Here is a roundup of stories from CanadaNewsMedia designed to bring you up to speed…
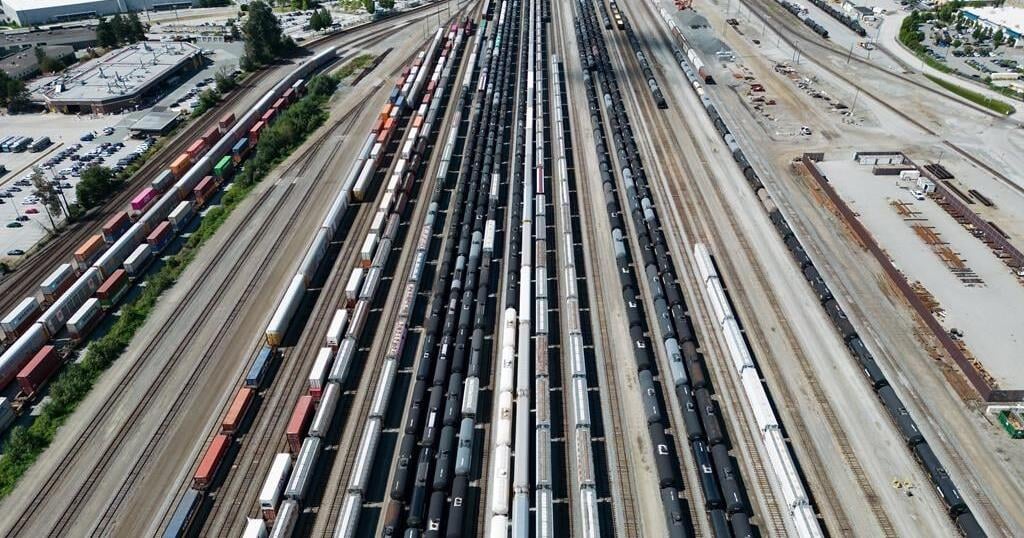
Rail shutdown begins as workers locked out
In a first for Canada, freight traffic on its two largest railways has simultaneously ground to a halt, threatening to upend supply chains trying to move forward from pandemic-related disruptions and a port strike last year.
In the culmination of months of increasingly bitter negotiations, Canadian National Railway Co. and Canadian Pacific Kansas City Ltd. locked out 9,300 engineers, conductors and yard workers after the parties failed to agree on a new contract before the midnight deadline.
The impasse also affects tens of thousands of commuters in Toronto, Montreal and Vancouver, whose lines run on CPKC-owned tracks. Without traffic controllers to dispatch them, passenger trains cannot run on those rails.
Pressure from industry groups and government to resolve the bargaining impasse has been mounting for weeks, with calls to hash out a resolution likely to ratchet up further now the work stoppage has begun.
More Canadians hit by extreme weather: poll
A new poll suggests more Canadians are feeling the direct impacts of extreme weather, but that has not changed overall opinions about climate change.
The results from a recent Leger poll suggest more than one in three Canadians have been touched directly by extreme weather such as forest fires, heat waves, floods or tornadoes.
When Leger asked the same question in June 2023, around one in four Canadians indicated they had been impacted by extreme weather.
The previous poll was taken as the record-breaking 2023 wildfire season was just getting underway.
Quebec grapples with ongoing teacher shortage
Quebec is still short nearly four-thousand teachers as students get ready to head back to school next week.
Education Minister Bernard Drainville says an influx of 20,000 new students is putting more strain on the system, which has been struggling with staff shortages for several years.
Unions in Quebec say the province also has thousands of unfilled positions for school daycare workers, special education technicians, psychologists and speech therapists.
School staff say their workloads have increased over the years, and many teachers and support workers don’t want to stay in the education system.
Quebec has turned to non-legally qualified teachers in recent years to help fill the gaps, and a 30-credit fast-track program now exists to certify new teachers more quickly.
Alberta oilpatch policies concern municipalities
Alberta’s United Conservative government is trying to increase production from the province’s declining conventional oil and gas fields at the expense of local tax bases, environmental oversight and the public interest, says the group representing rural municipalities.
Rural Municipalities of Alberta held a town hall meeting earlier this month to discuss the impacts of enacted and upcoming policy changes that they fear will cost them hundreds of millions of tax dollars, weaken rules over failing wells and hamstring regulatory authority.
The group has identified five government policies it fears could harm its members.
It says the relaxing of a ministerial order requiring companies to pay municipal taxes before being able to transfer well licences could see unprofitable wells shifted from one unstable company to another, allowing industry to avoid paying for their cleanup.
Avoid being stranded in a flood: Tips for drivers
Images of cars and SUVs stranded in flooded roadways with water rising past their windows have flashed across news and online feeds this summer as the Greater Toronto Area weathered torrential downpours that caused havoc for drivers in certain areas.
The visuals, and the stories of water rescues that have accompanied them, may have raised questions for motorists on how to best react if they find themselves in similar situations in the future, with emergency services saying there are several steps that can be taken to reduce risks.
“The first approach, of course, is to avoid areas of water,” said Deputy Chief Stephane Malo of Mississauga Fire and Emergency Services, which has had to carry out several water rescues in the city this summer, including 22 this past weekend.
“Vehicles can be stranded in water … and it’s a very hazardous thing for people to be stuck in their car.”
Japanese Canadian newspaper’s online archive saved
More than eighty years ago, Japanese Canadians came together to sustain The New Canadian, the only newspaper specifically for the community that was allowed to be published through the Second World War.
Now the community has come together again — and may have saved the newspaper’s archives from the digital scrap heap.
Supporters say the newspaper that published from 1938 to 2001 was a pillar of the community during the turmoil of the war when Japanese Canadians were interred, stripped of assets and had their patriotism questioned.
The New Canadian’s digital archives had been facing deletion, after Simon Fraser University Library announced recently it would no longer host them on its servers from this fall.
—
This report by The Canadian Press was first published August 22, 2024