Art
University of Chicago researchers seek to “poison” AI art generators with Nightshade – Ars Technica

On Friday, a team of researchers at the University of Chicago released a research paper outlining “Nightshade,” a data poisoning technique aimed at disrupting the training process for AI models, reports MIT Technology Review and VentureBeat. The goal is to help visual artists and publishers protect their work from being used to train generative AI image synthesis models, such as Midjourney, DALL-E 3, and Stable Diffusion.
The open source “poison pill” tool (as the University of Chicago’s press department calls it) alters images in ways invisible to the human eye that can corrupt an AI model’s training process. Many image synthesis models, with notable exceptions of those from Adobe and Getty Images, largely use data sets of images scraped from the web without artist permission, which includes copyrighted material. (OpenAI licenses some of its DALL-E training images from Shutterstock.)
AI researchers’ reliance on commandeered data scraped from the web, which is seen as ethically fraught by many, has also been key to the recent explosion in generative AI capability. It took an entire Internet of images with annotations (through captions, alt text, and metadata) created by millions of people to create a data set with enough variety to create Stable Diffusion, for example. It would be impractical to hire people to annotate hundreds of millions of images from the standpoint of both cost and time. Those with access to existing large image databases (such as Getty and Shutterstock) are at an advantage when using licensed training data.

Along those lines, some research institutions, like the University of California Berkeley Library, have argued for preserving data scraping as fair use in AI training for research and education purposes. The practice has not been definitively ruled on by US courts yet, and regulators are currently seeking comment for potential legislation that might affect it one way or the other. But as the Nightshade team sees it, research use and commercial use are two entirely different things, and they hope their technology can force AI training companies to license image data sets, respect crawler restrictions, and conform to opt-out requests.
“The point of this tool is to balance the playing field between model trainers and content creators,” co-author and University of Chicago professor Ben Y. Zhao said in a statement. “Right now model trainers have 100 percent of the power. The only tools that can slow down crawlers are opt-out lists and do-not-crawl directives, all of which are optional and rely on the conscience of AI companies, and of course none of it is verifiable or enforceable and companies can say one thing and do another with impunity. This tool would be the first to allow content owners to push back in a meaningful way against unauthorized model training.”
Shawn Shan, Wenxin Ding, Josephine Passananti, Haitao Zheng, and Zhao developed Nightshade as part of the Department of Computer Science at the University of Chicago. The new tool builds upon the team’s prior work with Glaze, another tool designed to alter digital artwork in a manner that confuses AI. While Glaze is oriented toward obfuscating the style of the artwork, Nightshade goes a step further by corrupting the training data. Essentially, it tricks AI models into misidentifying objects within the images.
For example, in tests, researchers used the tool to alter images of dogs in a way that led an AI model to generate a cat when prompted to produce a dog. To do this, Nightshade takes an image of the intended concept (e.g., an actual image of a “dog”) and subtly modifies the image so that it retains its original appearance but is influenced in latent (encoded) space by an entirely different concept (e.g., “cat”). This way, to a human or simple automated check, the image and the text seem aligned. But in the model’s latent space, the image has characteristics of both the original and the poison concept, which leads the model astray when trained on the data.
Art
Calvin Lucyshyn: Vancouver Island Art Dealer Faces Fraud Charges After Police Seize Millions in Artwork
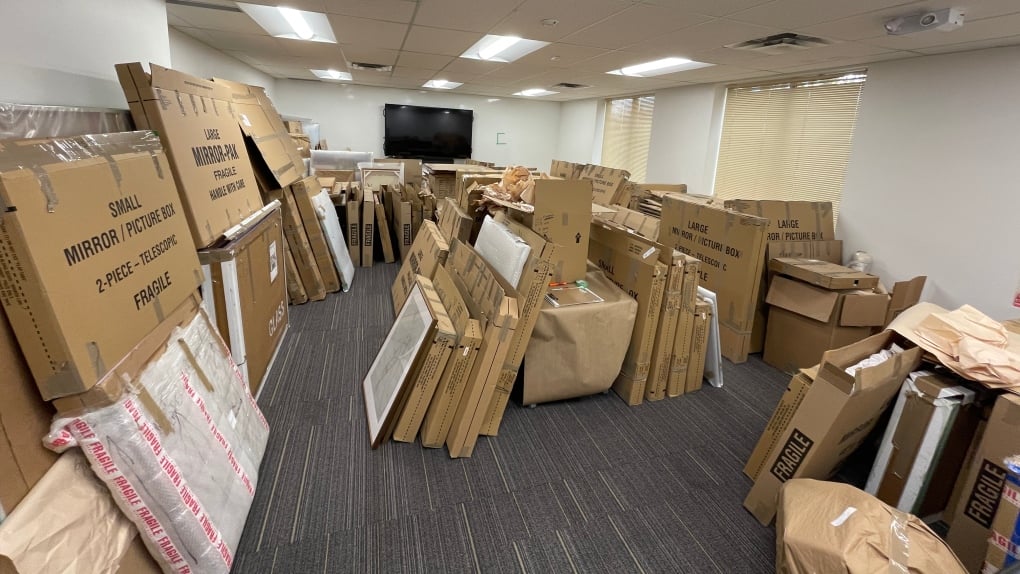

