Economy
Four weeks of war scar Russia's economy – Reuters
Russian Rouble coin is seen on a broken glass and displayed on the Russian flag in this illustration taken, February 24, 2022. REUTERS/Dado Ruvic/Illustration/File Photo
LONDON, March 24 (Reuters) – Russia’s invasion of Ukraine on Feb. 24 sparked sweeping sanctions that ripped the country out of the global financial fabric and sent its economy reeling.
A month on, Russia’s currency has lost a large part of its value and its bonds and stocks have been ejected from indexes. Its people are experiencing economic pain that is likely to last for years to come.
Below are five charts showing how the past month has changed Russia’s economy and its global standing:
Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.com
ECONOMIC PAIN
In 2020, Russia was the world’s 11th-largest economy, according to the World Bank. But by the end of this year, it may rank no higher than No. 15, based on the end-February rouble exchange rate, according to Jim O’Neill, the former Goldman Sachs economist who coined the BRIC acronym to describe the four big emerging economies Brazil, Russia, India and China.
Recession looks inevitable. Economists polled by the central bank predicted an 8% contraction this year and for inflation to reach 20%. read more
Forecasts from economists outside Russia are even gloomier. The Institute of International Finance predicts a 15% contraction in 2022, followed by a 3% contraction in 2023.
“Altogether, our projections mean that current developments are set to wipe out the economic gains of roughly fifteen years,” the IIF said in a note.
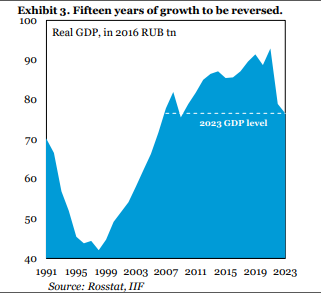

INFLATION BUSTING TURNS TO DUST
Since taking office in 2013, central bank governor Elvira Nabiullina’s biggest triumph was curbing inflation from 17% in 2015 to just above 2% in early-2018. As price pressures rose in the post-pandemic months, she defied industrialists by raising interest rates eight months straight.
Nabiullina also resisted calls in 2014-2015 for capital controls to stem outflows following the annexation of Crimea.
But those achievements have been torn to shreds in less than a month.
Annual price growth has accelerated to 14.5% and should surpass 20%, five times the target. Households’ inflation expectations for the year ahead are above 18%, an 11-year high.
While panic-buying accounts for some of this, rouble weakness may keep price pressures elevated read more .
With Russia’s reserves warchest frozen overseas, Nabiullina was forced to more than double interest rates on Feb. 28 and introduce capital controls. The central bank now expects inflation back at target only in 2024.
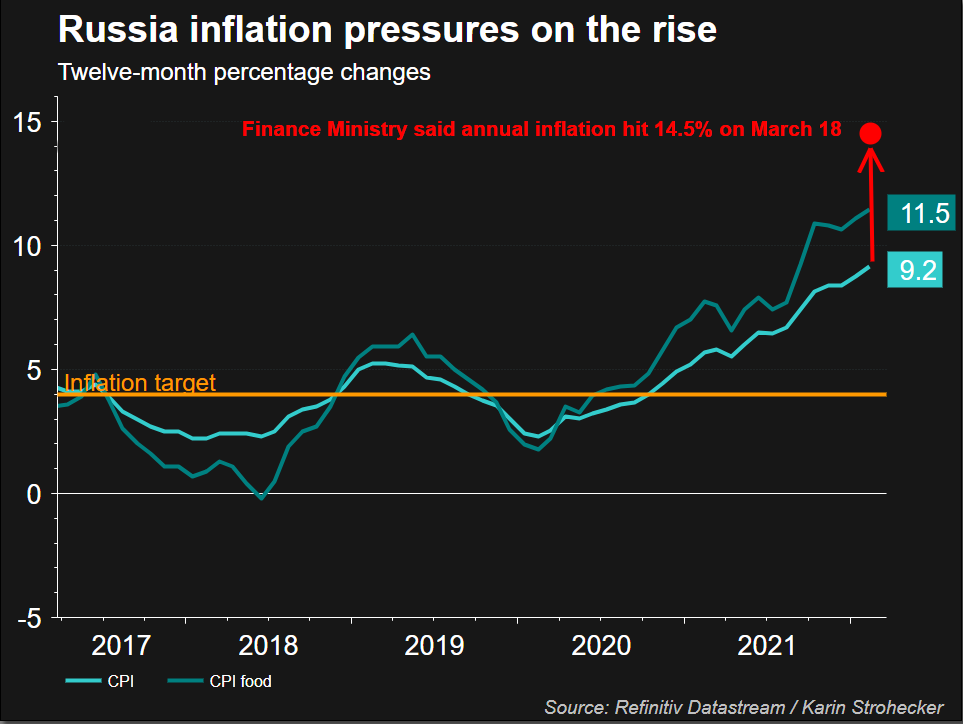

