Science
Colossal Black Holes Locked in an Epic Cosmic Dance at Heart of Galaxy – SciTechDaily

This artist’s concept shows two candidate supermassive black holes at the heart of a quasar called PKS 2131-021. In this view of the system, gravity from the foreground black hole (right) can be seen twisting and distorting the light of its companion, which has a powerful jet. Each black hole is about a hundred million times the mass of our sun, with the black hole in the foreground being slightly less massive. Credit: Caltech/R. Hurt (IPAC)
Astronomers find evidence for the tightest-knit supermassive <span class="glossaryLink" aria-describedby="tt" data-cmtooltip="
” data-gt-translate-attributes=”["attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"]”>black hole duo observed to date.
Locked in an epic cosmic waltz 9 billion light years away, two supermassive black holes appear to be orbiting around each other every two years. The two giant bodies each have masses that are hundreds of millions of times larger than that of our sun, and the objects are separated by a distance roughly 50 times that which separates our sun and <span class="glossaryLink" aria-describedby="tt" data-cmtooltip="
” data-gt-translate-attributes=”["attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"]”>Pluto. When the pair merge in roughly 10,000 years, the titanic collision is expected to shake space and time itself, sending <span class="glossaryLink" aria-describedby="tt" data-cmtooltip="
” data-gt-translate-attributes=”["attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"]”>gravitational waves across the universe.
A Caltech-led team of astronomers has discovered evidence for this scenario taking place within a fiercely energetic object known as a quasar. Quasars are active cores of galaxies in which a supermassive black hole is siphoning material from a disk encircling it. In some quasars, the supermassive black hole creates a jet that shoots out at near the speed of light. The quasar observed in the new study, PKS 2131-021, belongs to a subclass of quasars called blazars in which the jet is pointing toward the Earth. Astronomers already knew quasars could possess two orbiting supermassive black holes, but finding direct evidence for this has proved difficult.


Two supermassive black holes are seen orbiting each other in this artist’s loopable animation. The more massive black hole, which is hundreds of millions times the mass of our sun, is shooting out a jet that changes in its apparent brightness as the duo circles each other. Astronomers found evidence for this scenario in a quasar called PKS 2131-021 after analyzing 45-years-worth of radio observations that show the system periodically dimming and brightening. The observed cyclical pattern is thought to be caused by the orbital motion of the jet. Credit: Caltech/R. Hurt (IPAC)
Reporting in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, the researchers argue that PKS 2131-021 is now the second known candidate for a pair of supermassive black holes caught in the act of merging. The first candidate pair, within a quasar called OJ 287, orbit each other at greater distances, circling every nine years versus the two years it takes for the PKS 2131-021 pair to complete an orbit.
The telltale evidence came from radio observations of PKS 2131-021 that span 45 years. According to the study, a powerful jet emanating from one of the two black holes within PKS 2131-021 is shifting back and forth due to the pair’s orbital motion. This causes periodic changes in the quasar’s radio-light brightness. Five different observatories registered these oscillations, including Caltech’s Owens Valley Radio Observatory (OVRO), the University of Michigan Radio Astronomy Observatory (UMRAO), <span class="glossaryLink" aria-describedby="tt" data-cmtooltip="
” data-gt-translate-attributes=”["attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"]”>MIT’s Haystack Observatory, the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO), Metsähovi Radio Observatory in Finland, and <span class="glossaryLink" aria-describedby="tt" data-cmtooltip="
” data-gt-translate-attributes=”["attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"]”>NASA’s Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) space satellite.
