SAN FRANCISCO (AP) — Artificial intelligence‘s recent rise to the forefront of business has left most office workers wondering how often they should use the technology and whether a computer will eventually replace them.
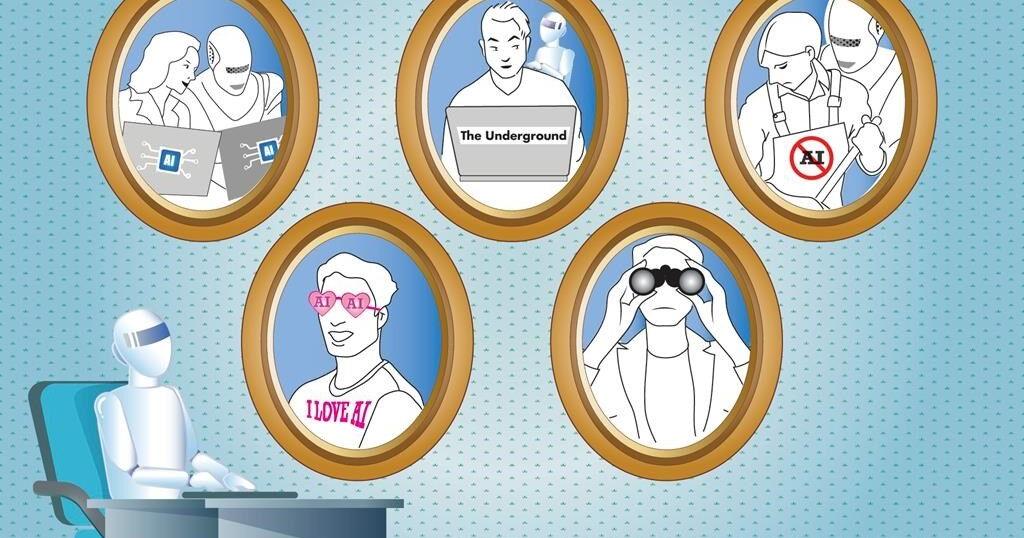
Those were among the highlights of a recent study conducted by the workplace communications platform Slack. After conducting in-depth interviews with 5,000 desktop workers, Slack concluded there are five types of AI personalities in the workplace: “The Maximalist” who regularly uses AI on their jobs; “The Underground” who covertly uses AI; “The Rebel,” who abhors AI; “The Superfan” who is excited about AI but still hasn’t used it; and “The Observer” who is taking a wait-and-see approach.
Only 50% of the respondents fell under the Maximalist or Underground categories, posing a challenge for businesses that want their workers to embrace AI technology. The Associated Press recently discussed the excitement and tension surrounding AI at work with Christina Janzer, Slack’s senior vice president of research and analytics.
Q: What do you make about the wide range of perceptions about AI at work?
A: It shows people are experiencing AI in very different ways, so they have very different emotions about it. Understanding those emotions will help understand what is going to drive usage of AI. If people are feeling guilty or nervous about it, they are not going to use it. So we have to understand where people are, then point them toward learning to value this new technology.
Q: The Maximalist and The Underground both seem to be early adopters of AI at work, but what is different about their attitudes?
A: Maximalists are all in on AI. They are getting value out of it, they are excited about it, and they are actively sharing that they are using it, which is a really big driver for usage among others.
The Underground is the one that is really interesting to me because they are using it, but they are hiding it. There are different reasons for that. They are worried they are going to be seen as incompetent. They are worried that AI is going to be seen as cheating. And so with them, we have an opportunity to provide clear guidelines to help them know that AI usage is celebrated and encouraged. But right now they don’t have guidelines from their companies and they don’t feel particularly encouraged to use it.
Overall, there is more excitement about AI than not, so I think that’s great We just need to figure out how to harness that.
Q: What about the 19% of workers who fell under the Rebel description in Slack’s study?
A: Rebels tend to be women, which is really interesting. Three out of five rebels are women, which I obviously don’t like to see. Also, rebels tend to be older. At a high level, men are adopting the technology at higher rates than women.
Q: Why do you think more women than men are resisting AI?
A: Women are more likely to see AI as a threat, more likely to worry that AI is going to take over their jobs. To me, that points to women not feeling as trusted in the workplace as men do. If you feel trusted by your manager, you are more likely to experiment with AI. Women are reluctant to adopt a technology that might be seen as a replacement for them whereas men may have more confidence that isn’t going to happen because they feel more trusted.
Q: What are some of the things employers should be doing if they want their workers to embrace AI on the job?
A: We are seeing three out of five desk workers don’t even have clear guidelines with AI, because their companies just aren’t telling them anything, so that’s a huge opportunity.
Another opportunity to encourage AI usage in the open. If we can create a culture where it’s celebrated, where people can see the way people are using it, then they can know that it’s accepted and celebrated. Then they can be inspired.
The third thing is we have to create a culture of experimentation where people feel comfortable trying it out, testing it, getting comfortable with it because a lot of people just don’t know where to start. The reality is you can start small, you don’t have to completely change your job. Having AI write an email or summarize content is a great place to start so you can start to understand what this technology can do.
Q: Do you think the fears about people losing their jobs because of AI are warranted?
A: People with AI are going to replace people without AI.