Plasmids and cloning
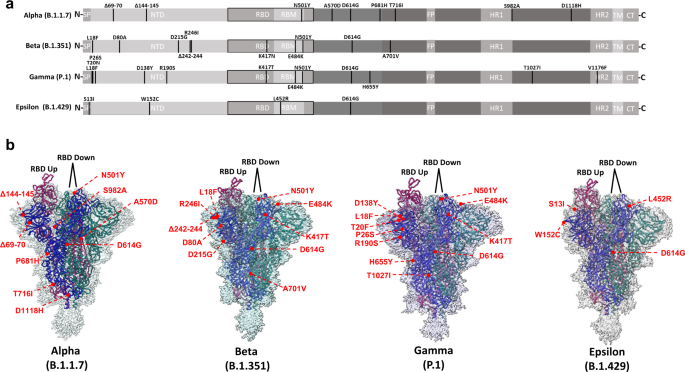
SARS-CoV-2 S protein Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Epsilon genes were synthesized and inserted into pcDNA3.1 (GeneArt Gene Synthesis, Thermo Fisher Scientific). Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Epsilon, Delta, and Kappa mutated S protein ectodomain genes were synthesized incorporating the hexa-proline stabilizing mutations, the transmembrane domain replaced with a fibrin trimerization motif, and a C-terminal hexa-histidine tag (GeneArt Gene Synthesis, Thermo Fisher Scientific). The HexaPro expression plasmid was a gift from Jason McLellan (Addgene plasmid #154754; http://n2t.net/addgene:154754; RRID: Addgene_154754) which we used to construct the D614G mutant via site-directed mutagenesis (Q5 Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit, New England Biolabs).
C-terminal 7x his tagged NTD (amino acids 1–305) and RBD (amino acids 319–541) constructs were PCR amplified from D614G, Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Epsilon full-length spike ORFs. NTD constructs were cloned into pcDNA 3.1 using NheI and MssI restriction enzyme cloning, while the RBD constructs were introduced in frame to the mu phosphatase signal sequence and incorporated within pcDNA3.1 via Gibson assembly (NEBuilder HiFi DNA Assembly Cloning Kit, New England Biolabs).
Human ACE2 (residues 1–615) with a C terminal 7x his tag was amplified from “hACE2”, a kind gift from Hyeryun Choe (Addgene plasmid # 1786) and cloned into pcDNA3.1 via BstXI and XbaI restriction enzyme cloning. Successful cloning was confirmed by Sanger sequencing (Genewiz, Inc.) for all constructs.
Ethics oversight
Patient-derived sera samples were collected according to the CARE COVID Study (http://www.bccdc.ca/health-professionals/clinical-resources/covid-19-care/covid-19-serology-care-covid-study) with ethics approval from the UBC Clinical Research Ethics Board. Informed consent was received from all study participants.
Pseudovirus neutralization assay
Variant and D614G spike pseudotyped retroviral particles were produced in HEK293T cells as described previously42. Briefly, a third-generation lentiviral packaging system was utilized in combination with plasmids encoding the full-length SARS-CoV-2 spike, along with a transfer plasmid encoding luciferase and GFP as a dual reporter gene. Pseudoviruses were harvested 60 h after transfection, filtered with a 0.45 µm PES filter, and frozen. For neutralization assays, HEK293T-ACE2-TMPRSS2 cells43 (BEI Resources cat# NR-55293) were seeded in 96-well plates at 50 000 cells. The next day, pseudovirus preparations normalized for viral capsid p24 levels (Lenti-X™ GoStix™ Plus) were incubated with dilutions of the indicated antibodies or sera, or media alone for 1 h at 37 °C prior to addition to cells and incubation for 48 h. Cells were then lysed and luciferase activity was assessed using the ONE-Glo™ EX Luciferase Assay System (Promega) according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Detection of relative luciferase units was carried out using a Varioskan Lux plate reader (Thermo Fisher). Percent neutralization was calculated relative to signals obtained in the presence of the virus alone for each experiment.
Expression and purification of recombinant proteins
Expi293F cells (Thermo Fisher, Cat# A14527) were grown in suspension culture using Expi293 Expression Medium (Thermo Fisher, Cat# A1435102) at 37 °C, 8% CO2. Cells were transiently transfected at a density of 3 × 106 cells/mL using linear polyethylenimine (Polysciences Cat# 23966-1). The media was supplemented 24 h after transfection with 2.2 mM valproic acid, and expression was carried out for 3–7 days at 37 °C, 8% CO2.