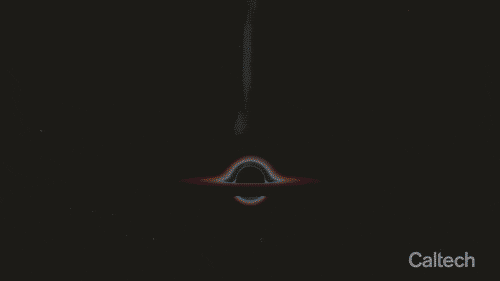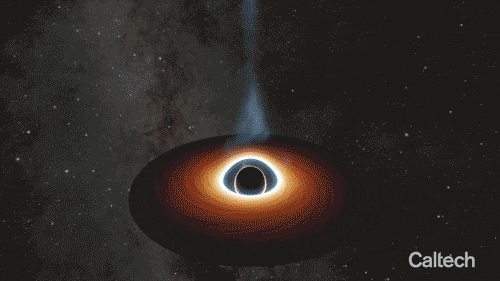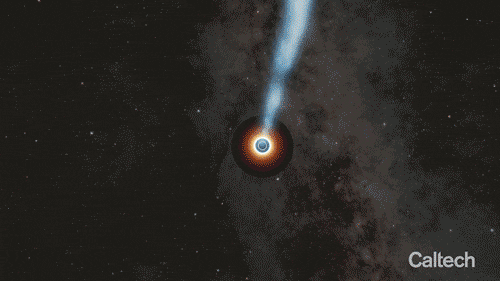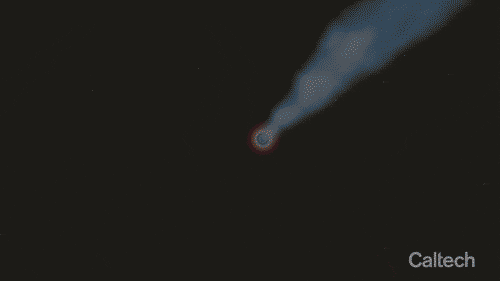

Artist’s animation of a supermassive black hole circled by a spinning disk of gas and dust. The black hole is shooting out a relativistic jet—one that travels at nearly the speed of light. Credit: Caltech/R. Hurt (IPAC)
The combination of the radio data yields a nearly perfect sinusoidal light curve unlike anything observed from quasars before.
“When we realized that the peaks and troughs of the light curve detected from recent times matched the peaks and troughs observed between 1975 and 1983, we knew something very special was going on,” says Sandra O’Neill, lead author of the new study and an undergraduate student at Caltech who is mentored by Tony Readhead, Robinson Professor of Astronomy, Emeritus.
[embedded content]
Ripples in Space and Time
Most, if not all, galaxies possess monstrous black holes at their cores, including our own <span class="glossaryLink" aria-describedby="tt" data-cmtooltip="
” data-gt-translate-attributes=”["attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"]”>Milky Way galaxy. When galaxies merge, their black holes “sink” to the middle of the newly formed galaxy and eventually join together to form an even more massive black hole. As the black holes spiral toward each other, they increasingly disturb the fabric of space and time, sending out gravitational waves, which were first predicted by Albert Einstein more than 100 years ago.
The National Science Foundation’s LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory), which is managed jointly by Caltech and MIT, detects gravitational waves from pairs of black holes up to dozens of times the mass of our sun. However, the supermassive black holes at the centers of galaxies have millions to billions of times as much mass as our sun, and give off lower frequencies of gravitational waves than those detected by <span class="glossaryLink" aria-describedby="tt" data-cmtooltip="
” data-gt-translate-attributes=”["attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"]”>LIGO.
