As Canadians wake up to news that Donald Trump will return to the White House, the president-elect’s protectionist stance is casting a spotlight on what effect his second term will have on Canada-U.S. economic ties.
Some Canadian business leaders have expressed worry over Trump’s promise to introduce a universal 10 per cent tariff on all American imports.
A Canadian Chamber of Commerce report released last month suggested those tariffs would shrink the Canadian economy, resulting in around $30 billion per year in economic costs.
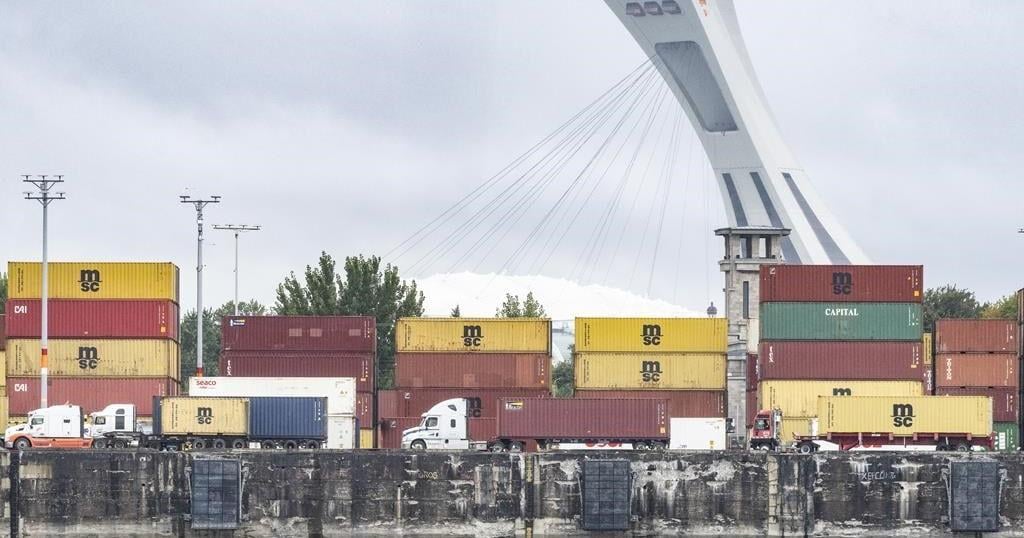
More than 77 per cent of Canadian exports go to the U.S.
Canada’s manufacturing sector faces the biggest risk should Trump push forward on imposing broad tariffs, said Canadian Manufacturers and Exporters president and CEO Dennis Darby. He said the sector is the “most trade-exposed” within Canada.
“It’s in the U.S.’s best interest, it’s in our best interest, but most importantly for consumers across North America, that we’re able to trade goods, materials, ingredients, as we have under the trade agreements,” Darby said in an interview.
“It’s a more complex or complicated outcome than it would have been with the Democrats, but we’ve had to deal with this before and we’re going to do our best to deal with it again.”
American economists have also warned Trump’s plan could cause inflation and possibly a recession, which could have ripple effects in Canada.
It’s consumers who will ultimately feel the burden of any inflationary effect caused by broad tariffs, said Darby.
“A tariff tends to raise costs, and it ultimately raises prices, so that’s something that we have to be prepared for,” he said.
“It could tilt production mandates. A tariff makes goods more expensive, but on the same token, it also will make inputs for the U.S. more expensive.”
A report last month by TD economist Marc Ercolao said research shows a full-scale implementation of Trump’s tariff plan could lead to a near-five per cent reduction in Canadian export volumes to the U.S. by early-2027, relative to current baseline forecasts.
Retaliation by Canada would also increase costs for domestic producers, and push import volumes lower in the process.
“Slowing import activity mitigates some of the negative net trade impact on total GDP enough to avoid a technical recession, but still produces a period of extended stagnation through 2025 and 2026,” Ercolao said.
Since the Canada-United States-Mexico Agreement came into effect in 2020, trade between Canada and the U.S. has surged by 46 per cent, according to the Toronto Region Board of Trade.
With that deal is up for review in 2026, Canadian Chamber of Commerce president and CEO Candace Laing said the Canadian government “must collaborate effectively with the Trump administration to preserve and strengthen our bilateral economic partnership.”
“With an impressive $3.6 billion in daily trade, Canada and the United States are each other’s closest international partners. The secure and efficient flow of goods and people across our border … remains essential for the economies of both countries,” she said in a statement.
“By resisting tariffs and trade barriers that will only raise prices and hurt consumers in both countries, Canada and the United States can strengthen resilient cross-border supply chains that enhance our shared economic security.”
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Nov. 6, 2024.