For ectodomain trimer and monomeric human ACE2 (residues 1–615) purification, the supernatant was harvested by centrifugation and filtered through a 0.22-μM filter prior to loading onto a 5 mL HisTrap excel column (Cytiva). The column was washed for 20 CVs with wash buffer (20 mM Tris pH 8.0, 500 mM NaCl), 5 CVs of wash buffer supplemented with 20 mM imidazole, and the protein eluted with elution buffer (20 mM Tris pH 8.0, 500 mM NaCl, 500 mM imidazole). Elution fractions containing the protein were pooled and concentrated (Amicon Ultra 100 kDa cut off for ectodomain, 10 kDa for monomeric ACE2) before gel filtration. Gel filtration was conducted using a Superose 6 10/300 GL column (Cytiva) pre-equilibrated with GF buffer (20 mM Tris pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl). Peak fractions corresponding to soluble protein were pooled and concentrated to 4.5–5.5 mg/mL (Amicon Ultra 100 kDa cut off for ectodomain, 10 kDa for monomeric ACE2). Protein samples were flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C.
For purification of the RBD and NTD constructs, the supernatant was harvested after 7 days of expression and incubated with 300 µL of Ni-NTA resin (Qiagen) at 4 °C overnight. The resin was washed three times with 5 mL of PBS, then three times with 5 mL of PBS supplemented with 20 mM of imidazole. Proteins were eluted in PBS containing 300 mM of imidazole and then buffer exchanged into PBS and concentrated to 5–10 mg/mL (Amicon Ultra 10 kDa cut off, Millipore Sigma) before flash freezing and storage at −80 °C.
For purification of dimeric human ACE2-FC, the supernatant was harvested after 6 days of expression and flowed through a gravity column containing over 400 µL of Protein A Plus Agarose (Thermo Fisher Cat# 22812) once. The column was washed once with 5 mL of PBS before elution with 0.1 M glycine pH3.5 and immediate neutralization with 1 M Tris pH 8.0. Elutions were pooled and concentrated using an Amicon Ultra 50 kDa cut-off concentrator before gel filtration. Gel filtration was conducted using a Superose 6 10/300 GL column (Cytiva) pre-equilibrated with GF buffer (20 mM Tris pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl). Peak fractions corresponding to soluble protein were pooled and concentrated to 2–5 mg/mL (Amicon Ultra 50 kDa cut-off). Protein samples were flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C.
Antibody production
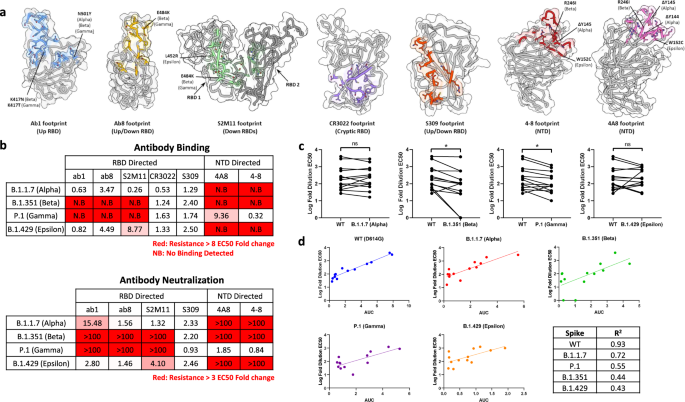
VH-FC ab8, IgG ab1, Fab S309, and Fab S2M11 were produced as previously described3,13,14. Plasmids encoding light and heavy chains for Fab 4A8 and Fab 4–8 were synthesized (GeneArt Gene Synthesis, Thermo Fischer Scientific). Heavy chains were designed to incorporate a C terminal 6x histidine tag. Expi293 cells were transfected at a density of 3 × 106 cells/mL using linear polyethylenimine (Polysciences Cat# 23966-1). Twenty-four hours following transfection, media was supplemented with 2.2 mM valproic acid, and expression was carried out for 3–5 days at 37 °C, 8% CO2. The supernatant was harvested by centrifugation and filtered through a 0.22 μM filter prior to loading onto a 5 mL HisTrap excel column (Cytiva). The column was washed for 20 CVs with wash buffer (20 mM Tris pH 8.0, 500 mM NaCl), 5 CVs of wash buffer supplemented with 20 mM imidazole. The protein was eluted with elution buffer (20 mM Tris pH 8.0, 500 mM NaCl, 500 mM imidazole). Elution fractions containing the protein were pooled and concentrated (Amicon Ultra 10 kDa cut-off, Millipore Sigma) for gel filtration. Gel filtration was conducted using a Superose 6 10/300 GL column (Cytiva) pre-equilibrated with GF buffer (20 mM Tris pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl). Peak fractions corresponding to soluble protein were pooled and concentrated to 8–20 mg/mL (Amicon Ultra 10 kDa cut-off, Millipore Sigma). Protein samples were stored at 4 °C until use.
Electron microscopy sample preparation and data collection
For cryo-EM, S protein samples were prepared at 2.25 mg/mL, with and without the addition of ACE2 or antibody (1:1.25 S protein trimer:ACE2 molar ratio, 1:9 S protein trimer:VHab6 molar ratio, 1:8 S protein trimer:S2M11 fab molar ratio, 1:4 S protein trimer:4A8/4-8 fab molar ratio). Mixtures were incubated on ice for 20 min prior to centrifugation at 14,000 × g for 10 min. Vitrified samples of all S protein samples were prepared by first glow discharging Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 Cu mesh 200 holey carbon grids for 30 seconds using a Pelco easiGlow glow discharge unit (Ted Pella) and then applying 1.8 µL of protein suspension to the surface of the grid at a temperature of 10 °C and a humidity level of >98%. Grids were blotted (12 s, blot force −10) and plunge frozen into liquid ethane using a Vitrobot Mark IV (Thermo Fisher Scientific). All cryo-EM samples were imaged using a 300 kV Titan Krios G4 transmission electron microscope (Thermo Fisher Scientific) equipped with a Falcon4 direct electron detector in electron event registration (EER) mode. Movies were collected at ×155,000 magnification (calibrated pixel size of 0.5 Å per physical pixel) over a defocus range of −0.5 µm to −3 μm with a total dose of 40 e−/Å2 using the EPU automated acquisition software.
Image processing
The detailed workflow for the data processing is summarized in Supplementary Figs. 1–4, 6–7, 11–14, 17, 23, and 25. In general, all data processing was performed in cryoSPARC v.3.244 unless stated otherwise. Patch mode motion correction (EER upsampling factor 1, EER number of fractions 40), patch mode CTF estimation, reference free particle picking, and particle extraction were carried out on-the-fly in cryoSPARC live. After preprocessing, particles were subjected to 2D classification and/or 3D heterogeneous classification. The final 3D refinement was performed with an estimation of per particle CTF and correction for high-order aberrations.
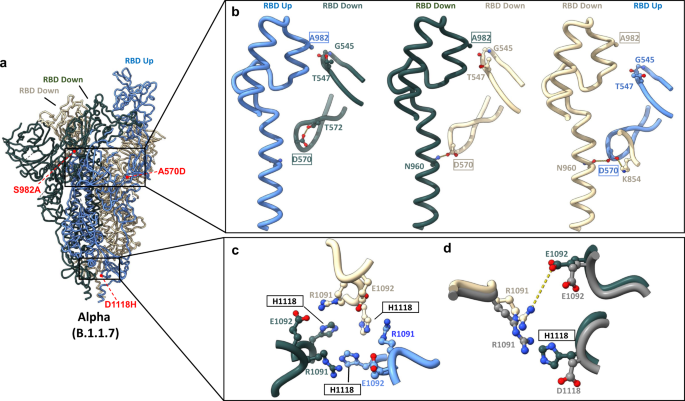
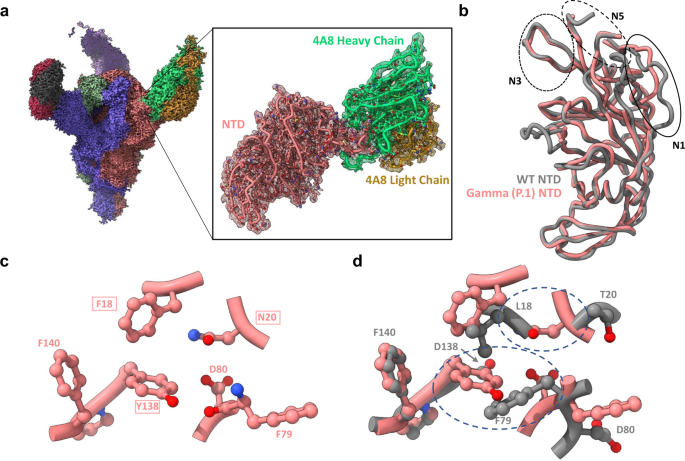
For the complexes of spike protein ectodomain and human ACE2, focused refinements were performed with a soft mask covering a single RBD and its bound ACE2. For the complexes of spike protein ectodomain and VH ab6, a soft mask covering VH-ab6 and its bound RBD was used in focused refinement. For the complexes of Gamma spike protein ectodomain and fab 4-8/4-A8, another round of 3D refinement with C3 symmetry was carried out, followed by symmetry expansion. The derived particles were then focused-refined with a soft mask covering single NTD and its bound fab.