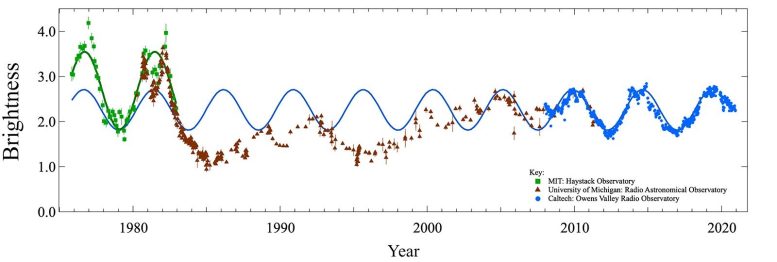

Three sets of radio observations of the quasar PKS 2131-02, spanning 45 years, are plotted here, with data from Owens Valley Radio Observatory (OVRO) in blue; University of Michigan Radio Astronomical Observatory (UMRAO) in brown; and Haystack Observatory in green. The observations match a simple sine wave, indicated in blue. Astronomers believe that the sine wave pattern is caused by two supermassive black holes at the heart of the quasar orbiting around each other every two years. (A period of five years was actually observed due to a Doppler effect caused by the expansion of the universe.) One of the black holes is shooting out a relativistic jet that dims and brightens periodically. Note that data from OVRO and UMRAO match for the peak in 2010, and the UMRAO and Haystack data match for the peak in 1981. The magnitudes of the peaks observed around 1980 are twice as large as those observed in recent times, presumably because more material was falling towards the black hole and being ejected at that time. Credit: Tony Readhead/Caltech
In the future, <span class="glossaryLink" aria-describedby="tt" data-cmtooltip="
” data-gt-translate-attributes=”["attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"]”>pulsar timing arrays—which consist of an array of pulsing dead stars precisely monitored by radio telescopes—should be able to detect the gravitational waves from supermassive black holes of this heft. (The upcoming Laser Interferometer Space Antenna, or LISA, mission would detect merging black holes whose masses are 1,000 to 10 million times greater than the mass of our sun.) So far, no gravitational waves have been registered from any of these heavier sources, but PKS 2131-021 provides the most promising target yet.
In the meantime, light waves are the best option to detect coalescing supermassive black holes.
The first such candidate, OJ 287, also exhibits periodic radio-light variations. These fluctuations are more irregular, and not sinusoidal, but they suggest the black holes orbit each other every nine years. The black holes within the new quasar, PKS 2131-021, orbit each other every two years and are 2,000 astronomical units apart, about 50 times the distance between our sun and Pluto, or 10 to 100 times closer than the pair in OJ 287. (An astronomical unit is the distance between Earth and the sun.)
Revealing the 45-Year Light Curve
Readhead says the discoveries unfolded like a “good detective novel,” beginning in 2008 when he and colleagues began using the 40-meter telescope at OVRO to study how black holes convert material they “feed” on into relativistic jets, or jets traveling at speeds up to 99.98 percent that of light. They had been monitoring the brightness of more than 1,000 blazars for this purpose when, in 2020, they noticed a unique case.
“PKS 2131 was varying not just periodically, but sinusoidally,” Readhead says. “That means that there is a pattern we can trace continuously over time.” The question, he says, then became how long has this sine wave pattern been going on?
The research team then went through archival radio data to look for past peaks in the light curves that matched predictions based on the more recent OVRO observations. First, data from NRAO’s Very Long Baseline Array and UMRAO revealed a peak from 2005 that matched predictions. The UMRAO data further showed there was no sinusoidal signal at all for 20 years before that time—until as far back as 1981 when another predicted peak was observed.
“The story would have stopped there, as we didn’t realize there were data on this object before 1980,” Readhead says. “But then Sandra picked up this project in June of 2021. If it weren’t for her, this beautiful finding would be sitting on the shelf.”
O’Neill began working with Readhead and the study’s second author Sebastian Kiehlmann, a postdoc at the University of Crete and former staff scientist at Caltech, as part of Caltech’s Summer Undergraduate Research Fellowship (SURF) program. O’Neill began college as a chemistry major but picked up the astronomy project because she wanted to stay active during the pandemic. “I came to realize I was much more excited about this than anything else I had worked on,” she says.
With the project back on the table, Readhead searched through the literature and found that the Haystack Observatory had made radio observations of PKS 2131-021 between 1975 and 1983. These data revealed another peak matching their predictions, this time occurring in 1976.
“This work shows the value of doing accurate monitoring of these sources over many years for performing discovery science,” says co-author Roger Blandford, Moore Distinguished Scholar in Theoretical Astrophysics at Caltech who is currently on sabbatical from Stanford University.
