OTTAWA – Canada’s inflation rate fell to two per cent last month, finally hitting the Bank of Canada’s target after a tumultuous battle with skyrocketing price growth.
The annual inflation rate fell from 2.5 per cent in July to reach the lowest level since February 2021.
Statistics Canada’s consumer price index report on Tuesday attributed the slowdown in part to lower gasoline prices.
Clothing and footwear prices also decreased on a month-over-month basis, marking the first decline in the month of August since 1971 as retailers offered larger discounts to entice shoppers amid slowing demand.
The Bank of Canada’s preferred core measures of inflation, which strip out volatility in prices, also edged down in August.
The marked slowdown in price growth last month was steeper than the 2.1 per cent annual increase forecasters were expecting ahead of Tuesday’s release and will likely spark speculation of a larger interest rate cut next month from the Bank of Canada.
“Inflation remains unthreatening and the Bank of Canada should now focus on trying to stimulate the economy and halting the upward climb in the unemployment rate,” wrote CIBC senior economist Andrew Grantham.
Benjamin Reitzes, managing director of Canadian rates and macro strategist at BMO, said Tuesday’s figures “tilt the scales” slightly in favour of more aggressive cuts, though he noted the Bank of Canada will have one more inflation reading before its October rate announcement.
“If we get another big downside surprise, calls for a 50 basis-point cut will only grow louder,” wrote Reitzes in a client note.
The central bank began rapidly hiking interest rates in March 2022 in response to runaway inflation, which peaked at a whopping 8.1 per cent that summer.
The central bank increased its key lending rate to five per cent and held it at that level until June 2024, when it delivered its first rate cut in four years.
A combination of recovered global supply chains and high interest rates have helped cool price growth in Canada and around the world.
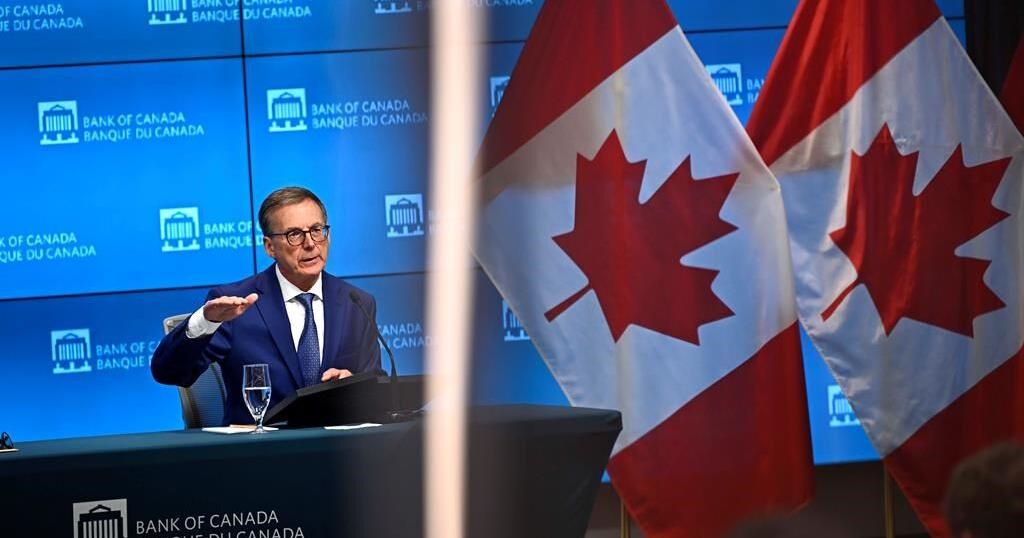
Bank of Canada governor Tiff Macklem recently signalled that the central bank is ready to increase the size of its interest rate cuts, if inflation or the economy slow by more than expected.
Its key lending rate currently stands at 4.25 per cent.
CIBC is forecasting the central bank will cut its key rate by two percentage points between now and the middle of next year.
The U.S. Federal Reserve is also expected on Wednesday to deliver its first interest rate cut in four years.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Sept. 17, 2024.