packaging facility.
Pregnant people, adults over 60, and those with weakened immune systems are most at risk of becoming sick with severe listeriosis. If the infection spreads to an unborn baby, Health Canada says it can cause miscarriage, stillbirth, premature birth or life-threatening illness in a newborn.
The Canadian Press spoke to 10 people, from the parents of a toddler to an 89-year-old senior, who say they became sick with listeria after drinking from cartons of plant-based milk stamped with the recalled product code. Here’s a look at some of their experiences.
Sanniah Jabeen, 32, Toronto
Jabeen says she regularly drank Silk oat and almond milk in smoothies while pregnant, and began vomiting seven times a day and shivering at night in December 2023. She had “the worst headache of (her) life” when she went to the emergency room on Dec. 15.
“I just wasn’t functioning like a normal human being,” Jabeen says.
Told she was dehydrated, Jabeen was given fluids and a blood test and sent home. Four days later, she returned to hospital.
“They told me that since you’re 18 weeks, there’s nothing you can do to save your baby,” says Jabeen, who moved to Toronto from Pakistan five years ago.
Jabeen later learned she had listeriosis and an autopsy revealed her baby was infected, too.
“It broke my heart to read that report because I was just imagining my baby drinking poisoned amniotic fluid inside of me. The womb is a place where your baby is supposed to be the safest,” Jabeen said.
Jabeen’s case is likely not included in PHAC’s count. Jabeen says she was called by Health Canada and asked what dairy and fresh produce she ate – foods more commonly associated with listeria – but not asked about plant-based beverages.
She’s pregnant again, and is due in several months. At first, she was scared to eat, not knowing what caused the infection during her last pregnancy.
“Ever since I learned about the almond, oat milk situation, I’ve been feeling a bit better knowing that it wasn’t something that I did. It was something else that caused it. It wasn’t my fault,” Jabeen said.
She’s since joined a proposed class action lawsuit launched by LPC Avocates against the manufacturers and sellers of Silk and Great Value plant-based beverages. The lawsuit has not yet been certified by a judge.
Natalie Grant and her seven year-old daughter, Bowmanville, Ont.
Natalie Grant says she was in a hospital waiting room when she saw a television news report about the recall. She wondered if the dark chocolate almond milk her daughter drank daily was contaminated.
She had brought the girl to hospital because she was vomiting every half hour, constantly on the toilet with diarrhea, and had severe pain in her abdomen.
“I’m definitely thinking that this is a pretty solid chance that she’s got listeria at this point because I knew she had all the symptoms,” Grant says of seeing the news report.
Once her daughter could hold fluids, they went home and Grant cross-checked the recalled product code – 7825 – with the one on her carton. They matched.
“I called the emerg and I said I’m pretty confident she’s been exposed,” Grant said. She was told to return to the hospital if her daughter’s symptoms worsened. An hour and a half later, her fever spiked, the vomiting returned, her face flushed and her energy plummeted.
Grant says they were sent to a hospital in Ajax, Ont. and stayed two weeks while her daughter received antibiotics four times a day until she was discharged July 23.
“Knowing that my little one was just so affected and how it affected us as a family alone, there’s a bitterness left behind,” Grant said. She’s also joined the proposed class action.
Thelma Feldman, 89, Toronto
Thelma Feldman says she regularly taught yoga to friends in her condo building before getting sickened by listeria on July 2. Now, she has a walker and her body aches. She has headaches and digestive problems.
“I’m kind of depressed,” she says.
“It’s caused me a lot of physical and emotional pain.”
Much of the early days of her illness are a blur. She knows she boarded an ambulance with profuse diarrhea on July 2 and spent five days at North York General Hospital. Afterwards, she remembers Health Canada officials entering her apartment and removing Silk almond milk from her fridge, and volunteers from a community organization giving her sponge baths.
“At my age, 89, I’m not a kid anymore and healing takes longer,” Feldman says.
“I don’t even feel like being with people. I just sit at home.”
Jasmine Jiles and three-year-old Max, Kahnawake Mohawk Territory, Que.
Jasmine Jiles says her three-year-old son Max came down with flu-like symptoms and cradled his ears in what she interpreted as a sign of pain, like the one pounding in her own head, around early July.
When Jiles heard about the recall soon after, she called Danone Canada, the plant-based milk manufacturer, to find out if their Silk coconut milk was in the contaminated batch. It was, she says.
“My son is very small, he’s very young, so I asked what we do in terms of overall monitoring and she said someone from the company would get in touch within 24 to 48 hours,” Jiles says from a First Nations reserve near Montreal.
“I never got a call back. I never got an email”
At home, her son’s fever broke after three days, but gas pains stuck with him, she says. It took a couple weeks for him to get back to normal.
“In hindsight, I should have taken him (to the hospital) but we just tried to see if we could nurse him at home because wait times are pretty extreme,” Jiles says, “and I don’t have child care at the moment.”
Joseph Desmond, 50, Sydney, N.S.
Joseph Desmond says he suffered a seizure and fell off his sofa on July 9. He went to the emergency room, where they ran an electroencephalogram (EEG) test, and then returned home. Within hours, he had a second seizure and went back to hospital.
His third seizure happened the next morning while walking to the nurse’s station.
In severe cases of listeriosis, bacteria can spread to the central nervous system and cause seizures, according to Health Canada.
“The last two months have really been a nightmare,” says Desmond, who has joined the proposed lawsuit.
When he returned home from the hospital, his daughter took a carton of Silk dark chocolate almond milk out of the fridge and asked if he had heard about the recall. By that point, Desmond says he was on his second two-litre carton after finishing the first in June.
“It was pretty scary. Terrifying. I honestly thought I was going to die.”
Cheryl McCombe, 63, Haliburton, Ont.
The morning after suffering a second episode of vomiting, feverish sweats and diarrhea in the middle of the night in early July, Cheryl McCombe scrolled through the news on her phone and came across the recall.
A few years earlier, McCombe says she started drinking plant-based milks because it seemed like a healthier choice to splash in her morning coffee. On June 30, she bought two cartons of Silk cashew almond milk.
“It was on the (recall) list. I thought, ‘Oh my God, I got listeria,’” McCombe says. She called her doctor’s office and visited an urgent care clinic hoping to get tested and confirm her suspicion, but she says, “I was basically shut down at the door.”
Public Health Ontario does not recommend listeria testing for infected individuals with mild symptoms unless they are at risk of developing severe illness, such as people who are immunocompromised, elderly, pregnant or newborn.
“No wonder they couldn’t connect the dots,” she adds, referencing that it took close to a year for public health officials to find the source of the outbreak.
“I am a woman in my 60s and sometimes these signs are of, you know, when you’re vomiting and things like that, it can be a sign in women of a bigger issue,” McCombe says. She was seeking confirmation that wasn’t the case.
Disappointed, with her stomach still feeling off, she says she decided to boost her gut health with probiotics. After a couple weeks she started to feel like herself.
But since then, McCombe says, “I’m back on Kawartha Dairy cream in my coffee.”
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Sept. 16, 2024.
Canadian Press health coverage receives support through a partnership with the Canadian Medical Association. CP is solely responsible for this content.