Article content
Oil’s surge toward US$100 a barrel for the first time since 2014 is threatening to deal a double-blow to the world economy by further denting growth prospects and driving up inflation.
Much of the world will take a hit as companies and consumers find bills rising and spending power squeezed by costlier food, transportation and heating

Oil’s surge toward US$100 a barrel for the first time since 2014 is threatening to deal a double-blow to the world economy by further denting growth prospects and driving up inflation.
That’s a worrying combination for the U.S. Federal Reserve and fellow central banks as they seek to contain the strongest price pressures in decades without derailing recoveries from the pandemic. Group of 20 finance chiefs meet virtually this week for the first time this year with inflation among their top concerns.
While energy exporters stand to benefit from the boom and oil’s influence on economies isn’t what it once was, much of the world will take a hit as companies and consumers find their bills rising and spending power squeezed by costlier food, transportation and heating.
According to Bloomberg Economics’ Shok model, a climb in crude to US$100 by the end of this month from around US $70 at the end of 2021 would lift inflation by about half a percentage point in the U.S. and Europe in the second half of the year.
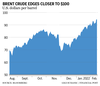
More broadly, JPMorgan Chase & Co. warns a run-up to US$150 a barrel would almost stall the global expansion and send inflation spiralling to over 7 per cent, more than three times the rate targeted by most monetary policy makers.
“The oil shock feeds into what is now a broader inflation problem,” said long-time Fed official Peter Hooper, who’s now global head of economic research for Deutsche Bank AG. “There’s a decent chance of a significant slowing of global growth” as a result.
Hopefully this is not the straw that breaks the camel’s back
Priyanka Kishore
Oil is about 50 per cent higher than a year ago, part of a broader rally in commodity prices that’s swept up natural gas too. Among the drivers: A post-lockdown resurgence in worldwide demand, geopolitical tensions ignited by oil giant Russia and strained supply chains. Prospects for a renewed Iranian nuclear deal have at times cooled the market.
Still, the rise has been piercing. Just two years ago, oil prices plunged briefly below zero.
Fossil fuels — oil, as well as coal and natural gas — provide more than 80 per cent of the global economy’s energy. And the cost of a typical basket of them is now up more than 50 per cent from a year ago, according to Gavekal Research Ltd., a consultancy.
The energy crunch also compounds the ongoing squeeze in global supply chains, which drove up costs and delayed raw materials and finished goods.
Vivian Lau, who runs a global logistics company based in Hong Kong, said her customers are already closely watching rising fuel costs.
“The price of oil is definitely a concern,” said Lau, vice chair and group chief executive officer of Pacific Air Holdings. “The increase is happening at a time when air freight prices are already very high.”

Economists are war gaming scenarios from here.
Goldman Sachs Group Inc., which sees oil at US$100 in the third quarter, estimates a 50 per cent increase lifts headline inflation by an average of 60 basis points, with emerging economies hit most.
The International Monetary Fund recently raised its forecast for global consumer prices to an average 3.9 per cent in advanced economies this year, up from 2.3 per cent, and 5.9 per cent in emerging and developing nations.
“With inflation currently at multi-decade highs and uncertainty surrounding the inflation outlook already unprecedented, the last thing the recovering global economy needs is another leg higher in energy prices,” HSBC economists Janet Henry and James Pomeroy wrote in a Feb. 4 report. “Yet that is what it is getting.”
China, the world’s biggest oil importer and goods exporter, has so far enjoyed benign inflation. But it’s economy remains vulnerable as producers are already juggling high input costs and concerns over energy shortages.
With price pressures proving more tenacious than earlier expected, central bankers are now prioritizing inflation fighting over demand support. U.S. consumer prices surprising to a four-decade high sent shocks through the system, increasing bets the Fed will raise rates seven times this year, a faster pace than earlier expected.
Bank of England Governor Andrew Bailey this month partly justified the decision to raise U.K. interest rates by pointing to a “squeeze from energy prices.” European Central Bank President Christine Lagarde said recently that officials will “carefully examine” how energy prices will impact the economy as they signal a shift toward tightening. The Reserve Bank of India on Thursday also flagged oil prices as a risk.
To be sure, the world economy is no longer the oil guzzler it was during previous decades, especially the 1970s, and alternative energy offers some buffer. Other pandemic-era insulators include swelling household savings and higher wages amid a tight labor market.




In the U.S. the emergence of the shale oil industry means its economy is less vulnerable to fuel shocks: While consumers are paying more for gasoline, domestic producers are earning more.
Mark Zandi, chief economist for Moody’s Analytics, estimates that each US$10 per barrel increase shaves 0.1 percentage point off of economic growth the following year. That compares with a 0.3 to 0.4 point blow prior to the fracking revolution.
Other oil producers will have reason to celebrate, too.
Russia’s budget, for example, could reap more than US$65 billion in extra revenue this year, helping buffer the Kremlin against possible sanctions over Ukraine. Other emerging market producers would benefit, as would Canada and Middle Eastern economies.
But for most consumers, and central bankers, much rides on how fast and how far energy goes, particularly if economies lose momentum globally.
“A continued rapid rise can raise risks of recession-like conditions in some countries, especially if fiscal policy is also tightening notably,” said Priyanka Kishore of Oxford Economics Ltd., which estimates that every US$10 per barrel increase in oil eats around 0.2 percentage points from world growth.
“Hopefully,” she said, “this is not the straw that breaks the camel’s back.”