Global resolution and focused resolution were determined according to the gold-standard FSC45.
Model building and refinement
Initial models either from published coordinates (PDB code 7MJG, 7MJM, 7MJN, 7LXY, 7K43, and 7MJI) or from homology modeling (for 4–8, 4-A8, and VH-ab6) were docked into the focused refinement maps or global refinement maps using UCSF Chimera v.1.1546. Then, mutation and manual adjustment were performed with COOT v.0.9.347, followed by iterative rounds of refinement in COOT and Phenix v.1.1948. Model validation was performed using MolProbity49. Figures were prepared using UCSF Chimera, UCSF ChimeraX v.1.1.150, and PyMOL (v.2.2 Schrodinger, LLC).
Biolayer interferometry (BLI) S protein—ACE2 binding assay
The kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 trimers and human ACE2 binding were analyzed with the biolayer interferometer BLItz (ForteBio, Menlo Park, CA). Protein-A biosensors (ForteBio: 18–5010) were coated with ACE2-mFc (40 µg/mL) for 2 min and incubated in DPBS (pH = 7.4) to establish baselines. Concentrations of 125, 250, 500, and 1000 nM spike trimers were used for the association for 2 min followed by dissociation in DPBS for 5 min. The association (kon) and dissociation (koff) rates were derived from the fitting of sensorgrams and used to calculate the binding equilibrium constant (KD).
Flow cytometry S protein—ACE2 binding assay
Expi293 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding the various full-length variant S proteins using linear PEI as performed during recombinant spike production. After 3 days of expression, cells were washed with PBS then pelleted and resuspended in incubation buffer (PBS pH 7.4 with 0.02% Tween-20 and 4% BSA) at a concentration of 5 × 106 cells/mL. In all, 100 µl of this mixture was deposited into each well within a 96-well plate followed by a 5 min incubation on ice. Cells were pelleted and resuspended in an incubation buffer containing increasing concentrations of recombinant FC-ACE2 (Sino Biological Cat# 10108-H05H-100) followed by incubation for 20 min on ice. The cells were pelleted and washed with 200 µl of wash buffer (PBS pH 7.4 with 0.02%Tween-20). Next, the cells were incubated in 100 µL of a 1:300 dilution of secondary antibody (Thermo Fisher Cat# A-21235) in an incubation buffer for 10 min. Cells were pelleted and washed twice in 100 µL of wash buffer prior to staining with propidium iodide (Biolegend). Cells were analyzed using a Cytoflex LX at the ubcFLOW cytometry facility. Data were analyzed using FlowJo. The gating strategy employed along with results for un-transfected (negative control) Expi293 cells are available in Supplementary Fig. 10B.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
For ELISA, 100 µL of wild-type (D614G), or variant SARS-CoV-2 S proteins, NTDs, and RBDs were coated onto 96-well MaxiSorp™ plates at 2 µg/mL in PBS + 1% casein overnight at 4 °C. All washing steps were performed 3 times with PBS + 0.05% Tween 20 (PBS-T). After washing, wells were incubated with blocking buffer (PBS-T + 1% casein) for 1 h at room temperature. After washing, wells were incubated with dilutions of primary antibodies in PBS-T + 0.5% BSA buffer for 1 h at room temperature. For fab and IgG primary antibodies, wells were incubated with goat anti-human IgG (Jackson ImmunoResearch) at a 1:8000 dilution in PBS-T + 1% casein buffer for 1 h at room temperature. For VH ab6, wells were incubated with mouse anti-FLAG M2 antibody (Sigma Aldrich) at a 1:50 dilution in PBS-T + 1% casein buffer for 1 h at room temperature, washed, and incubated with goat anti-mouse IgG (Thermo Fisher Scientific Cat# 31439) at a 1:5000 dilution