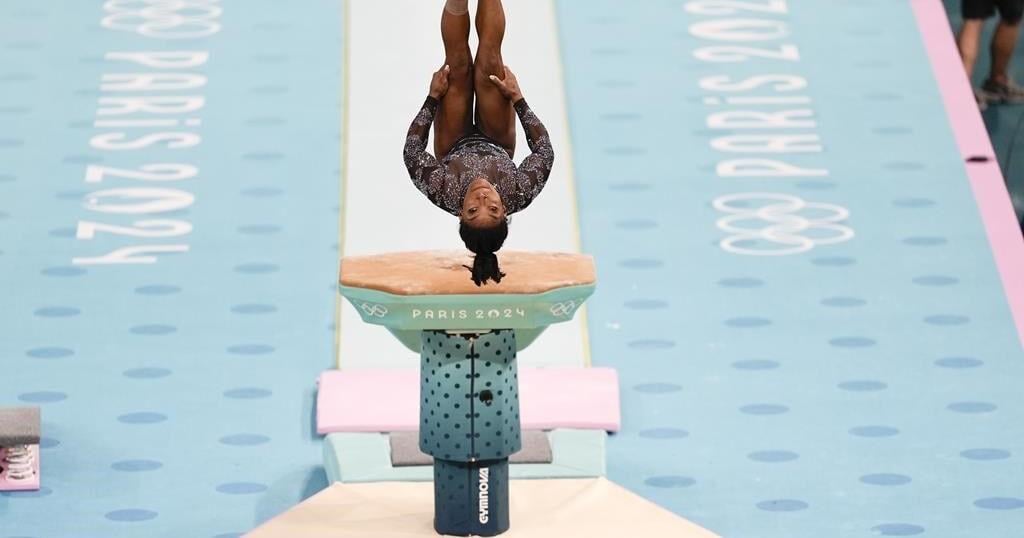PARIS (AP) — It is not enough — it has never been enough — for Simone Biles to do gymnastics.
The 27-year-old American star has been intent almost from the start on pushing the sport in new directions by doing things that have never been done before. That could continue this week when she tries for her eighth Olympic medal in Paris.
Five elements currently bear her name in the Code of Points after she successfully completed them in an international competition: two on vault, two on floor exercise and one on balance beam.
There’s a chance Biles could add a sixth if she tries the original skill — this one on uneven bars — she submitted to the International Gymnastics Federation before the Olympics. Biles did not attempt it during qualifying on Sunday, but could in the team final on Tuesday or the all-around final on Thursday.
A quick primer on what you could see Tuesday night as the U.S. women look to reclaim the top of the medal stand after finishing runner-up to Russia at the 2020 Games.
Biles I (Floor exercise version)
She was just a teenager and recently minted national champion when Biles performed a tumbling pass at the 2013 world championships that she completes by doing a double layout with a half-twist at the end.
The move looks dangerous — Biles is essentially flying blind — but she and former coach Aimee Boorman came up with it because it was less taxing on her legs.
“It was almost kind of necessity is the mother of invention,” Boorman told The Associated Press in 2015. “Her calf was hurting. She had bone spurs in her ankles and she’s really good at floor with landings.”
Biles II (floor exercise version)
Biles returned to the sport in 2018 following a two-year layoff after winning the all-around at the 2016 Olympics.
Not content to merely repeat herself, Biles began working on a triple-twisting, double flip that is now known simply as “ the triple-double.” She unveiled it while winning the 2019 U.S. Championships then did it again at the world championships a few months later when she won the fifth of her record six world all-around titles.
“I wanted to see how it looked,” she explained afterward.
Biles I (vault version)
As with a lot of gymnastics elements, Biles took a Cheng vault and added another layer of difficulty — this one an extra half twist on a vault originally done by China’s Cheng Fei.
The vault requires Biles to do a round-off onto the vault, then a half-twist onto the table before doing two full twists. It entered the Code after she made it part of her routine at the 2018 world championships.
“I’m embarrassed to do floor and vault after something like that,” U.S. men’s gymnast Yul Moldauer said in 2018. “You see Simone do that and she’s smiling the whole time. How does she do that?”
Biles II (vault version)
This may be the most dazzling, most daring one of them all.
The Yurchenko double pike had never been completed by a woman in competition, and few men have even tried. She began tinkering with it in 2021, but it’s in the last year that it has morphed into perhaps the most show-stopping thing done in the sport.
The vault asks Biles to do a round-off back handspring onto the table, then two backward flips in pike position with her hands essentially clasped to her knees. She does it with so much power, she can sometimes overcook it. At the U.S. Olympic trials last month, it drew a standing ovation.
“No, it’s not normal,” longtime coach Laurent Landi said after she drilled it at the 2023 U.S. Championships. “She’s not normal.”
Biles I (balance beam version)
For all of her explosive tumbling, Biles is a wonder on balance beam, too, where she can make doing intricate moves on a four-inch-wide piece of wood seem almost casual.
The same year she debuted the triple-double on floor, she added a double-twisting, double-tucked dismount off the beam. She stuck it at the 2019 world championships, though she has since taken it out of her repetoire.
What does the new uneven bars skill look like?
The skill Biles submitted requires her to do a forward circle around the lower bar before turning a handstand into a 540-degree pirouette. USA Gymnastics teased the move on X on Friday.
Bars is considered the weakest of Biles’ events in the sense that just one of her 37 Olympic and world championship medals have come on bars. The Americans even considered having Biles sit out bars during the team finals. She’s slated to compete there Tuesday, though, and could unveil the skill there.
___
AP Summer Olympics: