Economy
Can China handle the economic turmoil of its viral outbreak? – Aljazeera.com

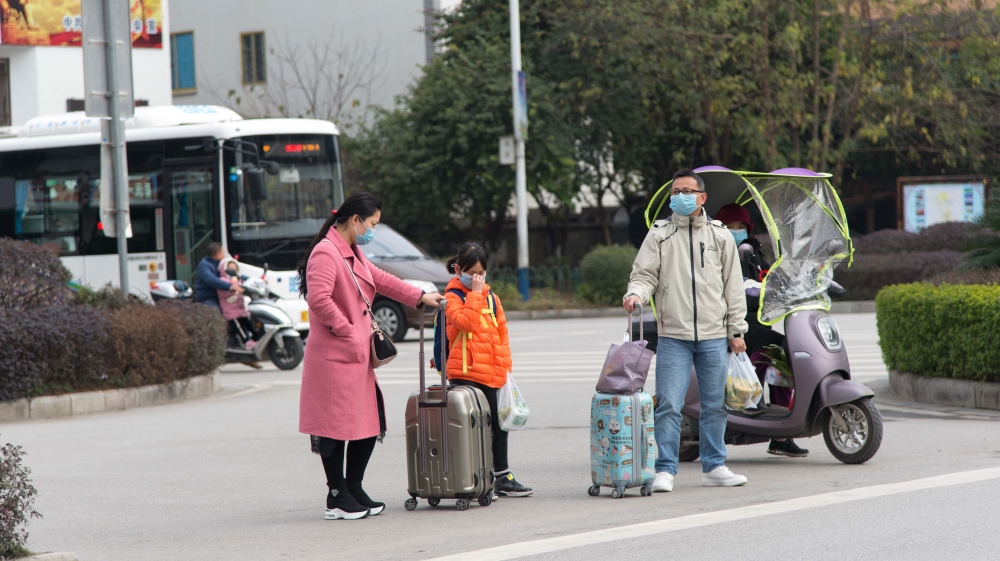
Shenzhen, China – For Eppu Makipaa, some quick thinking in late January as a new coronavirus swept through China and many other countries helped avert a significant disruption at the company he works for.
Makipaa – a sales engineer and manager at Lifa Air International, a Finnish company that makes air purifiers and protective masks in a factory with 3,000 workers in Dongguan in southern China – opted to keep manufacturing operations going even as most Chinese companies shut down for the Lunar New Year holiday that started on January 25.
“We decided to keep our factory open a little bit longer because we had some new product launch events going on,” Makipaa told Al Jazeera. “We saw the situation with the virus and decided that we would [only] close the factory for less than 24 hours [for the holiday].”
This was a challenge, as most of the workers wanted to return to their hometowns and villages for the holiday. But for the staff who stayed, doing so proved to be a blessing.
“We were able to find enough workers who were willing to work, and, of course, a lot of those people were from areas that are now affected by a virus,” Makipaa said.
He says his workers find it “important and meaningful” that they are able to help the fight against the virus by supplying medical equipment for those who need it the most.
But for many other firms in China, the coronavirus outbreak has been far more painful. And while the broader economic effect on China is still hard to gauge and likely yet to fully play out, some economists are already warning the public to brace for a sharp slowdown.
The number of infections has now exceeded those during the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) epidemic of 2002-2003 with the number of deaths climbing rapidly.
The latest outbreak brought the country to a standstill in the middle of the Chinese New Year holiday which was originally scheduled to last from January 24 to 30.
But central government authorities officially extended the holiday nationally through to February 2. Key economic powerhouses like Guangdong province in southern China have indicated that key sectors such as municipal utilities, public transport, medical supply producers, supermarkets, food production, and logistics should resume work first, with all others allowed to start after February 9.
‘A huge challenge’
Thousands of flights, trains, and long-distance buses have been cancelled or disrupted while road traffic has become snarled by checkpoints for body temperature scans and by villagers blocking roads to keep outsiders away.