INDEX ELIMINATION
Sanctions are forcing index providers to eject Russia from benchmarks used by investors to funnel billions of dollars into emerging markets.
JPMorgan (.JPMEGDR) and MSCI are among those that have announced they are removing Russia from their bond and stock indexes respectively (.MSCIEF).
Russia’s standing in these indexes had already taken a hit following the first set of Western sanctions in 2014 and then in 2018, following the poisoning of a former Russian spy in Britain and investigations into alleged Russian meddling in the 2016 U.S. elections.
On March 31, Russia’s weighting will be dialled to zero by nearly all major index providers.
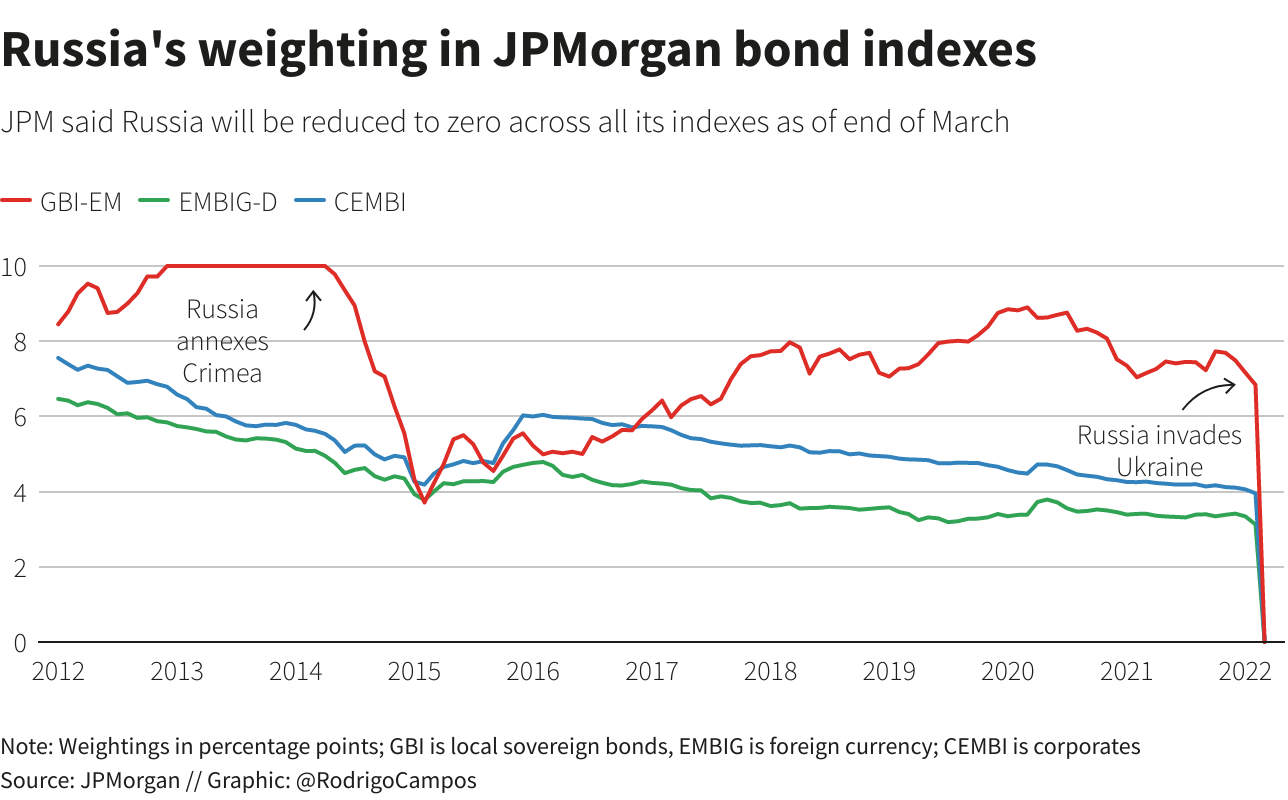

RATINGS RUPTURE
When Russian troops stormed into Ukraine, their country had a coveted “investment grade” credit rating with the three major agencies S&P Global, Moody’s and Fitch.
That allowed it to borrow relatively cheaply and a sovereign debt default appeared a distant prospect.
In the past four weeks, Russia has suffered the largest cuts ever made to a sovereign credit score. It is now at the bottom of the ratings ladder, flagging an imminent risk of default.

