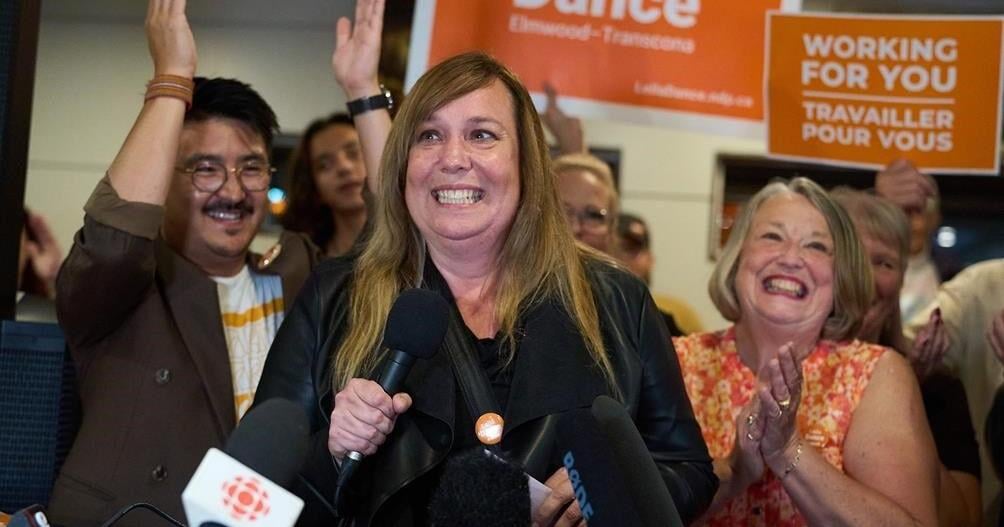
WINNIPEG – The federal New Democrats have kept a longtime stronghold in the Elmwood-Transcona riding in Winnipeg.
The NDP’s Leila Dance won a close battle over Conservative candidate Colin Reynolds, and says the community has spoken in favour of priorities such as health care and the cost of living.
Elmwood-Transcona has elected a New Democrat in every election except one since the riding was formed in 1988.
The seat became open after three-term member of Parliament Daniel Blaikie resigned in March to take a job with the Manitoba government.
A political analyst the NDP is likely relieved to have kept the seat in what has been one of their strongest urban areas.
Christopher Adams, an adjunct professor of political studies at the University of Manitoba, says NDP Leader Jagmeet Singh worked hard to keep the seat in a tight race.
“He made a number of visits to Winnipeg, so if they had lost this riding it would have been disastrous for the NDP,” Adams said.
The strong Conservative showing should put wind in that party’s sails, Adams added, as their percentage of the popular vote in Elmwood-Transcona jumped sharply from the 2021 election.
“Even though the Conservatives lost this (byelection), they should walk away from it feeling pretty good.”
Dance told reporters Monday night she wants to focus on issues such as the cost of living while working in Ottawa.
“We used to be able to buy a cart of groceries for a hundred dollars and now it’s two small bags. That is something that will affect everyone in this riding,” Dance said.
Liberal candidate Ian MacIntyre placed a distant third,
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Sept. 16, 2024