Millions of Chinese, many back in their rural hometowns for the holiday, have been staying indoors much of the time for fear of catching the virus or by order in over a dozen cities locked down in Hubei province, where the outbreak originated in the provincial capital of Wuhan in late December.
Wuhan is a key transport, steel and industrial hub between all four points on the compass for China, often compared with Chicago in the United States due to its geographic importance.
In the coming days, many of those millions home for the holidays will attempt to return to major cities where they work. They will try to travel by air, rail and highway, potentially creating a transport logjam worse than the usual travel problems at this time of year.
Once at their destination, they will need to navigate roadblocks, quarantined residences and offices, temperature scans at supermarkets and on the metro and enforced mask usage. And with mask supplies stretched, that could be difficult.
Many business owners say their most pressing concern right now is ensuring the health of their workers as they return from the Spring Festival if they can.
“It will be a huge challenge,” Everest Zhao, CEO of electronic cigarette company VooPoo, said of the possible labour shortages ahead.
“Right now we’re more concerned with helping the country through this and how to keep our colleagues safe,” Zhao told Al Jazeera.
China had already been experiencing its slowest economic growth rates in nearly 30 years before the coronavirus outbreak, as the United States engaged it in a trade war. Gross domestic product (GDP) – the total value of all finished goods and services produced in a country – expanded by 6 percent in the fourth quarter of last year compared with the same period in 2018.
Zhang Ming, an economist at the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences – a top government think-tank – estimates that the outbreak could cut first-quarter 2020 GDP growth by about 1 percentage point.
“GDP growth in the first quarter of 2020 could be about 5.0 percent, and we cannot rule out the possibility of falling below 5.0 percent,” Zhang was quoted as saying in Caijing magazine.
‘Freaking out’
With infection rates continuing to rise, the big unknown remains precisely how long and severe the coronavirus outbreak will be.
“The economic effect of this Wuhan coronavirus will depend on how long the outbreak lasts and its impacts, such as deaths and disabilities that result from it,” Yun Jiang, co-editor of the China Neican policy newsletter who formerly worked in the Australian government. “As the infection number is still rising, it appears unlikely that the outbreak will stop any time soon.”
Jiang told Al Jazeera that the most immediate impacts will be on tourism, retail and airlines already hurt in China and increasingly around the world as carriers halt flights to the country.
“This [crisis] will make China reaching its GDP target of around 6 percent in 2020 more challenging,” Jiang said. “On the other hand, it may provide the Chinese Government with a quite reasonable excuse to miss its target.”
Chinese authorities are rolling out measures to help the worst-affected areas of the economy.
For instance, The People’s Bank of China (PBOC), the central bank, is urging commercial lenders to ease credit terms for companies finding it hard to meet their debt obligations.
“During the period of epidemic control, key enterprises that produce, transport and sell important medical supplies and daily necessities should be put on a list, and the PBC will provide them with credit support at favorable rates,” the central bank said in a statement on Monday.
But it is not clear whether such measures will be enough. Analysts say much of the economic damage could be caused by panic over the potential effect of the virus, rather than actual deaths or infections of people.
“Our clients are freaking out,” Dan Harris, partner at US law firm Harris Bricken, told Al Jazeera. “The big fear is that people will not be going back to work.”
But psychology aside, logistical challenges due to measures to contain the spread of the virus are causing very real headaches for manufacturers and the broader economy.
School start times could be another factor in key areas like Guangdong where the start is expected to be pushed back from February 17. The longer children have to stay at home, the longer the disruptions for families trying to figure out how to navigate their return to the cities, factories and offices where they work.
“The teachers put on unpaid leave are starting to realise that there is no end in sight and they too are freaking out because many of them don’t have enough money to fly out or to pay their rent, and their employers are going radio silent,” Harris said.
