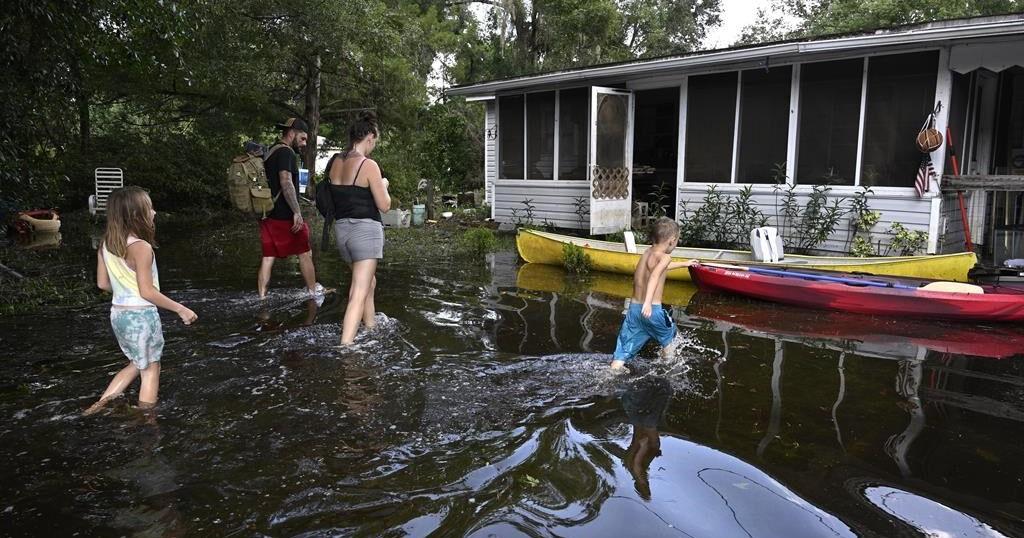
More than 40 trillion gallons of rain drenched the Southeast United States in the last week from Hurricane Helene and a run-of-the-mill rainstorm that sloshed in ahead of it — an unheard of amount of water that has stunned experts.
That’s enough to fill the Dallas Cowboys’ stadium 51,000 times, or Lake Tahoe just once. If it was concentrated just on the state of North Carolina that much water would be 3.5 feet deep (more than 1 meter). It’s enough to fill more than 60 million Olympic-size swimming pools.
“That’s an astronomical amount of precipitation,” said Ed Clark, head of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s National Water Center in Tuscaloosa, Alabama. “I have not seen something in my 25 years of working at the weather service that is this geographically large of an extent and the sheer volume of water that fell from the sky.”
The flood damage from the rain is apocalyptic, meteorologists said. More than 100 people are dead, according to officials.
Private meteorologist Ryan Maue, a former NOAA chief scientist, calculated the amount of rain, using precipitation measurements made in 2.5-mile-by-2.5 mile grids as measured by satellites and ground observations. He came up with 40 trillion gallons through Sunday for the eastern United States, with 20 trillion gallons of that hitting just Georgia, Tennessee, the Carolinas and Florida from Hurricane Helene.
Clark did the calculations independently and said the 40 trillion gallon figure (151 trillion liters) is about right and, if anything, conservative. Maue said maybe 1 to 2 trillion more gallons of rain had fallen, much if it in Virginia, since his calculations.
Clark, who spends much of his work on issues of shrinking western water supplies, said to put the amount of rain in perspective, it’s more than twice the combined amount of water stored by two key Colorado River basin reservoirs: Lake Powell and Lake Mead.
Several meteorologists said this was a combination of two, maybe three storm systems. Before Helene struck, rain had fallen heavily for days because a low pressure system had “cut off” from the jet stream — which moves weather systems along west to east — and stalled over the Southeast. That funneled plenty of warm water from the Gulf of Mexico. And a storm that fell just short of named status parked along North Carolina’s Atlantic coast, dumping as much as 20 inches of rain, said North Carolina state climatologist Kathie Dello.
Then add Helene, one of the largest storms in the last couple decades and one that held plenty of rain because it was young and moved fast before it hit the Appalachians, said University of Albany hurricane expert Kristen Corbosiero.
“It was not just a perfect storm, but it was a combination of multiple storms that that led to the enormous amount of rain,” Maue said. “That collected at high elevation, we’re talking 3,000 to 6000 feet. And when you drop trillions of gallons on a mountain, that has to go down.”
The fact that these storms hit the mountains made everything worse, and not just because of runoff. The interaction between the mountains and the storm systems wrings more moisture out of the air, Clark, Maue and Corbosiero said.
North Carolina weather officials said their top measurement total was 31.33 inches in the tiny town of Busick. Mount Mitchell also got more than 2 feet of rainfall.
Before 2017’s Hurricane Harvey, “I said to our colleagues, you know, I never thought in my career that we would measure rainfall in feet,” Clark said. “And after Harvey, Florence, the more isolated events in eastern Kentucky, portions of South Dakota. We’re seeing events year in and year out where we are measuring rainfall in feet.”
Storms are getting wetter as the climate change s, said Corbosiero and Dello. A basic law of physics says the air holds nearly 4% more moisture for every degree Fahrenheit warmer (7% for every degree Celsius) and the world has warmed more than 2 degrees (1.2 degrees Celsius) since pre-industrial times.
Corbosiero said meteorologists are vigorously debating how much of Helene is due to worsening climate change and how much is random.
For Dello, the “fingerprints of climate change” were clear.
“We’ve seen tropical storm impacts in western North Carolina. But these storms are wetter and these storms are warmer. And there would have been a time when a tropical storm would have been heading toward North Carolina and would have caused some rain and some damage, but not apocalyptic destruction. ”
___
Follow AP’s climate coverage at https://apnews.com/hub/climate
___
Follow Seth Borenstein on Twitter at @borenbears
___
Associated Press climate and environmental coverage receives support from several private foundations. See more about AP’s climate initiative here. The AP is solely responsible for all content.