Like Clockwork
Readhead compares the system of the jet moving back and forth to a ticking clock, where each cycle, or period, of the sine wave corresponds to the two-year orbit of the black holes (though the observed cycle is actually five years due to light being stretched by the expansion of the universe). This ticking was first seen in 1976 and it continued for eight years before disappearing for 20 years, likely due to changes in the fueling of the black hole. The ticking has now been back for 17 years.
“The clock kept ticking,” he says, “The stability of the period over this 20-year gap strongly suggests that this blazar harbors not one supermassive black hole, but two supermassive black holes orbiting each other.”
The physics underlying the sinusoidal variations were at first a mystery, but Blandford came up with a simple and elegant model to explain the sinusoidal shape of the variations.
“We knew this beautiful sine wave had to be telling us something important about the system,” Readhead says. “Roger’s model shows us that it is simply the orbital motion that does this. Before Roger worked it out, nobody had figured out that a binary with a relativistic jet would have a light curve that looked like this.”
Says Kiehlmann: “Our study provides a blueprint for how to search for such blazar binaries in the future.”
Reference: “The Unanticipated Phenomenology of the Blazar PKS 2131–021: A Unique Supermassive Black Hole Binary Candidate” by S. O’Neill, S. Kiehlmann, A. C. S. Readhead, M. F. Aller, R. D. Blandford, I. Liodakis, M. L. Lister, P. Mróz, C. P. O’Dea, T. J. Pearson, V. Ravi, M. Vallisneri, K. A. Cleary, M. J. Graham, K. J. B. Grainge, M. W. Hodges, T. Hovatta, A. Lähteenmäki, J. W. Lamb, T. J. W. Lazio, W. Max-Moerbeck, V. Pavlidou, T. A. Prince, R. A. Reeves, M. Tornikoski, P. Vergara de la Parra and J. A. Zensus, 23 February 2022, The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
DOI: 10.3847/2041-8213/ac504b
The Astrophysical Journal Letters study titled “The Unanticipated Phenomenology of the Blazar PKS 2131-021: A Unique Super-Massive Black hole Binary Candidate” was funded by Caltech, the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy, NASA, National Science Foundation (NSF), the Academy of Finland, the European Research Council, ANID-FONDECYT (Agencia Nacional de Investigación y Desarrollo-Fondo Nacional de Desarrollo Científico y Tecnológico in Chile), the Natural Science and Engineering Council of Canada, the Foundation for Research and Technology – Hellas in Greece, the Hellenic Foundation for Research and Innovation in Greece, and the University of Michigan. Other Caltech authors include Tim Pearson, Vikram Ravi, Kieran Cleary, Matthew Graham, and Tom Prince. Other authors from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed by Caltech for NASA, include Michele Vallisneri and Joseph Lazio.
Science
Giant, 82-foot lizard fish discovered on UK beach could be largest marine reptile ever found – Livescience.com


Scientists have unearthed the remains of a gigantic, 200 million-year-old sea monster that may be the largest marine reptile ever discovered.
The newfound creature is a member of a group called ichthyosaurs, which were among the dominant sea predators during the Mesozoic era (251.9 million to 66 million years ago). The newly described species lived during the end of the Triassic period (251.9 million to 201.4 million years ago).
Ichthyosaurs had already attained massive sizes by the early portion of the Mesozoic, but it was not until the late Triassic that the largest species emerged.
While the Mesozoic is known as the age of the dinosaurs, ichthyosaurs were not themselves dinosaurs. Instead, they evolved from another group of reptiles. Their evolutionary path closely mirrors that of whales, which evolved from terrestrial mammals that later returned to the sea. And like whales, they breathed air and gave birth to live young.
The newly discovered ichthyosaur species was unearthed in pieces between 2020 and 2022 at Blue Anchor, Somerset in the United Kingdom. The first chunk of the fossil was noticed atop a rock on the beach, indicating that a passerby had found it and set it there for others to examine, the researchers explained in the paper. The researchers published their findings April 17 in the journal PLOS One.