Financial markets reopened on Monday for the first time since the Lunar New Year holidays and for anyone invested in stocks or commodities, it was probably a day to forget.
Mainland China’s Shanghai Composite Index of leading stocks fell by 7.9 percent, its biggest one-day drop since 2015. The sell-off had been expected, as markets elsewhere had already reacted to the rapidly spreading virus. But still, economists say it reflects the economic pain that could lie ahead.
Massive impact
“I think the impact could be massive,” said Francesco Sisci, an Italian Sinologist who has been in Beijing since the late 1980s and who witnessed the SARS outbreak of 2003.
“There was a boost in productivity once SARS was dealt with, but I think this time is different,” Sisci told Al Jazeera by phone.
China’s already-slowing economy and its continuing trade war with the US leave the country vulnerable to a protracted economic crisis, Sisci said.
“Whether the Chinese financial institutions have enough firepower to support the market, that is the most immediate challenge and that will impact the economy,” he said. “I would say that is what we have to pay attention to.”
On Monday, the PBOC tried to ease the panic selling by injecting 1.2 trillion yuan ($171bn) into the market. But it is not clear whether this will be enough to support the broader economy in the coming weeks and months.
Sisci also says a political crisis could be forthcoming regarding the upcoming National People’s Congress (NPC) meetings which start each year on March 5, where officials from across the country converge in Beijing to craft policy for the coming year.
The 2020 meetings are particularly important as leaders will chart the path forward for the next five-year economic and development plans with the 14th Five-Year Plan set to start from 2021.
Looking back to 2003, Sisci says that year’s NPC meetings helped accelerate the spread of the SARS virus.
“That was the occasion when SARS spread to Beijing, because all the [provincial] delegations go to Beijing,” Sisci said. “So in a sense, they have to deal with this outbreak by the end of February.”
Additional research assistance provided by Zhong Yunfan.
Economy
Charting the Global Economy: Fed Delay Recalibrates All Rates – BNN Bloomberg

(Bloomberg) — Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell signaled US central bankers will wait longer to cut borrowing costs following a series of surprisingly high inflation readings, which reduces room for easier policy around the world.
Global finance chiefs convening in Washington for the International Monetary Fund-World Bank spring meetings are sweating the strength of the US economy, as elevated interest rates and a strong dollar force other currencies lower and complicate plans to bring down borrowing costs.
Meanwhile, an escalation of the conflict in the Middle East is raising concerns of a wider regional war that could send oil prices over $100 a barrel.
Here are some of the charts that appeared on Bloomberg this week on the latest developments in the global economy, geopolitics and markets:
World
The high tide for global interest rates has passed, but respite for the world economy may be limited as policymakers stay wary at the threat of inflation. Powell’s latest pivot creates a quandary for central bankers around the world.
The IMF inched up its expectations for global economic growth this year, citing strength in the US and some emerging markets, while warning the outlook remains cautious amid persistent inflation and geopolitical risks.
The increasingly hopeful economic story of 2024 so far is that of a world headed for a soft landing. Unfortunately that same world is also becoming more dangerous, divided, indebted and unequal.
US
US retail sales rose by more than forecast in March and the prior month was revised higher, showcasing resilient consumer demand that keeps fueling a surprisingly strong economy. So-called control-group sales — which are used to calculate gross domestic product — jumped by the most since the start of last year.
As President Joe Biden this week hailed America’s booming economy as the strongest in the world during a reelection campaign tour of battleground-state Pennsylvania, global finance chiefs convening in Washington had a different message: cool it. While the world’s largest economy is helping support global growth, it also means the US is “slightly overheated,” the IMF’s Kristalina Georgieva said — thanks in part to Washington’s fiscal stance, with the budget gap pushing toward 7% of GDP.
