NEMASKA, QUE. — Type the word “Nemaska” into a search engine and most results refer to Nemaska Lithium, the company that sought bankruptcy protection in 2019 before being partly bought out by the Quebec government’s investment agency. The episode resulted in tens of thousands of small investors losing significant savings.
However, Nemaska is above all a Cree community in the heart of the boreal forest, more than 1,500 kilometres from Montreal. They share their territory with a wide variety of species, and caribou herds have long visited the area, drawn by its abundance of lichen.
These fragile ecosystems are home to a multitude of threatened species that will soon have to deal with new visitors: starting in 2025, approximately 15 heavy trucks a day will roar through these ancestral hunting grounds carrying the thousands of tonnes of ore that Nemaska Lithium plans to mine.
According to the promoters, the region contains some of the world’s largest deposits of spodumene, a rock from which lithium — key to the energy transition and the electrification of transport networks — is extracted.
Nemaska Lithium describes itself as a corporation that “intends to facilitate access to green energy, for the benefit of humanity.”
The Whabouchi open pit mine will be located about 30 kilometres from the village of Nemaska, in the watershed of the Rupert River, considered one of Quebec’s ecological gems.
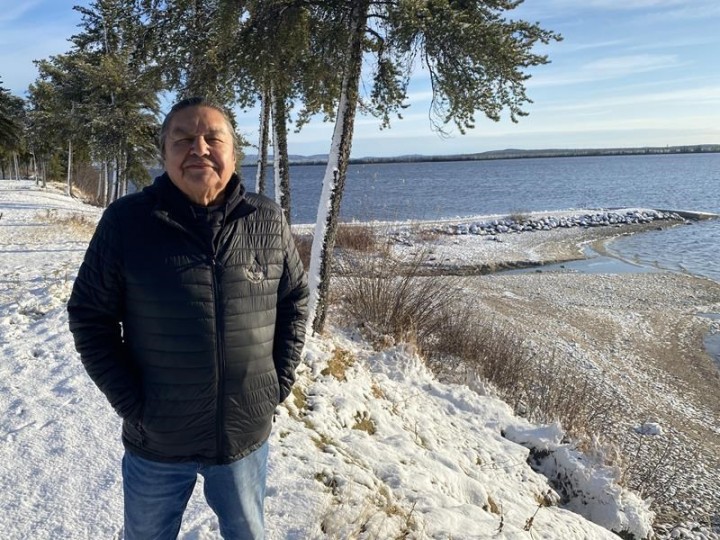
“If the water becomes contaminated by the mine, I don’t see how we can limit the damage to the food chain,” says Thomas Jolly, who was chief of Nemaska from 2015 to 2019, stressing the importance of fishing to his community.
Nemaska means “Place of Plentiful Fish,” and that is what led the Cree to build their community here in 1979 after a proposed Hydro-Québec dam project threatened to flood their ancestral village. (In the end, the Crown corporation chose to build its reservoirs elsewhere, and the flooding of Old Nemaska never occurred.)
“At the time, the Department of Indian Affairs wanted to impose another site on us, but it was partly a swamp … so we chose to settle here instead, where it’s dry, in a place where there is everything we need to hunt and fish,” Jolly said in an interview in Nemaska.
Various other Hydro-Québec projects have led to an increase in mercury levels in lakes and rivers near Nemaska, to the point where for some bodies of water, public health authorities recommend eating no more than two fish of certain species per month.
According to public health data, one of the waterways with the highest mercury levels is the Nemiscau River, which is also set to receive mine effluent from Nemaska Lithium.
“How much more contamination can these streams handle?” Jolly wonders.
He explains that history has taught him to be wary of the studies carried out by the mining company on the environmental impacts of lithium extraction. “Hydro-Québec said they didn’t know (the mercury contamination) would happen,” he says. “Come on!”
The construction of the mine will cause the elimination of a lake and a stream in addition to modifying several other bodies of water. In total, the negative effects on fish and fish habitat are estimated at 54,600 square metres, according to the Impact Assessment Agency of Canada, and Nemaska Lithium is working to implement a compensation plan for this loss of habitat.
The federal government’s approval of the mine comes with dozens of conditions, including protecting water quality. In an interview with The Canadian Press, Vincent Perron, the director of environment and stakeholder relations at Nemaska Lithium, says the company has “a very comprehensive and rigorous water quality monitoring program.”
Perron explains that Nemaska Lithium, among other things, is committed to verifying every three years “the level of heavy metals in the flesh of fish, starting during the construction of the mine and until the end of a five-year period following its closure.”
He stresses that “a water treatment plant will be installed to treat the excess drainage water before it is released into the Nemiscau River.”
Company documents show that 10 species of mammals with a special status — either threatened, vulnerable or at risk — may frequent the mine area, including the wolverine and the woodland caribou as well as various species of birds, such as the golden eagle.
The Impact Assessment Agency of Canada cited potential “habitat loss and fragmentation” for those species but said the impact would not be significant because of the availability of similar habitat nearby and mitigation measures proposed by the proponent.