The reptile’s remains are made up of a series of 12 fragments from a surangular bone, which is found in the upper portion of the lower jaw. The researchers estimate the bone was 6.5 feet (2 meters) long and that the living animal was about 82 feet (25 m) long.
The researchers named the sea monster Ichthyotitan severnensis, meaning giant lizard fish of the Severn, after the Severn Estuary where it was found. The team believes it is not only a new species but an entirely new genus of ichthyosaur. More than 100 species are already known.
window.sliceComponents = window.sliceComponents || ;
externalsScriptLoaded.then(() => {
window.reliablePageLoad.then(() => {
var componentContainer = document.querySelector(“#slice-container-newsletterForm-articleInbodyContent-5Tm52KifRnJsTxFt8noX8R”);
if (componentContainer)
var data = “layout”:”inbodyContent”,”header”:”Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now”,”tagline”:”Get the worldu2019s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.”,”formFooterText”:”By submitting your information you agree to the Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy and are aged 16 or over.”,”successMessage”:”body”:”Thank you for signing up. You will receive a confirmation email shortly.”,”failureMessage”:”There was a problem. Please refresh the page and try again.”,”method”:”POST”,”inputs”:[“type”:”hidden”,”name”:”NAME”,”type”:”email”,”name”:”MAIL”,”placeholder”:”Your Email Address”,”required”:true,”type”:”hidden”,”name”:”NEWSLETTER_CODE”,”value”:”XLS-D”,”type”:”hidden”,”name”:”LANG”,”value”:”EN”,”type”:”hidden”,”name”:”SOURCE”,”value”:”60″,”type”:”hidden”,”name”:”COUNTRY”,”type”:”checkbox”,”name”:”CONTACT_OTHER_BRANDS”,”label”:”text”:”Contact me with news and offers from other Future brands”,”type”:”checkbox”,”name”:”CONTACT_PARTNERS”,”label”:”text”:”Receive email from us on behalf of our trusted partners or sponsors”,”type”:”submit”,”value”:”Sign me up”,”required”:true],”endpoint”:”https://newsletter-subscribe.futureplc.com/v2/submission/submit”,”analytics”:[“analyticsType”:”widgetViewed”],”ariaLabels”:;
var triggerHydrate = function()
window.sliceComponents.newsletterForm.hydrate(data, componentContainer);
if (window.lazyObserveElement)
window.lazyObserveElement(componentContainer, triggerHydrate);
else
triggerHydrate();
}).catch(err => console.log(‘Hydration Script has failed for newsletterForm-articleInbodyContent-5Tm52KifRnJsTxFt8noX8R Slice’, err));
}).catch(err => console.log(‘Externals script failed to load’, err));
A number of rib fragments and a coprolite, or fossilized feces, were found in the area as well, but they were not definitively attributed to the same animal.
The sediments in which these specimens were found contained rocks that indicated earthquakes and tsunamis occurred during that time, which suggests that this species lived during a time of intense volcanic activity that may have led to a massive extinction event at the end of the Triassic according to the researchers.
A similar specimen was discovered in Lilstock, Somerset in 2016 and described in 2018. Both were found in what is known at the Westbury Mudstone Formation, within 6 miles (10 kilometers) of each other. This ichthyosaur was estimated to have been as much as 85 feet (26 m) long, although the authors of the latest study believe it was slightly smaller.
The previous contender for the largest marine reptile was another ichthyosaur, Shonisaurus sikanniensis, which was up to 69 feet (21 m) long. S. sikanniensis appeared 13 million years earlier than I. severnensis and was found in British Columbia, making it unlikely that the new discovery represents another specimen of the previously known species.
A similarly massive ichthyosaur called Himalayasaurus tibetensis, which may have reached lengths of 49 feet (15 m), was discovered in Tibet and described in 1972. It dates to the same period, meaning that it probably is not the same species as the new discovery either.
I. severnensis was likely among the last of the giant ichthyosaurs, the researchers claim. Ichthyosaurs persisted into the Cenomanian Age (100.5 million to 93.9 million years ago) of the late Cretaceous period (100.5 million to 66 million years ago). They were eventually supplanted by plesiosaurs — long-necked marine reptiles that went extinct at the end of the Cretaceous, alongside all non-avian dinosaurs.
