News
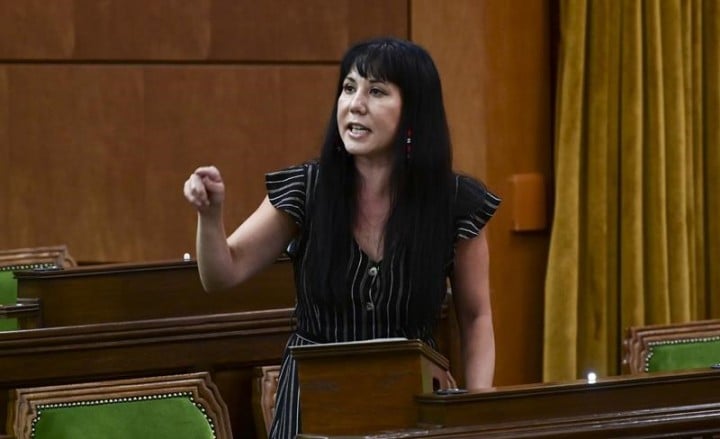
After Pope called residential schools ‘genocide,’ House of Commons should too: NDP MP Leah Gazan

|
|
OTTAWA — A New Democrat member of Parliament said Tuesday she hopes all of her colleagues will recognize the residential school system as genocide, now that Pope Francis has used the term.
Leah Gazan, who represents Winnipeg Centre, tried last year to get unanimous consent from MPs in the House of Commons to press the Canadian government to call what unfolded inside residential schools a genocide.
Her motion referred to the United Nations convention on genocide adopted in 1948, which defines genocide as killing members of a group, causing them serious physical or mental harm, placing them under conditions to destroy them, imposing measures to prevent births or forcibly transferring children to another group.
Gazan said at the time that Canada’s residential school policy met all five criteria, but some voices in the House of Commons said “no,” so her motion requiring unanimous consent failed.
“Having the experience of residential school survivors continually up for debate is another act of violence,” Gazan, a member of Wood Mountain Lakota Nation,said in an interview Tuesday.
“We need to be mindful of that.”
The 2015 final report from the Truth and Reconciliation Commission of Canada labelled what happened inside residential schools a “cultural genocide,” but some Indigenous leaders have since said it needs to be called a genocide, without the qualifying adjective.
During his six-day visit to Canada last week, Pope Francis apologized multiple times for the “evil” of what happened inside residential schools. But it was not until the Pope was asked about it by reporters on the flight back to Rome that he said he considered it to be a genocide.
Francis said he felt “genocide” was a technical term, when asked why he did not say it in Canada.
In a statement Tuesday, Crown-Indigenous Relations Minister Marc Miller’s office said it was encouraged “that Pope Francis’ thoughts evolved over the course of his trip.”
“He heard poignant, painful and direct testimony from survivors and their family members as they courageously shared their truth,” it said.
More than 150,000 First Nations, Métis and Inuit children were forced to attend these institutions, which the federal government funded and different churches operated for over a century. The Catholic Church ran the majority of the residential schools in Canada.
Thousands of Indigenous adults who were sent there as children have reported rampant physical, sexual and emotional abuse, along with neglect and malnutrition. The National Centre for Truth and Reconciliation maintains a memorial register for students who died at residential schools and that number is now at 4,120 children.
Gazan presented her motion in June 2021, not long after the Tk’emlúps te Secwépemc Nation announced that ground-penetrating radar had located what appeared to be the remains of about 200 children buried on the site of a former residential school in Kamloops, B.C.
She said she is now planning to present another motion, but is still thinking about what it should say while the House of Commons is on its summer break.
“I hope that, you know, particularly members of Parliament who are really committed to reconciliation, committed to justice, will finally recognize what happened in residential schools for exactly what it was, which was a genocide.
“It’s time for Parliament to acknowledge it as a genocide.”
The Native Women’s Association of Canada said there is much left to do following the papal tour and apology.
“That starts with the government recognizing that what happened to Indigenous children in this country’s Indian Residential Schools was a genocide,” its CEO, Lynne Groulx, said in a statement, adding it was unfortunate Gazan’s motion failed.
“That means it is now up to the government to formally recognize this genocide in Parliament when sittings resume in the fall.”
Upon the discovery of unmarked graves last year, Prime Minister Justin Trudeau said he continues to accept the conclusion from the 2019 inquiry into missing and murdered Indigenous women and girls that “what happened amounts to genocide.”
Conservative interim leader Candice Bergen has not yet responded to a request for comment from The Canadian Press about whether she sees the residential school system as a genocide.
Some of those running for the party’s permanent job did.
“Residential schools were a monstrous attack on Indigenous people and an odious intrusion of the state and the church into the lives of innocent people,” leadership candidate Pierre Poilievre said in a statement.
He pointed to the fact that both the inquiry into missing and murdered Indigenous women and the Truth and Reconciliation Commission of Canada used the terms “genocide” and “cultural genocide.”
“I accept and agree with these findings.”
A spokeswoman for ex-Quebec premier Jean Charest said he agreed with the finding that residential schools amounted to a “cultural genocide.”
Rural Ontario MP and leadership contestant Scott Aitchison said Pope Francis’ recognition of the system as a genocide “is an important step in reconciliation.”
Leslyn Lewis’ campaign declined to provide comment and Roman Baber did not respond.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Aug. 2, 2022.
Stephanie Taylor, The Canadian Press
News
Canada Child Benefit payment on Friday | CTV News – CTV News Toronto