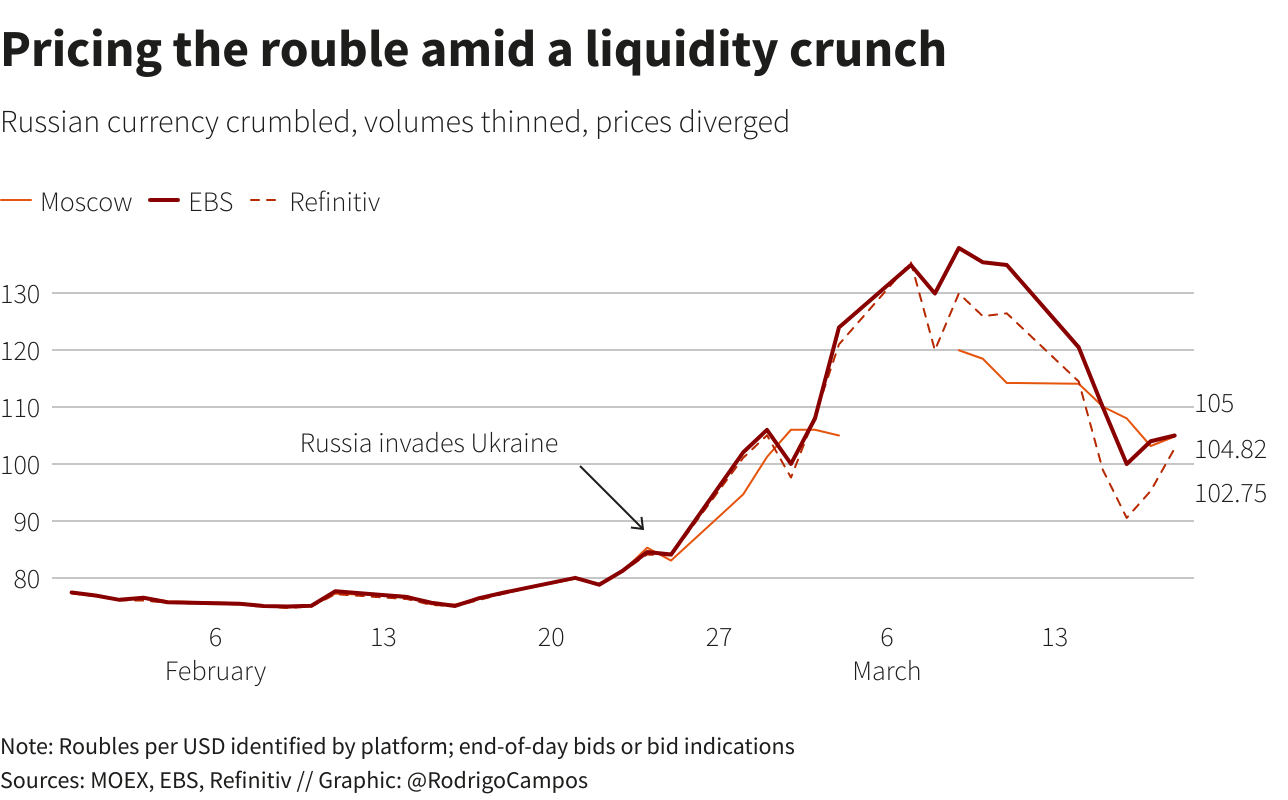
ROUBLE TROUBLE
A month ago, the rouble’s one-year average exchange rate sat at 74 per dollar. Trading on different platforms showed the ample liquidity and tight bid/ask spreads expected for a major emerging market currency.
All that has changed. With the central bank bereft of a large portion of it hard currency reserves, the rouble plunged to record lows of more than 120 per dollar locally. In offshore trade it fell as low as 160 to the greenback.
As liquidity dried up and bid/ask spreads widened, pricing the rouble has become haphazard. The exchange rate is yet to find a balance on- and offshore.

Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.com
Reporting by Karin Strohecker, Sujata Rao, Rodrigo Campos and Marc Jones; Editing by Sam Holmes
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles.
Economy
Opinion: Higher capital gains taxes won't work as claimed, but will harm the economy – The Globe and Mail
Canada’s Prime Minister Justin Trudeau and Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland hold the 2024-25 budget, on Parliament Hill in Ottawa, on April 16.Patrick Doyle/Reuters
Alex Whalen and Jake Fuss are analysts at the Fraser Institute.
Amid a federal budget riddled with red ink and tax hikes, the Trudeau government has increased capital gains taxes. The move will be disastrous for Canada’s growth prospects and its already-lagging investment climate, and to make matters worse, research suggests it won’t work as planned.
Currently, individuals and businesses who sell a capital asset in Canada incur capital gains taxes at a 50-per-cent inclusion rate, which means that 50 per cent of the gain in the asset’s value is subject to taxation at the individual or business’s marginal tax rate. The Trudeau government is raising this inclusion rate to 66.6 per cent for all businesses, trusts and individuals with capital gains over $250,000.
The problems with hiking capital gains taxes are numerous.
First, capital gains are taxed on a “realization” basis, which means the investor does not incur capital gains taxes until the asset is sold. According to empirical evidence, this creates a “lock-in” effect where investors have an incentive to keep their capital invested in a particular asset when they might otherwise sell.
For example, investors may delay selling capital assets because they anticipate a change in government and a reversal back to the previous inclusion rate. This means the Trudeau government is likely overestimating the potential revenue gains from its capital gains tax hike, given that individual investors will adjust the timing of their asset sales in response to the tax hike.
Second, the lock-in effect creates a drag on economic growth as it incentivizes investors to hold off selling their assets when they otherwise might, preventing capital from being deployed to its most productive use and therefore reducing growth.
Budget’s capital gains tax changes divide the small business community
And Canada’s growth prospects and investment climate have both been in decline. Canada currently faces the lowest growth prospects among all OECD countries in terms of GDP per person. Further, between 2014 and 2021, business investment (adjusted for inflation) in Canada declined by $43.7-billion. Hiking taxes on capital will make both pressing issues worse.
Contrary to the government’s framing – that this move only affects the wealthy – lagging business investment and slow growth affect all Canadians through lower incomes and living standards. Capital taxes are among the most economically damaging forms of taxation precisely because they reduce the incentive to innovate and invest. And while taxes on capital gains do raise revenue, the economic costs exceed the amount of tax collected.
Previous governments in Canada understood these facts. In the 2000 federal budget, then-finance minister Paul Martin said a “key factor contributing to the difficulty of raising capital by new startups is the fact that individuals who sell existing investments and reinvest in others must pay tax on any realized capital gains,” an explicit acknowledgment of the lock-in effect and costs of capital gains taxes. Further, that Liberal government reduced the capital gains inclusion rate, acknowledging the importance of a strong investment climate.
At a time when Canada badly needs to improve the incentives to invest, the Trudeau government’s 2024 budget has introduced a damaging tax hike. In delivering the budget, Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland said “Canada, a growing country, needs to make investments in our country and in Canadians right now.” Individuals and businesses across the country likely agree on the importance of investment. Hiking capital gains taxes will achieve the exact opposite effect.
Economy
Nigeria's Economy, Once Africa's Biggest, Slips to Fourth Place – Bloomberg


Nigeria’s economy, which ranked as Africa’s largest in 2022, is set to slip to fourth place this year and Egypt, which held the top position in 2023, is projected to fall to second behind South Africa after a series of currency devaluations, International Monetary Fund forecasts show.
The IMF’s World Economic Outlook estimates Nigeria’s gross domestic product at $253 billion based on current prices this year, lagging energy-rich Algeria at $267 billion, Egypt at $348 billion and South Africa at $373 billion.
Economy
IMF Sees OPEC+ Oil Output Lift From July in Saudi Economic Boost – BNN Bloomberg

