VANCOUVER – The federal government is urging both sides in the British Columbia port dispute to return to the table after Saturday’s collapse of mediated talks to end the lockout at container terminals that has entered its second week.
A statement issued by the office of federal Labour Minister Steven MacKinnon on Monday said both the port employers and the union representing more than 700 longshore supervisors “must understand the urgency of the situation.”
The statement also urged both sides to “do the work necessary to reach an agreement.”
“Canadians are counting on them,” the statement from MacKinnon’s office said.
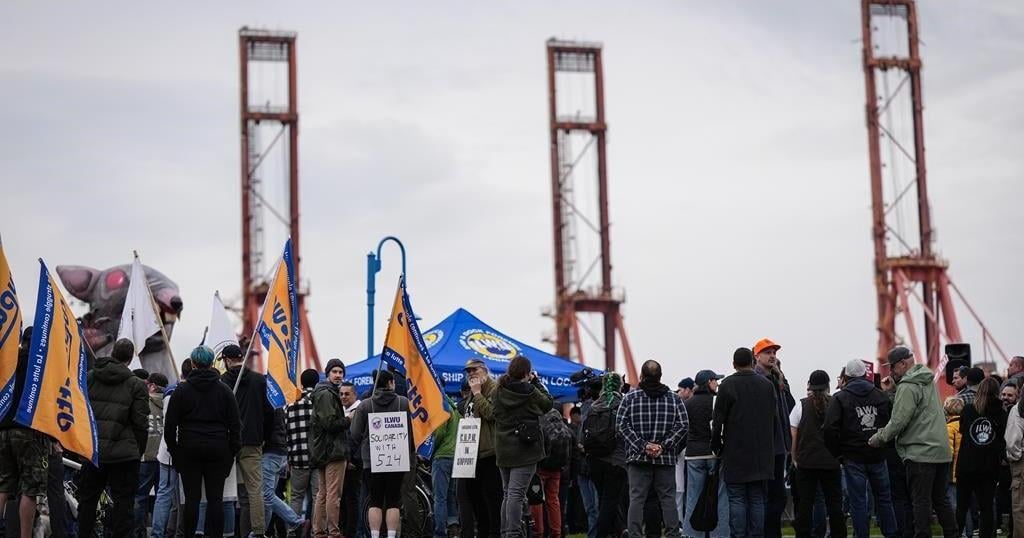
The lockout at B.C. container terminals including those in Vancouver — Canada’s largest port — began last week after the BC Maritime Employers Association said members of International Longshore and Warehouse Union Ship and Dock Foremen Local 514 began strike activity in response to a “final offer” from employers.
The union said the plan was only for an overtime ban and a refusal to implement automation technology, calling the provincewide lockout a reckless overreaction.
On Saturday, the two sides began what was scheduled to be up to three days of mediated talks, after MacKinnon spoke to both sides and said on social media that there was a “concerning lack of urgency” to resolve the dispute.
But the union said the talks lasted “less than one hour” Saturday without resolution, accusing the employers of cutting them off.
The employers denied ending the talks, saying the mediator concluded the discussions after “there was no progress made” in talks conducted separately with the association and the union.
“The BCMEA went into the meeting with open minds and seeking to achieve a negotiated settlement at the bargaining table,” a statement from the employers said.
“In a sincere effort to bring these drawn-out negotiations to a close, the BCMEA provided a competitive offer to ILWU Local 514 … the offer did not require any concessions from the union and, if accepted, would have ended this dispute.”
The employers said the offer includes a 19.2 per cent wage increase over a four-year term along with an average lump sum payment of $21,000 per qualified worker, but the union said it did not address staffing levels given the advent of port automation technology in terminals such as DP World’s Centerm in Vancouver.
After talks broke off, the union accused the employers of “showing flagrant disregard for the seriousness of their lockout.”
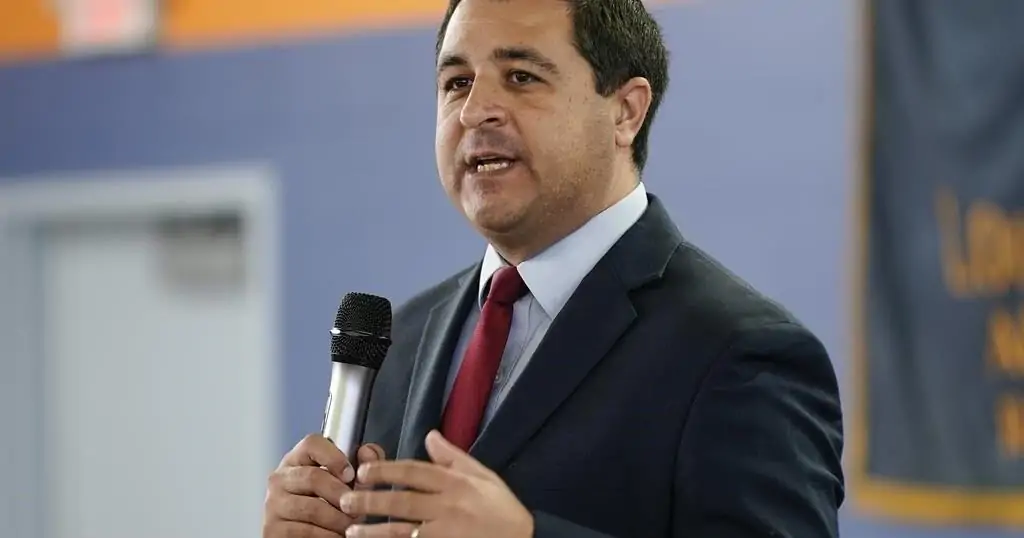
Local 514 president Frank Morena said in a statement on Saturday that the union is “calling on the actual individual employers who run the terminals to order their bargaining agent — the BCMEA — to get back to the table.”
“We believe the individual employers who actually run the terminals need to step up and order their bargaining agent to get back to the table and start negotiations and stop the confrontation,” Morena said.
No further talks are currently scheduled.
According to the Canada Labour Code, the labour minister or either party in a dispute can request a mediator to “make recommendations for settlement of the dispute or the difference.”
In addition, Section 107 of the Code gives the minister additional powers to take action that “seem likely to maintain or secure industrial peace and to promote conditions favourable to the settlement of industrial disputes,” and could direct the Canada Industrial Relations Board “to do such things as the Minister deems necessary.”
Liam McHugh-Russell, assistant professor at Schulich School of Law at Dalhousie University, said Section 107 “is very vague about what it allows a minister to do.”
“All it says is that the minister can refer a problem and a solution to the Labour Board. They can ask the Labour Board to try and solve the problem,” he said.
“Maybe the minister will try to do that. It remains to be seen.”
The other option if mediated talks fail — beyond the parties reaching a solution on their own — would be a legislated return to work, which would be an exception to the normal way labour negotiations operate under the Labour Code.
Parliament is not scheduled to sit this week and will return on Nov. 18.
The labour strife at B.C. ports is happening at the same time another dispute is disrupting Montreal, Canada’s second-largest port.
The employers there locked out almost 1,200 workers on Sunday night after a “final” offer was not accepted, greatly reducing operations.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Nov. 11, 2024.