More money will land in the pockets of Canadian families on Friday for the latest Canada Child Benefit (CCB) installment.
The federal government program helps low and middle-income families struggling with the soaring cost of raising a child.
Canadian citizens, permanent residents, or refugees who are the primary caregivers for children under 18 years old are eligible for the program, introduced in 2016.
The non-taxable monthly payments are based on a family’s net income and how many children they have. Families that have an adjusted net income under $34,863 will receive the maximum amount per child.
For a child under six years old, an applicant can annually receive up to $7,437 per child, and up to $6,275 per child for kids between the ages of six through 17.
That translates to up to $619.75 per month for the younger cohort and $522.91 per month for the older group.
The benefit is recalculated every July and most recently increased 6.3 per cent in order to adjust to the rate of inflation, and cost of living.
To apply, an applicant can submit through a child’s birth registration, complete an online form or mail in an application to a tax centre.
The next payment date will take place on May 17.
News
Capital gains tax change draws ire from some Canadian entrepreneurs worried it will worsen brain drain – CBC.ca
A chorus of Canadian entrepreneurs and investors is blasting the federal government’s budget for expanding a tax on the rich. They say it will lead to brain drain and further degrade Canada’s already poor productivity.
In the 2024 budget unveiled Tuesday, Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland said the government would increase the inclusion rate of the capital gains tax from 50 per cent to 67 per cent for businesses and trusts, generating an estimated $19 billion in new revenue.
Capital gains are the profits that individuals or businesses make from selling an asset — like a stock or a second home. Individuals are subject to the new changes on any profits over $250,000.
The government estimates that the changes would impact 40,000 individuals (or 0.13 per cent of Canadians in any given year) and 307,000 companies in Canada.
However, some members of the business community say that expanding the taxable amount will devastate productivity, investment and entrepreneurship in Canada, and might even compel some of the country’s talent and startups to take their business elsewhere.
Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland unveiled the government’s 2024 federal budget, with spending targeted at young voters and a plan to raise capital gains taxes for some of the wealthiest Canadians.
Benjamin Bergen, president of the Council of Canadian Innovators (CCI), said the capital gains tax has overshadowed parts of the federal budget that the business community would otherwise be excited about.
“There were definitely some other stars in the budget that were interesting,” he said. “However, the … capital gains piece really is the sun, and it’s daylight. So this is really the only thing that innovators can see.”
The CCI has written and is circulating an open letter signed by more than 1,000 people in the Canadian business community to Trudeau’s government asking it to scrap the tax change.
Shopify CEO Tobi Lütke and president Harley Finkelstein also weighed in on the proposed hike on X, formerly known as Twitter.
We need to be doing everything we can to turn Canada into the best place for entrepreneurs to build 🇨🇦<br><br>What’s proposed in the federal budget will do the complete opposite. Innovators and entrepreneurs will suffer and their success will be penalized — this is not a wealth tax,…
—@harleyf
Former finance minister Bill Morneau said his successor’s budget disincentivizes businesses from investing in the country’s innovation sector: “It’s probably very troubling for many investors.”
Canada’s productivity — a measure that compares economic output to hours worked — has been relatively poor for decades. It underperforms against the OECD average and against several other G7 countries, including the U.S., Germany, U.K. and Japan, on the measure.
Bank of Canada senior deputy governor Carolyn Rogers sounded the alarm on Canada’s lagging productivity in a speech last month, saying the country’s need to increase the rate had reached emergency levels, following one of the weakest years for the economy in recent memory.
The government said it was proposing the tax change to make life more affordable for younger generations and fund efforts to boost housing supply — and that it would support productivity growth.
A challenge for investors, founders and workers
The change could have a chilling effect for several reasons, with companies already struggling to access funding in a high interest rate environment, said Bergen.
He questioned whether investors will want to fund Canadian companies if the government’s taxation policies make it difficult for those firms to grow — and whether founders might just pack up.
The expanded inclusion rate “is just one of the other potential concerns that firms are going to have as they’re looking to grow their companies.”


He said the rejigged tax is also an affront to high-skilled workers from low-innovation sectors who might have taken the risk of joining a startup for the opportunity, even taking a lower wage on the chance that a firm’s stock options grow in value.
But Lindsay Tedds, an associate economics professor at the University of Calgary, said the tax change is one of the most misunderstood parts of the federal budget — and that its impact on the country’s talent has been overstated.
“This is not a major innovation-biting tax change treatment,” Tedds said. “In fact, when you talk to real grassroots entrepreneurs that are setting up businesses, tax rates do not come into their decision.”
As for productivity, Tedds said Canadians might see improvements in the long run “to the degree that some of our productivity problems are driven by stresses like housing affordability, access to child care, things like that.”
‘One foot on the gas, one foot on the brake’
Some say the government is sending mixed messages to entrepreneurs by touting tailored tax breaks — like the Canada Entrepreneurs’ Incentive, which reduces the capital gains inclusion rate to 33 per cent on a lifetime maximum of $2 million — while introducing measures they say would dampen investment and innovation.
“They seem to have one foot on the gas, one foot on the brake on the very same file,” said Dan Kelly, president of the Canadian Federation of Independent Business.
Some business groups are worried that new capital gains tax changes could hurt economic growth. But according to Small Business Minister Rechie Valdez, most Canadians won’t be impacted by that change — and it’s a move to create fairness.
A founder may be able to sell their successful company with a lower capital gains treatment than otherwise possible, he said.
“At the same time, though, big chunks of it may be subject to a higher rate of capital gains inclusion.”
Selling a company can fund an individual’s retirement, he said, which is why it’s one of the first things founders consider when they think about capital gains.
Mainstreet NS7:03Ottawa is proposing a hike to capital gains tax. What does that mean?
Tuesday’s federal budget includes nearly $53 billion in new spending over the next five years with a clear focus on affordability and housing. To help pay for some of that new spending, Ottawa is proposing a hike to the capital gains tax. Moshe Lander, an economics lecturer at Concordia University, joins host Jeff Douglas to explain.
Dennis Darby, president and CEO of Canadian Manufacturers & Exporters, says he was disappointed by the change — and that it sends the wrong message to Canadian industries like his own.
He wants to see the government commit to more tax credit proposals like the Canada Carbon Rebate for Small Businesses, which he said would incentivize business owners to stay and help make Canada competitive with the U.S.
“We’ve had a lot of difficulties attracting investment over the years. I don’t think this will make it any better.”
Tech titan says change will only impact richest of the rich


Toronto tech entrepreneur Ali Asaria will be one of those subject to the expanded capital gains inclusion rate — but he says it’s only fair.
“It’s going to really affect the richest of the rich people,” Asaria, CEO of open source platform Transformer Lab and founder of well.ca, told CBC News.
“The capital gains exemption is probably the largest tax break that I’ve ever received in my life,” he said. “So I know a lot about what that benefit can look like, but I’ve also always felt like it was probably one of the most unfair parts of the tax code today.”
While Asaria said Canada needs to continue encouraging talent to take risks and build companies in the country, taxation policies aren’t the most major problem.
“I think that the biggest central issue to the reason why people will leave Canada is bigger issues, like housing,” he said.
“How do we make it easier to live in Canada so that we can all invest in ourselves and invest in our companies? That’s a more important question than, ‘How do we help the top 0.13 per cent of Canadians make more money?'”
News
Canada Child Benefit payment on Friday | CTV News – CTV News Toronto



More money will land in the pockets of Canadian families on Friday for the latest Canada Child Benefit (CCB) installment.
The federal government program helps low and middle-income families struggling with the soaring cost of raising a child.
Canadian citizens, permanent residents, or refugees who are the primary caregivers for children under 18 years old are eligible for the program, introduced in 2016.
The non-taxable monthly payments are based on a family’s net income and how many children they have. Families that have an adjusted net income under $34,863 will receive the maximum amount per child.
For a child under six years old, an applicant can annually receive up to $7,437 per child, and up to $6,275 per child for kids between the ages of six through 17.
That translates to up to $619.75 per month for the younger cohort and $522.91 per month for the older group.
The benefit is recalculated every July and most recently increased 6.3 per cent in order to adjust to the rate of inflation, and cost of living.
To apply, an applicant can submit through a child’s birth registration, complete an online form or mail in an application to a tax centre.
The next payment date will take place on May 17.
-
Media20 hours ago
DJT Stock Rises. Trump Media CEO Alleges Potential Market Manipulation. – Barron's
-
Media22 hours ago
Trump Media alerts Nasdaq to potential market manipulation from 'naked' short selling of DJT stock – CNBC
-
Investment20 hours ago
Private equity gears up for potential National Football League investments – Financial Times
-
Real eState12 hours ago
Botched home sale costs Winnipeg man his right to sell real estate in Manitoba – CBC.ca
-
News19 hours ago
Canada Child Benefit payment on Friday | CTV News – CTV News Toronto
-
Business21 hours ago
Gas prices see 'largest single-day jump since early 2022': En-Pro International – Yahoo Canada Finance
-
Art24 hours ago
Enter the uncanny valley: New exhibition mixes AI and art photography – Euronews
-



 Politics21 hours ago
Politics21 hours agoIran news: Canada, G7 urge de-escalation after Israel strike – CTV News