in PBS-T + 1% casein buffer for 1 h at room temperature. For ACE2 competition experiments, serial dilutions of VH ab6 were incubated in wells in PBS-T + 1% casein buffer for 1 h at room temperature and washed before incubation with either 0.2 or 1 ng/mL of human ACE2-FC in PBS-T + 0.5% casein for 1 h at room temperature. After washing, wells were incubated with goat anti-human IgG (Jackson ImmunoResearch) at a 1:8000 dilution in PBS-T + 1% casein buffer for 1 h at room temperature. After washing, the substrate solution (Pierce™ 1-Step™) was used for color development according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Optical density at 450 nm was read on a Varioskan Lux plate reader (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR)
SPR experiments were performed on a Biacore T200 instrument. CM5 chips were functionalized with monoclonal anti-Strep-Tag antibody (BIO-RAD Cat# MCA2489) at a concentration of 50 µg/mL for the capture of spike protein ectodomains. After the capture of D614G hexapro ectodomain, either buffer, 175 nM, or 440 nM of VH ab6 was injected onto the chip, followed by 500 nM human ACE2-FC. The surface was regenerated in 10 mM glycine, pH 1 between experiments. The experiments were performed at 25 degrees Celsius, using 10 mM HEPES, 150 mM NaCl, 3 mM EDTA, and 0.05% v/v Surfactant P20 as running buffer. Reference-subtracted curves were utilized for the qualitative assessment of ACE2 competition. Relative response units (RUs) were normalized to a value of 0 immediately before ACE2-FC injection for ease of ACE2-FC binding assessment.
Authentic SARS-CoV-2 plaque reduction neutralization assay
Neutralization assays were performed using Vero E6 cells (ATCC CRL-1586) that were seeded 24 h prior to the assay in 24-well tissue culture plates at a density of 3 × 105 cells per well. Antibodies were serially diluted twofold (starting concentration of 4, 10, or 40 µg/mL, depending on the antibody being tested) and mixed with an equal volume of 30–50 plaque-forming units of SARS-CoV-2. This results in a final antibody concentration of 2, 5, or 20 µg/mL in the antibody–virus mixture. The following SARS-CoV-2 variants were used: isolate USA-WA1/2020 (NR-52281, BEI Resources); isolate hCoV-19/South Africa/KRISP-EC-K005321/2020 (NR-54008, BEI Resources); isolate hCoV-19/USA/CA_UCSD_5574/2020 (NR-54008, BEI Resources); and isolate hCoV-19/USA/PHC658/2021 (NR-55611, BEI Resources). The antibody-virus mixture was then incubated at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 incubator for 1 h and added to the Vero E6 cell seeded monolayers, in duplicate. Plates were then incubated for 1 h at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 incubator. Following incubation, an overlay media with 1% agarose-containing media (2× Minimal Essential Medium, 7.5% bovine albumin serum, 10 mM HEPES, 100 µg/mL penicillin G, and 100 U/mL streptomycin) was added to the monolayers. The plates were incubated for 48–72 h (depending on the SARS-CoV2 variant) and then cells were fixed with formaldehyde for 2 h. Following fixation, agar plugs were removed, and cells were stained with crystal violet. In order to assess the input virus, a viral back-titration was performed using a culture medium as a replacement for the antibodies. To estimate the neutralizing capability of each antibody, IC50s were calculated by non-linear regression using the sigmoidal dose–response equation in GraphPad Prism 9. All assays were performed in the University of Pittsburgh Regional Biocontainment Laboratory BSL-3 facility.
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Research Reporting Summary linked to this article.