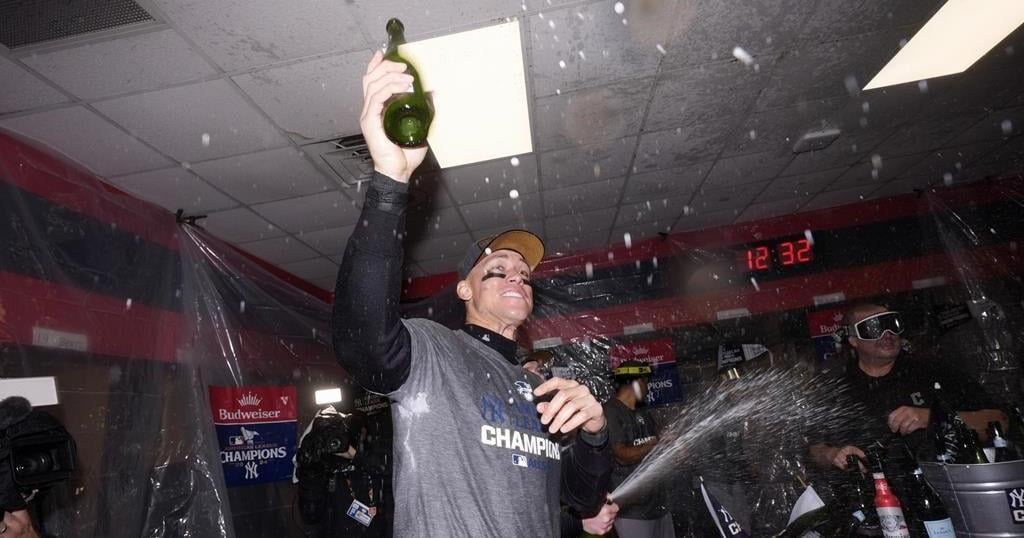
NEW YORK (AP) — For the New York Yankees, the real opening day is World Series Game 1.
A little bubbly for a playoff berth, the AL East, the Division Series and their 41st pennant were just warmups.
World Series rings are the only numbers that count when you are measured not among the living but against the ghosts: Yogi, Joltin’ Joe, the Iron Horse, the Babe and the Mick.
“That’s why we’re here. That’s why I get up every single day. That’s why I put in the work not only at the field but in the offseason, is to just bring a championship home back to the city and back to this team,” Yankees captain Aaron Judge said when spring training started in February.
“It’s been quite a long time since we’ve got to that finish line,” he added, “but I think a lot of the guys and pieces that we’ve added into this room, especially a couple of changes we made in approaches, guys we brought in, it’s all going to push us towards the right direction, which is ultimately being the last team standing.”
The Yankees are in the World Series for the first time since winning title No. 27 in 2009, starting Friday at the Los Angeles Dodgers or in the Bronx against the New York Mets.
A core in its 30s covets a championship as validation as much as accomplishment. Giancarlo Stanton is in his 15th major league season, Gerrit Cole his 12th and Judge his ninth.
Stanton has been restrained in his assessment.
“As far as I’m concerned, we haven’t done nothing,” he said after Game 4 against the Guardians.
Stanton’s edge was visible during Saturday night’s celebration when Gleyber Torres handed him the AL championship trophy, saying “Take the baby. Take the baby.” Stanton cradled the prize and rocked it back and forth — an apparent reference to Josh Naylor’s home run celebration when he connected against Cole in the 2022 ALDS.
Baseball’s winningest tradition is in the players’ faces from the day they arrive at Yankee Stadium. Oversized photos of pinstriped greats line the tunnel leading to the clubhouse. The walls of the locker room corridor are filled with paintings of recent luminaries.
Players don’t have to be reminded that Yogi Berra won 10 titles, Joe DiMaggio nine, Babe Ruth and Mickey Mantle seven each (though only four of Ruth’s were with the Yankees), and Lou Gehrig six. Hall of Famers Derek Jeter and Mariano Rivera, both five-time champions, mingled with the current players in August when the 2009 champions were honored on Old-Timers’ Day.
“What makes the Yankees the Yankees is winning and winning a World Series” said Anthony Volpe, a 23-year-old shortstop who is in his second big league season.
The Yankees missed the playoffs last year for the first time since 2016, skidding to an 82-80 record and narrowly avoiding their first losing season since 1992.
Expectations soared after they obtained Juan Soto from San Diego in December, and he set an attitude when he arrived at spring training wearing a T-shirt that proclaimed: “The Generational Juan Soto.” The free-agent-to-be turned to the dugout and pounded his chest after the Yankees’ signature shot of the postseason thus far, his 10th-inning, three-run homer that won their 41st pennant.
A 50-22 start raised confidence but a 10-23 slide from mid-June through late July sparked skepticism. The acquisition of Jazz Chisholm Jr. from Miami ahead of the trade deadline injected some energy, and New York finished an AL-best 94-68, clinching a playoff berth in Game No. 152 and the AL East in No. 159.
Stanton (.294, five homers, 11 RBIs in the postseason), Soto (.333, three, eight), Judge (two homers, six RBIs despite a .161 average) have provided key hits and Torres has reached leading off in eight of nine postseason games.
Bullpen contributors include Tim Hill (signed in June after he was released by the woeful Chicago White Sox), Jake Cousins (purchased from the White Sox in late March), Tim Mayza (signed in July after he was released by Toronto) and Mark Leiter Jr. (a trade-deadline arrival added to the active roster Friday after Ian Hamilton got hurt).
Aaron Boone reminded players in February to be ready no matter their depth chart status.
“I talked to those guys first day of camp,” the manager recalled Saturday. ”’You’re sitting in here right now, you think, ah, I probably won’t be with the big club this year or whatever.’ I’m like, ‘You might find yourself in the batter’s box or on the mound in the biggest moment of the year, so try and prepare that.’
“And then there’s always the X factors of the trade deadline that happens, but even the other moves like getting Tim Hill and Jake Cousins that have become really significant parts of our bullpen that were in a way cast-offs from other organizations. So you never know how it’s all going to shape up.”
___