Emerging Markets
Israel reportedly struck back at Iran on Friday morning, following days of frantic diplomacy from the US and European nations in which they tried to convince Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu not to respond too aggressively, if at all, to the Iranian attack. Their main concern is to avoid a wider war in a region already roiled by the Israel-Hamas conflict and which could send oil prices above $100 a barrel.
India forecast an above-normal monsoon this year, raising optimism that ample rains will spur crop output and economic growth, as well as prompt the government to ease curbs on exports of wheat, rice and sugar. Forecast of a normal monsoon bodes well for easing food costs, and headline consumer price inflation eventually, said Anubhuti Sahay, head of economic research, South Asia, at Standard Chartered Plc.
Europe
European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen is unleashing a barrage of trade restrictions against China as she seeks to follow through on a pledge to make the EU a more relevant political player on the global stage. It’s in the area of clean tech where the EU is most fervently fighting to stave off competition from cheap Chinese imports of everything from EVs to solar panels.
UK inflation slowed less than expected last month as fuel prices crept higher, prompting traders to further unwind bets on how many interest rate cuts the Bank of England will deliver this year.
Asia
China reported faster-than-expected economic growth in the first quarter – along with some numbers that suggest things are set to get tougher in the rest of the year. Gross domestic product climbed 5.3% in the period, accelerating slightly from the previous quarter and beating estimates. But much of the bounce came in the first two months of the year. In March, growth in retail sales slumped and industrial output fell short of forecasts, suggesting challenges on the horizon.
–With assistance from John Ainger, Irina Anghel, Enda Curran, Shawn Donnan, James Hirai, Rajesh Kumar Singh, John Liu, Lucille Liu, Eric Martin, Alberto Nardelli, Tom Orlik (Economist), Pratik Parija, Zoe Schneeweiss, Craig Stirling and Fran Wang.
©2024 Bloomberg L.P.
Economy
Bobby Kennedy And The Ownership Economy – Forbes


In recent decades, populist presidential campaigns have arisen from the left (Bernie Sanders) and the right (Pat Buchanan). Both of these campaigns had limited appeal across the political spectrum or even attempted to engage Americans of diverse political views.
Over the past year in his independent presidential campaign, Bobby Kennedy Jr. has sought to bring together members of both major political parties, with a form of economic populism that expands ownership opportunities. In contrast to Sanders, Kennedy’s goal is not to grow the welfare state or state control over the economy. His economic populism is free-market oriented, aimed at building a broader property-owning middle class. It is aimed at widening the number of worker-owners with a stake in the market system, through their ownership of homes, businesses, employee stock and profit sharing, and other assets.
Whether Kennedy’s economic strategies can achieve the goals of ownership and the middle class he has set, remains to be determined. But his “ownership economy” is one that should be discussed and debated. Currently, it is largely ignored by the legacy media—or subsumed by the parade of articles speculating about of how many votes he will “take away” from President Biden or President Trump.
I wrote about Kennedy’s heterodox jobs program late last summer. In the eight months since, he has sharpened his jobs agenda, and connected it to a broader platform of worker ownership. It is time to revisit the campaign’s economic themes, briefly noting three of the subjects Kennedy often speaks about in 2024: the abandonment of vast sections of the blue collar economy, low wage workforces, and the marginalization of small businesses.
Abandonment Of Blue Collar Economy
“Compensate the losers” is the way that political scientist Ruy Teixeira characterizes the Democratic Party approach to the blue collar economy since the 1990s. According to this approach, workers whose jobs are impacted by environmental policies (oil and gas workers) or trade polices (heavy manufacturing workers) will be retrained for jobs in the green economy or in advanced manufacturing or even as white collar fields like information technology (the oil worker as coder). Since the 1990s a vast network of dislocated worker programs and rapid-response programs have arisen and are prominent under the Biden administration.
As might be expected, retraining hasn’t proved so easy in practice. One example: here in Northern California, the Marathon Oil
MRO
refinery closed in October 2020, laying off 345 workers. The federal and state government immediately came in with the union offering a range of retraining and job placement services. A study by the UC Berkeley Labor Center found that even a year after closure, a quarter of the workers were still unemployed. Those that were employed earned a median of $12 less than their previous jobs. Other studies similarly have identified the gap between theories of skills transference and re-employment and the realities for most blue collar workers—including the realties of alternative energy jobs today that usually pay considerably less than oil and gas jobs.
Each refinery closure or plant closure has its own business dynamics, and in many cases, like the Marathon Oil refinery, the facility will not be able to avoid closing. Re-employment cannot be avoided. Kennedy has spoken of improving the re-training and re-employment process for laid off workers, implementing best practices in retraining with the participation of unions and worker organizations.
function loadConnatixScript(document)
if (!window.cnxel)
window.cnxel = ;
window.cnxel.cmd = [];
var iframe = document.createElement(‘iframe’);
iframe.style.display = ‘none’;
iframe.onload = function()
var iframeDoc = iframe.contentWindow.document;
var script = iframeDoc.createElement(‘script’);
script.src = ‘//cd.elements.video/player.js’ + ‘?cid=’ + ’62cec241-7d09-4462-afc2-f72f8d8ef40a’;
script.setAttribute(‘defer’, ‘1’);
script.setAttribute(‘type’, ‘text/javascript’);
iframeDoc.body.appendChild(script);
;
document.head.appendChild(iframe);
loadConnatixScript(document);
(function()
function createUniqueId()
return ‘xxxxxxxx-xxxx-4xxx-yxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx’.replace(/[xy]/g, function(c) 0x8);
return v.toString(16);
);
const randId = createUniqueId();
document.getElementsByClassName(‘fbs-cnx’)[0].setAttribute(‘id’, randId);
document.getElementById(randId).removeAttribute(‘class’);
(new Image()).src = ‘https://capi.elements.video/tr/si?token=’ + ’44f947fb-a5ce-41f1-a4fc-78dcf31c262a’ + ‘&cid=’ + ’62cec241-7d09-4462-afc2-f72f8d8ef40a’;
cnxel.cmd.push(function ()
cnxel(
playerId: ’44f947fb-a5ce-41f1-a4fc-78dcf31c262a’,
playlistId: ‘4ed6c4ff-975c-4cd3-bd91-c35d2ff54d17’,
).render(randId);
);
)();
Manufacturing jobs as a share of total jobs have been in decline for the past four decades, and even as he urges trade policies for reshoring jobs, Kennedy recognizes that manufacturing going forward will be a limited part of the blue collar economy. The blue collar jobs of the future will increasingly be in the trades and services. Kennedy has enlisted “Dirty Jobs” host Mike Rowe to highlight the importance of the trades, and identify policies that can improve conditions and wages for the trades. Among these policies: a greater share of the higher education federal budget redirected from colleges into training in the trades, and support for the workers who seek to enter and remain in the trades.
Improving the economic position of blue collar workers also means expanding employee stock ownership and profit sharing. While worker cooperatives have failed to gain traction in America, forms of employee stock ownership and profit sharing are being implemented in companies with significant blue collar workforces, such as Procter & Gamble
PG
, Southwest Airlines
LUV
and Chobani. Kennedy poses the challenge: Let’s have workers-as-owners more fully share in the economic success of their employers.
Inflation Impact On Low Wage Workers
In nearly all of his talks on the economy, Kennedy addresses the issue of affordability, and how inflation has undercut wages of America’s lower wage workforces. He posts regularly on the increased cost of food, transportation, and housing, the financial strains on working class and middle class families, the number of workers who live paycheck to paycheck. When the March national jobs report was issued earlier this month, he noted the slowdown in year-over wage growth (at 4.1% the lowest year-over increase since 2021) and the increase in part-time jobs.
Kennedy recognizes that many of the low wage workforces are in such sectors as long-term care, retail, and hospitality, in which profit margins for employers are tight, and employers have limited flexibility individually to raise wages. Kennedy continues his calls for a higher minimum wage, reducing health care costs, strengthening protections and benefits for workers in the gig economy. He urges a reconsideration of trade and tax policies and the need for immigration policies that secure the nation’s borders. Kennedy’s strict border policies reflect both the “humanitarian crisis” he sees with the drug cartels and migrants, as well as the impact of unchecked immigration on the wages of low wage service and production workers.
Home ownership has a special place in Kennedy’s ownership economy, as part of bringing more workers into the middle class, and he has stepped up his advocacy on home ownership. Across society, widespread home ownership stabilizes communities, promotes civic involvement, serves as a hedge against social disorders.
Small And Independent Businesses
During the pandemic, Kennedy warned that economic lockdowns were devastating the small business economy. Today, in a regular series of podcasts on small business, he highlights the ongoing small business struggles. Just this past week, the National Federation of Independent Business, the nation’s largest small business organization, released a survey showing small business optimism is at its lowest level since 2012.
As with home ownership, Kennedy characterizes widespread small business ownership in terms of the social values as well as the values to the individual owners. Small business drives enterprise and service to others, in providing goods and services that customers value and will pay for. It drives job creation, including for individuals who do not fit easily into larger employment venues. A Kennedy Administration will prioritize rebuilding the small business economy, particularly in rural and inner city communities.
Kennedy’s small business agenda goes beyond a laundry list of small business grant and loan programs. As with the wage question, Kennedy seeks to tie a vibrant small business economy to underlying trade and tax policies. He also seeks to tie this economy to reforms in federal government procurement policies, which he describes as ineffectual.
Economic Challenges And Alternatives
The middle class society and economy of the 1950s that Kennedy grew up in and is central to his worldview was the product of unique economic forces and America’s dominant position in the post-World War II period. There is no way to get back to it, and recreating it will be more difficult than in the past, in the now global economy, and with rapidly advancing technologies.
But a broad middle class of worker-owners, is the right goal, and private sector ownership the right approach. People may find Kennedy’s strategies insufficiently detailed or unrealistic or even counterproductive. But Kennedy raises thoughtful challenges and alternatives to the economic platforms of the two main parties—just as he is raising serious challenges on a range of other issues.
Economy
Biden's Hot Economy Stokes Currency Fears for the Rest of World – Bloomberg


As Joe Biden this week hailed America’s booming economy as the strongest in the world during a reelection campaign tour of battleground-state Pennsylvania, global finance chiefs convening in Washington had a different message: cool it.
The push-back from central bank governors and finance ministers gathering for the International Monetary Fund-World Bank spring meetings highlight how the sting from a surging US economy — manifested through high interest rates and a strong dollar — is ricocheting around the world by forcing other currencies lower and complicating plans to bring down borrowing costs.
-
Media23 hours ago
DJT Stock Rises. Trump Media CEO Alleges Potential Market Manipulation. – Barron's
-
Investment23 hours ago
Private equity gears up for potential National Football League investments – Financial Times
-
Real eState15 hours ago
Botched home sale costs Winnipeg man his right to sell real estate in Manitoba – CBC.ca
-
News22 hours ago
Canada Child Benefit payment on Friday | CTV News – CTV News Toronto
-
Business24 hours ago
Gas prices see 'largest single-day jump since early 2022': En-Pro International – Yahoo Canada Finance
-
Business15 hours ago
Dow Jones Rises But S&P, Nasdaq Fall; Nvidia, SMCI Flash Sell Signals As Bitcoin's Fourth Halving Arrives – Investor's Business Daily
-



 Science20 hours ago
Science20 hours agoMarine plankton could act as alert in mass extinction event: UVic researcher – Langley Advance Times
-
Media24 hours ago
Three drones downed after explosions heard in Iran’s Isfahan: State media – Al Jazeera English







