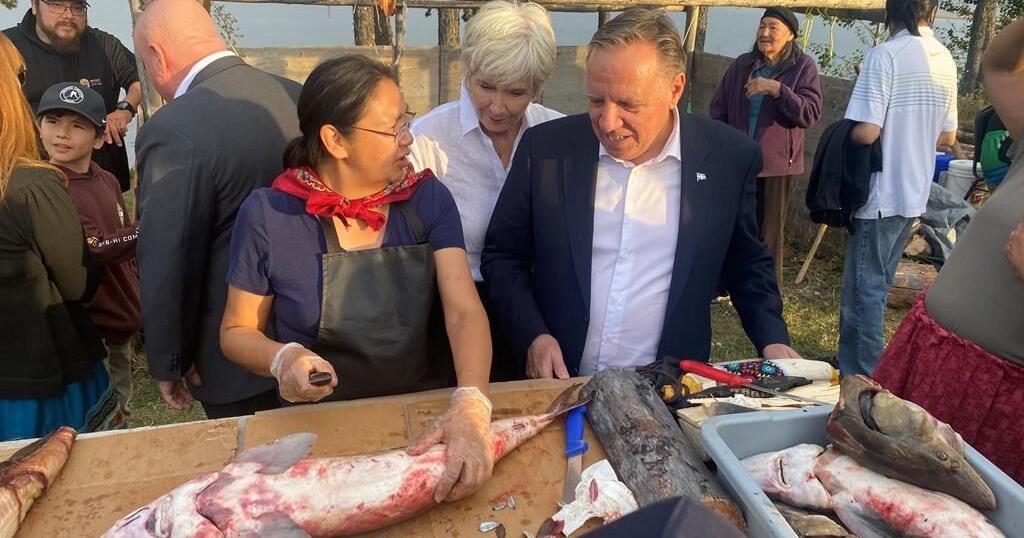
For the first time in their history, members of the Cree community of Nemaska received a visit from a sitting Quebec premier on Sunday and were able to share first-hand the story of how they were displaced by a hydroelectric project in the 1970s.
François Legault was greeted in Nemaska by men and women who arrived by canoe to re-enact the founding of their new village in the Eeyou Istchee James Bay region, in northern Quebec, 47 years ago. The community was forced in the early 1970s to move from its original location because members were told it would be flooded as part of the Nottaway-Broadback-Rupert hydro project.
The reservoir was ultimately constructed elsewhere, but by then the members of the village had already left for other places, abandoning their homes and many of their belongings in the process.
George Wapachee, co-author of the book “Going Home,” said community members were “relocated for nothing.”
“We didn’t know what the rights were, or who to turn to,” he said in an interview. “That turned us into refugees and we were forced to abandon the life we knew.”
Nemaska’s story illustrates the challenges Legault’s government faces as it looks to build new dams to meet the province’s power needs, which are anticipated to double by 2050. Legault has promised that any new projects will be developed in partnership with Indigenous people and have “social acceptability,” but experts say that’s easier said than done.
François Bouffard, an associate professor of electrical engineering at McGill University, said the earlier era of hydro projects were developed without any consideration for the Indigenous inhabitants living nearby.
“We live in a much different world now,” he said. “Any kind of hydro development, no matter where in Quebec, will require true consent and partnership from Indigenous communities.” Those groups likely want to be treated as stakeholders, he added.
Securing wider social acceptability for projects that significantly change the landscape — as hydro dams often do — is also “a big ask,” he said. The government, Bouchard added, will likely focus on boosting capacity in its existing dams, or building installations that run off river flow and don’t require flooding large swaths of land to create reservoirs.
Louis Beaumier, executive director of the Trottier Energy Institute at Polytechnique Montreal, said Legault’s visit to Nemaska represents a desire for reconciliation with Indigenous people who were traumatized by the way earlier projects were carried about.
Any new projects will need the consent of local First Nations, Beaumier said, adding that its easier to get their blessing for wind power projects compared to dams, because they’re less destructive to the environment and easier around which to structure a partnership agreement.
Beaumier added that he believes it will be nearly impossible to get the public — Indigenous or not — to agree to “the destruction of a river” for a new dam, noting that in recent decades people have come to recognize rivers as the “unique, irreplaceable riches” that they are.
Legault’s visit to northern Quebec came on Sept. 15, when the community gathers every year to remember the founding of the “New Nemaska,” on the shores of Lake Champion in the heart of the boreal forest, some 1,500 kilometres from Montreal. Nemaska Chief Clarence Jolly said the community invited Legault to a traditional feast on Sunday, and planned to present him with Wapachee’s book and tell him their stories.
The book, published in 2022 along with Susan Marshall, is filled with stories of Nemaska community members. Leaving behind sewing machines and hunting dogs, they were initially sent to two different villages, Wapachee said.
In their new homes, several of them were forced to live in “deplorable conditions,” and some were physically and verbally abused, he said. The new village of Nemaska was only built a few years later, in 1977.
“At this time, families were losing their children to prison-schools,” he said, in reference to the residential school system. “Imagine the burden of losing your community as well.”
Thomas Jolly, a former chief, said he was 15 years old when he was forced to leave his village with all his belongings in a single bag.
Meeting Legault was important “because have to recognize what happened and we have to talk about the repercussions that the relocation had on people,” he said, adding that those effects are still felt today.
Earlier Sunday, Legault was in the Cree community of Eastmain, where he participated in the official renaming of a hydro complex in honour of former premier Bernard Landry. At the event, Legault said he would follow the example of his late predecessor, who oversaw the signing of the historic “Paix des Braves” agreement between the Quebec government and the Cree in 2002.
He said there is “significant potential” in Eeyou Istchee James Bay, both in increasing the capacity of its large dams and in developing wind power projects.
“Obviously, we will do that with the Cree,” he said.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Sept. 16, 2024.


























Comments