For Jolly, regardless of mitigation measures, “it’s obvious” that animals will be negatively affected by the blasting, the extraction and transportation of ore. He wants the mine administrators to consider traditional Indigenous knowledge and not just “book science” in managing the risks.
“You, people from the south, when you talk about animals and plants, you use the word species,” he says, “but we call them educators.”
Nemaska Lithium says it wants its mine project to set a benchmark for environmental responsibility. Powered by renewable electricity from Hydro-Québec, it will be one of “the greenest lithium producers in the world,” says Perron.
The project will have “one of the lowest intensities of production in the world in terms of CO2 equivalent emissions from processing and transportation combined,” he said. “It is nearly three times lower than the global average, and more than six times lower than China.”
However, Jolly stresses that hydro power is not as green as some people make it out to be. The environmental impacts of large dams are considerable, he says, citing examples of entire communities that have had to relocate because of flooding. Hunting grounds were submerged and mercury levels shot up in fish, among other upheavals in the James Bay Cree’s traditional way of life.
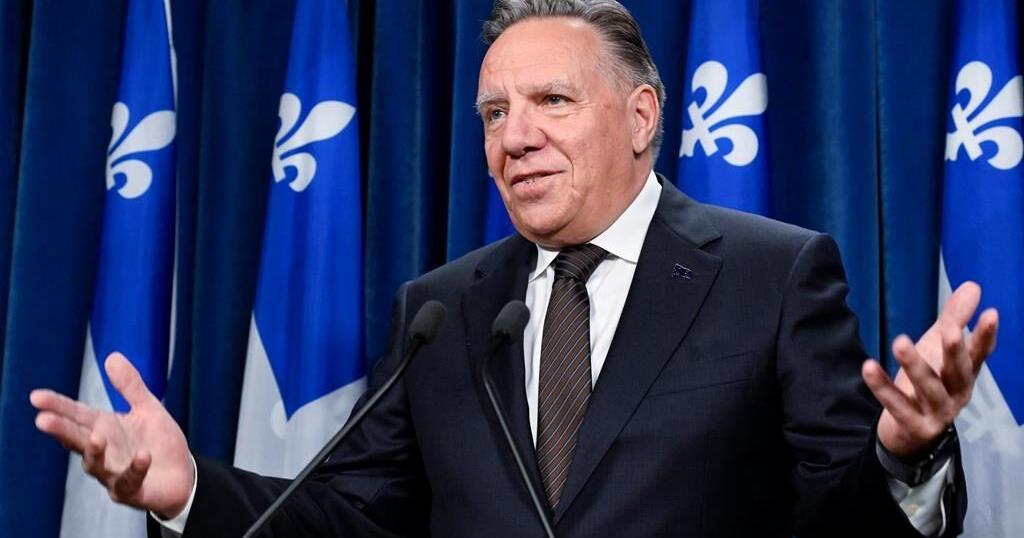
The Quebec government has invested hundreds of millions of dollars in Nemaska Lithium. Premier François Legault, who wants Quebec to export electric vehicle batteries worldwide and be a leader in 21st-century transportation, considers the company “an important component of the green economy.”
Jolly questions why lithium mined from Cree lands should be a central part of the government’s plan to combat climate change. “Who is responsible (for the climate crisis)?” he asked. “Is it up to us to pay and suffer for what they have done?”
He says the project was approved by the band council without properly consulting the population, a critique echoed by another former chief, George Wapachee. In his book “Going Home”, published last fall, Wapachee writes that the decision to accept the lithium mine “was made without the approval of community members.”
But while many in Nemaska are worried about the mine, it also gives hope to those who see it as an important tool for economic development. At a hearing in 2015, former Chief Matthew Wapachee presented a petition that included about 100 signatures in support of the project.
“Nemaska Lithium should be commended in recognizing and ensuring that this partnership is founded on mutual trust, protection of the environment and respect of Cree rights and traditional way of life,” Matthew Coon Come, who was then grand chief of the Grand Council of the Crees, said in a press release at the time.
Even though some in Nemaska say they were not sufficiently informed about the mine project, Nemaska band council spokesperson Laurence Gagnon maintains that the community was regularly consulted at annual general meetings. The council accepted the project “100 per cent for the economic benefits,” she said in an interview.
She said the village is expected to receive annual royalties. “We are talking about several million dollars over 30 years for the community,” she said. This money “returns to our citizens for better infrastructures, better services.”
Current Chief Clarence Jolly was among the elected officials who in 2014 voted to ratify the agreement with the mine.
Over a period of several months, The Canadian Press made numerous attempts to speak with him to discuss the impacts of the mine and its social acceptance, but he declined all requests. Gagnon explained the chief’s refusal by noting that the lithium mine was “a sensitive subject” that he preferred “not to discuss during an election period.”
The chief offered to provide an interview after the community elections later this month.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Feb. 5, 2023.
—
Stéphane Blais received the support of the Michener Foundation, which awarded him a Michener–Deacon Investigative Journalism fellowship in 2022 to report on the impact of lithium extraction in northern Quebec.
Stéphane Blais, The Canadian Press
Related