In a case that has sent shockwaves through the Vancouver Island art community, a local art dealer has been charged with one count of fraud over $5,000. Calvin Lucyshyn, the former operator of the now-closed Winchester Galleries in Oak Bay, faces the charge after police seized hundreds of artworks, valued in the tens of millions of dollars, from various storage sites in the Greater Victoria area.
Alleged Fraud Scheme
Police allege that Lucyshyn had been taking valuable art from members of the public under the guise of appraising or consigning the pieces for sale, only to cut off all communication with the owners. This investigation began in April 2022, when police received a complaint from an individual who had provided four paintings to Lucyshyn, including three works by renowned British Columbia artist Emily Carr, and had not received any updates on their sale.
Further investigation by the Saanich Police Department revealed that this was not an isolated incident. Detectives found other alleged victims who had similar experiences with Winchester Galleries, leading police to execute search warrants at three separate storage locations across Greater Victoria.
Massive Seizure of Artworks
In what has become one of the largest art fraud investigations in recent Canadian history, authorities seized approximately 1,100 pieces of art, including more than 600 pieces from a storage site in Saanich, over 300 in Langford, and more than 100 in Oak Bay. Some of the more valuable pieces, according to police, were estimated to be worth $85,000 each.
Lucyshyn was arrested on April 21, 2022, but was later released from custody. In May 2024, a fraud charge was formally laid against him.
Artwork Returned, but Some Remain Unclaimed
In a statement released on Monday, the Saanich Police Department confirmed that 1,050 of the seized artworks have been returned to their rightful owners. However, several pieces remain unclaimed, and police continue their efforts to track down the owners of these works.
Court Proceedings Ongoing
The criminal charge against Lucyshyn has not yet been tested in court, and he has publicly stated his intention to defend himself against any pending allegations. His next court appearance is scheduled for September 10, 2024.
Impact on the Local Art Community
The news of Lucyshyn’s alleged fraud has deeply affected Vancouver Island’s art community, particularly collectors, galleries, and artists who may have been impacted by the gallery’s operations. With high-value pieces from artists like Emily Carr involved, the case underscores the vulnerabilities that can exist in art transactions.
For many art collectors, the investigation has raised concerns about the potential for fraud in the art world, particularly when it comes to dealing with private galleries and dealers. The seizure of such a vast collection of artworks has also led to questions about the management and oversight of valuable art pieces, as well as the importance of transparency and trust in the industry.
As the case continues to unfold in court, it will likely serve as a cautionary tale for collectors and galleries alike, highlighting the need for due diligence in the sale and appraisal of high-value artworks.
While much of the seized artwork has been returned, the full scale of the alleged fraud is still being unraveled. Lucyshyn’s upcoming court appearances will be closely watched, not only by the legal community but also by the wider art world, as it navigates the fallout from one of Canada’s most significant art fraud cases in recent memory.
Art collectors and individuals who believe they may have been affected by this case are encouraged to contact the Saanich Police Department to inquire about any unclaimed pieces. Additionally, the case serves as a reminder for anyone involved in high-value art transactions to work with reputable dealers and to keep thorough documentation of all transactions.
As with any investment, whether in art or other ventures, it is crucial to be cautious and informed. Art fraud can devastate personal collections and finances, but by taking steps to verify authenticity, provenance, and the reputation of dealers, collectors can help safeguard their valuable pieces.
Art
Ukrainian sells art in Essex while stuck in a warzone – BBC.com
[unable to retrieve full-text content]
Ukrainian sells art in Essex while stuck in a warzone BBC.com