OTTAWA – Canada’s unemployment rate held steady at 6.5 per cent last month as hiring remained weak across the economy.
Statistics Canada’s labour force survey on Friday said employment rose by a modest 15,000 jobs in October.
Business, building and support services saw the largest gain in employment.
Meanwhile, finance, insurance, real estate, rental and leasing experienced the largest decline.
Many economists see weakness in the job market continuing in the short term, before the Bank of Canada’s interest rate cuts spark a rebound in economic growth next year.
Despite ongoing softness in the labour market, however, strong wage growth has raged on in Canada. Average hourly wages in October grew 4.9 per cent from a year ago, reaching $35.76.
Friday’s report also shed some light on the financial health of households.
According to the agency, 28.8 per cent of Canadians aged 15 or older were living in a household that had difficulty meeting financial needs – like food and housing – in the previous four weeks.
That was down from 33.1 per cent in October 2023 and 35.5 per cent in October 2022, but still above the 20.4 per cent figure recorded in October 2020.
People living in a rented home were more likely to report difficulty meeting financial needs, with nearly four in 10 reporting that was the case.
That compares with just under a quarter of those living in an owned home by a household member.
Immigrants were also more likely to report facing financial strain last month, with about four out of 10 immigrants who landed in the last year doing so.
That compares with about three in 10 more established immigrants and one in four of people born in Canada.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Nov. 8, 2024.
The Canadian Press. All rights reserved.
The Canadian Institute for Health Information says health-care spending in Canada is projected to reach a new high in 2024.
The annual report released Thursday says total health spending is expected to hit $372 billion, or $9,054 per Canadian.
CIHI’s national analysis predicts expenditures will rise by 5.7 per cent in 2024, compared to 4.5 per cent in 2023 and 1.7 per cent in 2022.
This year’s health spending is estimated to represent 12.4 per cent of Canada’s gross domestic product. Excluding two years of the pandemic, it would be the highest ratio in the country’s history.
While it’s not unusual for health expenditures to outpace economic growth, the report says this could be the case for the next several years due to Canada’s growing population and its aging demographic.
Canada’s per capita spending on health care in 2022 was among the highest in the world, but still less than countries such as the United States and Sweden.
The report notes that the Canadian dental and pharmacare plans could push health-care spending even further as more people who previously couldn’t afford these services start using them.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Nov. 7, 2024.
Canadian Press health coverage receives support through a partnership with the Canadian Medical Association. CP is solely responsible for this content.
The Canadian Press. All rights reserved.

As Canadians wake up to news that Donald Trump will return to the White House, the president-elect’s protectionist stance is casting a spotlight on what effect his second term will have on Canada-U.S. economic ties.
Some Canadian business leaders have expressed worry over Trump’s promise to introduce a universal 10 per cent tariff on all American imports.
A Canadian Chamber of Commerce report released last month suggested those tariffs would shrink the Canadian economy, resulting in around $30 billion per year in economic costs.
More than 77 per cent of Canadian exports go to the U.S.
Canada’s manufacturing sector faces the biggest risk should Trump push forward on imposing broad tariffs, said Canadian Manufacturers and Exporters president and CEO Dennis Darby. He said the sector is the “most trade-exposed” within Canada.
“It’s in the U.S.’s best interest, it’s in our best interest, but most importantly for consumers across North America, that we’re able to trade goods, materials, ingredients, as we have under the trade agreements,” Darby said in an interview.
“It’s a more complex or complicated outcome than it would have been with the Democrats, but we’ve had to deal with this before and we’re going to do our best to deal with it again.”
American economists have also warned Trump’s plan could cause inflation and possibly a recession, which could have ripple effects in Canada.
It’s consumers who will ultimately feel the burden of any inflationary effect caused by broad tariffs, said Darby.
“A tariff tends to raise costs, and it ultimately raises prices, so that’s something that we have to be prepared for,” he said.
“It could tilt production mandates. A tariff makes goods more expensive, but on the same token, it also will make inputs for the U.S. more expensive.”
A report last month by TD economist Marc Ercolao said research shows a full-scale implementation of Trump’s tariff plan could lead to a near-five per cent reduction in Canadian export volumes to the U.S. by early-2027, relative to current baseline forecasts.
Retaliation by Canada would also increase costs for domestic producers, and push import volumes lower in the process.
“Slowing import activity mitigates some of the negative net trade impact on total GDP enough to avoid a technical recession, but still produces a period of extended stagnation through 2025 and 2026,” Ercolao said.
Since the Canada-United States-Mexico Agreement came into effect in 2020, trade between Canada and the U.S. has surged by 46 per cent, according to the Toronto Region Board of Trade.
With that deal is up for review in 2026, Canadian Chamber of Commerce president and CEO Candace Laing said the Canadian government “must collaborate effectively with the Trump administration to preserve and strengthen our bilateral economic partnership.”
“With an impressive $3.6 billion in daily trade, Canada and the United States are each other’s closest international partners. The secure and efficient flow of goods and people across our border … remains essential for the economies of both countries,” she said in a statement.
“By resisting tariffs and trade barriers that will only raise prices and hurt consumers in both countries, Canada and the United States can strengthen resilient cross-border supply chains that enhance our shared economic security.”
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Nov. 6, 2024.
The Canadian Press. All rights reserved.


Affordability or bust: Nova Scotia election campaign all about cost of living


Canada’s Denis Shapovalov wins Belgrade Open for his second ATP Tour title

11 new cases of measles confirmed in New Brunswick, bringing total cases to 25


First World War airmen from New Brunswick were pioneers of air warfare


Talks to resume in B.C. port dispute in bid to end multi-day lockout


Museum to honour Chinese Canadian troops who fought in war and for citizenship rights


The Royal Canadian Legion turns to Amazon for annual poppy campaign boost