(Bloomberg) — The International Monetary Fund expects OPEC and its partners to start increasing oil output gradually from July, a transition that’s set to catapult Saudi Arabia back into the ranks of the world’s fastest-growing economies next year.
“We are assuming the full reversal of cuts is happening at the beginning of 2025,” Amine Mati, the lender’s mission chief to the kingdom, said in an interview in Washington, where the IMF and the World Bank are holding their spring meetings.
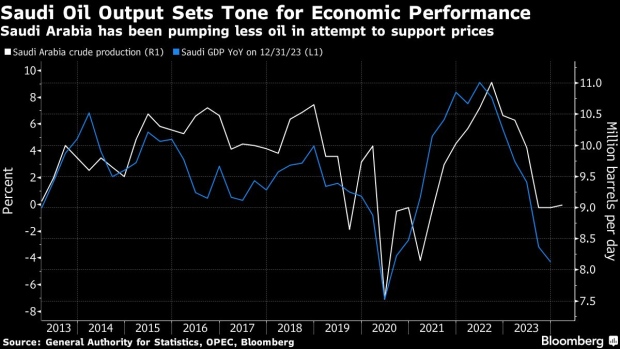
The view explains why the IMF is turning more upbeat on Saudi Arabia, whose economy contracted last year as it led the OPEC+ alliance alongside Russia in production cuts that squeezed supplies and pushed up crude prices. In 2022, record crude output propelled Saudi Arabia to the fastest expansion in the Group of 20.
Under the latest outlook unveiled this week, the IMF improved next year’s growth estimate for the world’s biggest crude exporter from 5.5% to 6% — second only to India among major economies in an upswing that would be among the kingdom’s fastest spurts over the past decade.
The fund projects Saudi oil output will reach 10 million barrels per day in early 2025, from what’s now a near three-year low of 9 million barrels. Saudi Arabia says its production capacity is around 12 million barrels a day and it’s rarely pumped as low as today’s levels in the past decade.
Mati said the IMF slightly lowered its forecast for Saudi economic growth this year to 2.6% from 2.7% based on actual figures for 2023 and the extension of production curbs to June. Bloomberg Economics predicts an expansion of 1.1% in 2024 and assumes the output cuts will stay until the end of this year.
Worsening hostilities in the Middle East provide the backdrop to a possible policy shift after oil prices topped $90 a barrel for the first time in months. The Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries and its allies will gather on June 1 and some analysts expect the group may start to unwind the curbs.
After sacrificing sales volumes to support the oil market, Saudi Arabia may instead opt to pump more as it faces years of fiscal deficits and with crude prices still below what it needs to balance the budget.
Saudi Arabia is spending hundreds of billions of dollars to diversify an economy that still relies on oil and its close derivatives — petrochemicals and plastics — for more than 90% of its exports.
Restrictive US monetary policy won’t necessarily be a drag on Saudi Arabia, which usually moves in lockstep with the Federal Reserve to protect its currency peg to the dollar.
Mati sees a “negligible” impact from potentially slower interest-rate cuts by the Fed, given the structure of the Saudi banks’ balance sheets and the plentiful liquidity in the kingdom thanks to elevated oil prices.
The IMF also expects the “non-oil sector growth momentum to remain strong” for at least the next couple of years, Mati said, driven by the kingdom’s plans to develop industries from manufacturing to logistics.
The kingdom “has undertaken many transformative reforms and is doing a lot of the right actions in terms of the regulatory environment,” Mati said. “But I think it takes time for some of those reforms to materialize.”
©2024 Bloomberg L.P.
-



 Investment23 hours ago
Investment23 hours agoUK Mulls New Curbs on Outbound Investment Over Security Risks – BNN Bloomberg
-



 Sports21 hours ago
Sports21 hours agoAuston Matthews denied 70th goal as depleted Leafs lose last regular-season game – Toronto Sun
-
Media2 hours ago
DJT Stock Rises. Trump Media CEO Alleges Potential Market Manipulation. – Barron's
-
Business20 hours ago
BC short-term rental rules take effect May 1 – CityNews Vancouver
-
Media4 hours ago
Trump Media alerts Nasdaq to potential market manipulation from 'naked' short selling of DJT stock – CNBC
-
Art19 hours ago
Collection of First Nations art stolen from Gordon Head home – Times Colonist
-



 Investment20 hours ago
Investment20 hours agoBenjamin Bergen: Why would anyone invest in Canada now? – National Post
-



 Tech22 hours ago
Tech22 hours agoSave $700 Off This 4K Projector at Amazon While You Still Can – CNET