Source link
Art
Somerset House Fire: Courtauld Gallery Reopens, Rest of Landmark Closed
The Courtauld Gallery at Somerset House has reopened its doors to the public after a fire swept through the historic building in central London. While the gallery has resumed operations, the rest of the iconic site remains closed “until further notice.”
On Saturday, approximately 125 firefighters were called to the scene to battle the blaze, which sent smoke billowing across the city. Fortunately, the fire occurred in a part of the building not housing valuable artworks, and no injuries were reported. Authorities are still investigating the cause of the fire.
Despite the disruption, art lovers queued outside the gallery before it reopened at 10:00 BST on Sunday. One visitor expressed his relief, saying, “I was sad to see the fire, but I’m relieved the art is safe.”
The Clark family, visiting London from Washington state, USA, had a unique perspective on the incident. While sightseeing on the London Eye, they watched as firefighters tackled the flames. Paul Clark, accompanied by his wife Jiorgia and their four children, shared their concern for the safety of the artwork inside Somerset House. “It was sad to see,” Mr. Clark told the BBC. As a fan of Vincent Van Gogh, he was particularly relieved to learn that the painter’s famous Self-Portrait with Bandaged Ear had not been affected by the fire.
Blaze in the West Wing
The fire broke out around midday on Saturday in the west wing of Somerset House, a section of the building primarily used for offices and storage. Jonathan Reekie, director of Somerset House Trust, assured the public that “no valuable artefacts or artworks” were located in that part of the building. By Sunday, fire engines were still stationed outside as investigations into the fire’s origin continued.
About Somerset House
Located on the Strand in central London, Somerset House is a prominent arts venue with a rich history dating back to the Georgian era. Built on the site of a former Tudor palace, the complex is known for its iconic courtyard and is home to the Courtauld Gallery. The gallery houses a prestigious collection from the Samuel Courtauld Trust, showcasing masterpieces from the Middle Ages to the 20th century. Among the notable works are pieces by impressionist legends such as Edouard Manet, Claude Monet, Paul Cézanne, and Vincent Van Gogh.
Somerset House regularly hosts cultural exhibitions and public events, including its popular winter ice skating sessions in the courtyard. However, for now, the venue remains partially closed as authorities ensure the safety of the site following the fire.
Art lovers and the Somerset House community can take solace in knowing that the invaluable collection remains unharmed, and the Courtauld Gallery continues to welcome visitors, offering a reprieve amid the disruption.
-

 News21 hours ago
News21 hours agoMK-ULTRA: Ottawa, health centre seek to dismiss Montreal brainwashing lawsuit
-

 Sports20 hours ago
Sports20 hours agoFledgling Northern Super League adds four to front office ahead of April kickoff
-

 Health20 hours ago
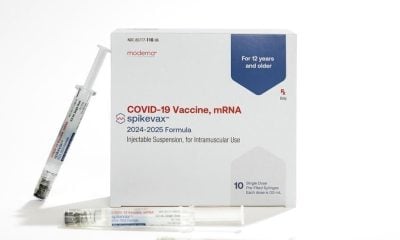
Health20 hours agoHealth Canada approves updated Moderna COVID-19 vaccine
-

 News20 hours ago
News20 hours agoRCMP warn of armed robbery suspects west of Edmonton
-

 News20 hours ago
News20 hours agoOttawa threatens to pull funds for Chignecto Isthmus if N.B., N.S. don’t partner
-

 Politics21 hours ago
Politics21 hours agoNDP beat Conservatives in federal byelection in Winnipeg
-

 Economy20 hours ago
Economy20 hours agoEnergy stocks help lift S&P/TSX composite, U.S. stock markets also up
-

 News21 hours ago
News21 hours agoCanadanewsmedia news September 17, 2024: Bloc wins Montreal Liberal stronghold