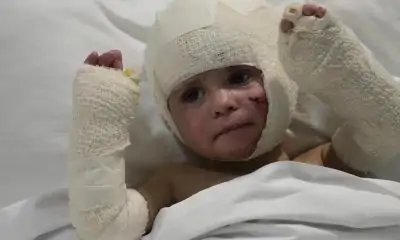
A B.C. teen has a suspected case of H5N1 avian flu — the first known human to acquire the virusin Canada.
The provincial government said on the weekend that B.C.’s chief veterinarian and public health teamsare still investigating the source of exposure, but that it’s “very likely” an animal or bird.
Human-to-human transmission is very rare, but as cases among animals rise, many experts are worried the virus could develop that ability.
The teen was being treated at BC Children’s Hospital on Saturday. The provincial health officer said there were no updates on the patient Monday.
“I’m very concerned, obviously, for the young person who was infected,” said Dr. Matthew Miller, director of the Michael G. DeGroote Institute for Infectious Disease Research at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ont.
Miller, who is also the co-director of the Canadian Pandemic Preparedness Hub, said there have been several people infected with H5N1 in the U.S.,and almost all were livestock workers.
In an email to The Canadian Press on Monday afternoon, the Public Health Agency of Canada said “based on current evidence in Canada, the risk to the general public remains low at this time.”
WHAT IS H5N1?
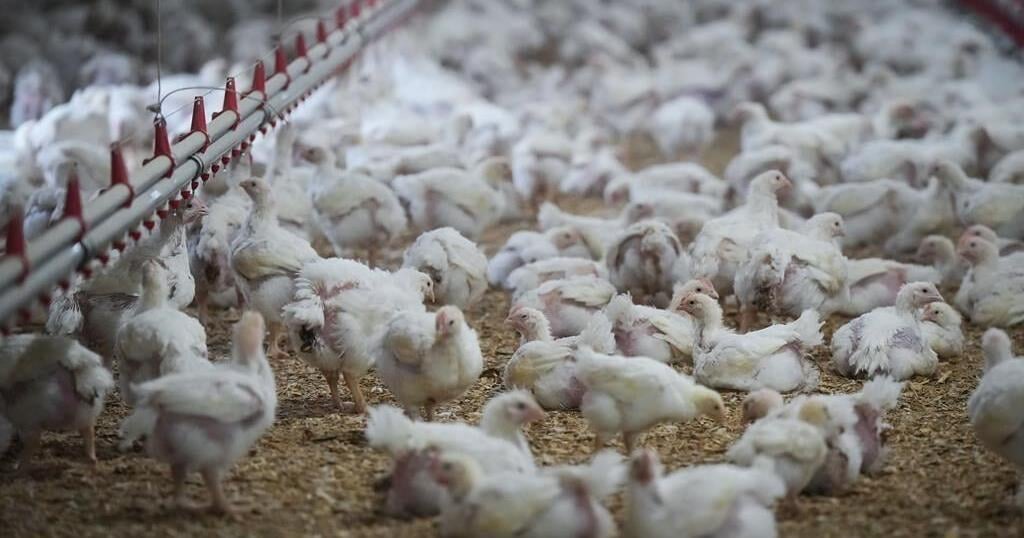
H5N1 is a subtype of influenza A virus that has mainly affected birds, so it’s also called “bird flu” or “avian flu.” The H5N1 flu that has been circulating widely among birds and cattle this year is one of the avian flu strains known as Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) because it causes severe illness in birds, including poultry.
According to the World Health Organization, H5N1 has been circulating widely among wild birds and poultry for more than two decades. The WHO became increasingly concerned and called for more disease surveillance in Feb. 2023 after worldwide reports of the virus spilling over into mammals.
HOW COMMON IS INFECTION IN HUMANS?
H5N1 infections in humans are rare and “primarily acquired through direct contact with infected poultry or contaminated environments,” the WHO’s website says.
Prior to the teen in B.C., Canada had one human case of H5N1 in 2014 and it was “travel-related,” according to the Public Health Agency of Canada.
As of Nov. 8, there have been 46 confirmed human cases of H5N1 in the U.S. this year, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says. There is an ongoing outbreak among dairy cattle, “sporadic” outbreaks in poultry farms and “widespread” cases in wild birds, the CDC website says.
There has been no sign of human-to-human transmission in any of the U.S. cases.
But infectious disease and public health experts are worried that the more H5N1 spreads between different types of animals, the bigger the chance it can mutateand spread more easily between humans.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF H5N1?
Although H5N1 causes symptoms similar to seasonal flu, such as cough, fever, shortness of breath, headache, muscle pain, sore throat, runny nose and fatigue, the strain also has key features that can cause other symptoms.
Unlike seasonal flu, most of the people infected in the U.S. have had conjunctivitis, or “pink-eye,” said Miller.
One reason for that is likely that many have been dairy cattle workers.
“At these milking operations, it’s easy to get contamination on your hands and rub your eyes. We touch our face like all the time without even knowing it,” he said.
“Also, those operations can produce droplets or aerosols, both during milking and during cleaning that can get into the eye relatively easily.”
But the other reason for the conjunctivitis seen in H5N1 cases is that the strain binds to receptors in the eye, Miller said.
While seasonal flu binds to receptors in the upper respiratory tract, H5N1 also binds to receptors in the lower respiratory tract, he said.
“That’s a concern … because if the virus makes its way down there, those lower respiratory infections tend to be a lot more severe. They tend to lead to more severe outcomes, like pneumonias for example, that can cause respiratory distress,” Miller said.
WILL THE FLU VACCINE PROTECT AGAINST H5N1?
We don’t know “with any degree of certainty,” whether the seasonal flu vaccine could help prevent infection with H5N1, said Miller.
Although there’s no data yet, it’s quite possible that it could help prevent more severe disease once a person is infected, he said.
That’s because the seasonal flu vaccine contains a component of H1N1 virus, which “is relatively closely related to H5N1.”
“So the immunity that might help protect people against H5N1 is almost certainly conferred by either prior infection with or prior vaccination against H1N1 viruses that circulate in people,” Miller said.
HOW ELSE CAN I PROTECT MYSELF?
The Public Health Agency of Canada said as a general precaution, people shouldn’t handle live or dead wild birds or other wild animals, and keep pets away from sick or dead animals.
Those who work with animals or in animal-contaminated places should take personal protective measures, the agency said.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Nov. 11, 2024.
Canadian Press health coverage receives support through a partnership with the Canadian Medical Association. CP is solely responsible for this content.