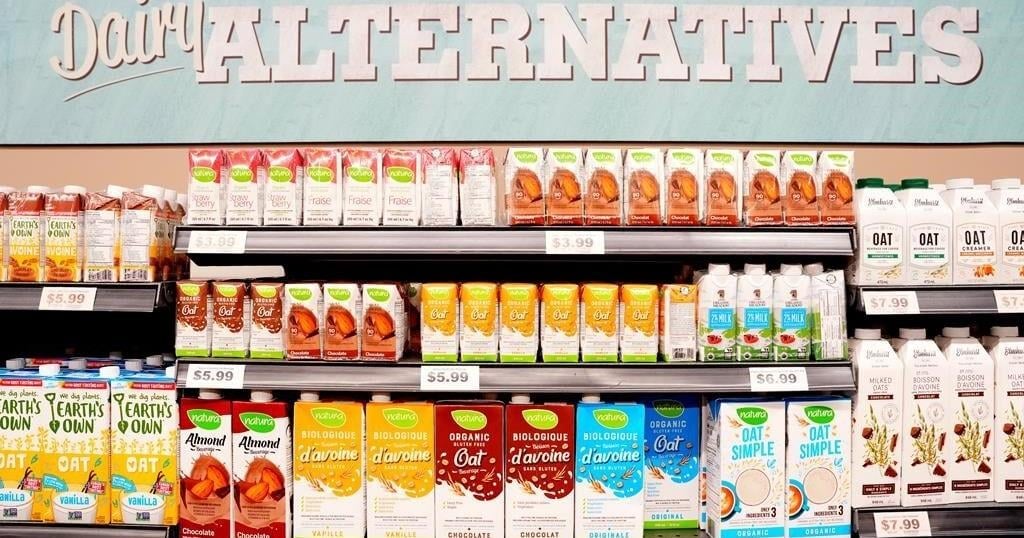
When it comes to plant-based alternatives, Canadians have never had so many options — and nowhere is that choice more abundantly clear than in the milk section of the dairy aisle.
To meet growing demand, companies are investing in new products and technology to keep up with consumer tastes and differentiate themselves from all the other players on the shelf.
“The product mix has just expanded so fast,” said Liza Amlani, co-founder of the Retail Strategy Group.
She said younger generations in particular are driving growth in the plant-based market as they are consuming less dairy and meat.
Commercial sales of dairy milk have been weakening for years, according to research firm Mintel, likely in part because of the rise of plant-based alternatives — even though many Canadians still drink dairy.
The No. 1 reason people opt for plant-based milk is because they see it as healthier than dairy, said Joel Gregoire, Mintel’s associate director for food and drink.
“Plant-based milk, the one thing about it — it’s not new. It’s been around for quite some time. It’s pretty established,” said Gregoire.
Because of that, it serves as an “entry point” for many consumers interested in plant-based alternatives to animal products, he said.
Plant-based milk consumption is expected to continue growing in the coming years, according to Mintel research, with more options available than ever and more consumers opting for a diet that includes both dairy and non-dairy milk.
A 2023 report by Ernst & Young for Protein Industries Canada projected that the plant-based dairy market will reach US$51.3 billion in 2035, at a compound annual growth rate of 9.5 per cent.
Because of this growth opportunity, even well-established dairy or plant-based companies are stepping up their game.
It’s been more than three decades since Saint-Hyacinthe, Que.-based Natura first launched a line of soy beverages. Over the years, the company has rolled out new products to meet rising demand, and earlier this year launched a line of oat beverages that it says are the only ones with a stamp of approval from Celiac Canada.
Competition is tough, said owner and founder Nick Feldman — especially from large American brands, which have the money to ensure their products hit shelves across the country.
Natura has kept growing, though, with a focus on using organic ingredients and localized production from raw materials.
“We’re maybe not appealing to the mass market, but we’re appealing to the natural consumer, to the organic consumer,” Feldman said.
Amlani said brands are increasingly advertising the simplicity of their ingredient lists. She’s also noticing more companies offering different kinds of products, such as coffee creamers.
Companies are also looking to stand out through eye-catching packaging and marketing, added Amlani, and by competing on price.
Besides all the companies competing for shelf space, there are many different kinds of plant-based milk consumers can choose from, such as almond, soy, oat, rice, hazelnut, macadamia, pea, coconut and hemp.
However, one alternative in particular has enjoyed a recent, rapid ascendance in popularity.
“I would say oat is the big up-and-coming product,” said Feldman.
Mintel’s report found the share of Canadians who say they buy oat milk has quadrupled between 2019 and 2023 (though almond is still the most popular).
“There seems to be a very nice marriage of coffee and oat milk,” said Feldman. “The flavour combination is excellent, better than any other non-dairy alternative.”
The beverage’s surge in popularity in cafés is a big part of why it’s ascending so quickly, said Gregoire — its texture and ability to froth makes it a good alternative for lattes and cappuccinos.
It’s also a good example of companies making a strong “use case” for yet another new entrant in a competitive market, he said.
Amid the long-standing brands and new entrants, there’s another — perhaps unexpected — group of players that has been increasingly investing in plant-based milk alternatives: dairy companies.
For example, Danone has owned the Silk and So Delicious brands since an acquisition in 2014, and long-standing U.S. dairy company HP Hood LLC launched Planet Oat in 2018.
Lactalis Canada also recently converted its facility in Sudbury, Ont., to manufacture its new plant-based Enjoy! brand, with beverages made from oats, almonds and hazelnuts.
“As an organization, we obviously follow consumer trends, and have seen the amount of interest in plant-based products, particularly fluid beverages,” said Mark Taylor, president and CEO of Lactalis Canada, whose parent company Lactalis is the largest dairy products company in the world.
The facility was a milk processing plant for six decades, until Lactalis Canada began renovating it in 2022. It now manufactures not only the new brand, but also the company’s existing Sensational Soy brand, and is the company’s first dedicated plant-based facility.
“We’re predominantly a dairy company, and we’ll always predominantly be a dairy company, but we see these products as complementary,” said Taylor.
It makes sense that major dairy companies want to get in on plant-based milk, said Gregoire. The dairy business is large — a “cash cow,” if you will — but not really growing, while plant-based products are seeing a boom.
“If I’m looking for avenues of growth, I don’t want to be left behind,” he said.
Gregoire said there’s a potential for consumers to get confused with so many options, which is why it’s so important for brands to find a way to differentiate themselves, whether it’s with taste, health, or how well the drink froths for a latte.
Competition in a more crowded market is challenging, but Taylor believes it results in better products for consumers.
“It keeps you sharp, and it forces you to be really good at what you’re doing. It drives innovation,” he said.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Sept. 15, 2024.