Science
Federal government announces creation of National Space Council | RCI – Radio-Canada.ca


- Home
- Politics
- Federal Politics
The Canadian Space Agency also received a proposed $8.6 million for its lunar program
Nicole Mortillaro (new window) · CBC News
Canada’s space sector received a boost from the federal government in its budget, both in terms of money and vision.
The 2024 budget (new window) included a proposal for $8.6 million in 2024-25 to the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) for the Lunar Exploration Accelerator Program (new window) (LEAP), which invests in technologies for humanity’s return to the moon and beyond.
In addition to the funding, the federal government also announced the creation of a National Space Council, which will be a new whole-of-government approach to space exploration, technology development, and research.
For Space Canada (new window), an organization comprised of roughly 80 space sector companies including some of Canada’s largest, such as Magellan Aerospace (new window), Maritime Launch (new window) and MDA Space (new window), it was a welcome announcement.
We’ve been advocating for it since the inception of our organization, and we were really very happy, and we applaud the federal government’s commitment announced in the budget,
said Brian Gallant, CEO of Space Canada.
Gallant said that investment in space is an investment in Canada.
Two-thirds of space sector jobs are STEM jobs. These are good paying solid jobs for Canadians. And on top of that, we have approximately $2.8 billion that is injected into the Canadian economy because of the space sector,
he said.
The U.S. formed its National Space Council in 1989, but it was disbanded in 1992 and reestablished in 2017.
In the 2023 budget (new window), the government announced proposed spending of $1.2 billion over 13 years, that was to begin in 2024-25, to the CSA’s contribution of a lunar utility (new window) vehicle that would assist astronauts on the moon. The as–yet–developed vehicle could help astronauts move cargo from landing sites to habitats, perform science investigations or support them during spacewalks on the surface of the moon.
It also proposed to invest $150 million over five years for the LEAP program.
MDA Space, the company behind Canadarm, was also pleased with the announcement.
Canada has an enviable global competitive advantage in space and the creation of a National Space Council is critical to Canada maintaining that leadership position,
CEO Mike Greenley said in an email to CBC News.
Space is now a rapidly growing, highly strategic and competitive domain, and there is a real and urgent need to recognize its importance to the lives of Canadians and to our economy and national security.
The next project for MDA is Canadarm3, which will be part of Lunar Gateway, a international space station that will orbit the moon. It will serve as a sort of jumping-off point for astronauts heading to the moon and eventually beyond.
The Lunar Gateway is a great opportunity for Canada and for MDA Space to not only provide the next generation of Canadarm robotics but to clearly plant our flag as a core national and industry participant in the Artemis era,
Greenley said.
Lunar Gateway is set to begin construction no earlier than 2025 (new window), according to NASA.
Science
Paleontologists unearth what may be the largest known marine reptile – Science Daily


The fossilised remains of a second gigantic jawbone measuring more than two metres long has been found on a beach in Somerset, UK.
Experts have identified the bones as belonging to the jaws of a new species of enormous ichthyosaur, a type of prehistoric marine reptile. Estimates suggest the oceanic titan would have been more than 25 metres long.
Father and daughter, Justin and Ruby Reynolds from Braunton, Devon, found the first pieces of the second jawbone to be found in May 2020, while searching for fossils on the beach at Blue Anchor, Somerset. Ruby, then aged 11, found the first chunk of giant bone before searching together for additional pieces.
Realising they had discovered something significant, they contacted leading ichthyosaur expert, Dr Dean Lomax, a palaeontologist at The University of Manchester. Dr Lomax, who is also a 1851 Research Fellow at the University of Bristol, contacted Paul de la Salle, a seasoned fossil collector who had found the first giant jawbone in May 2016 from further along the coast at Lilstock.
Dr Dean Lomax said: “I was amazed by the find. In 2018, my team (including Paul de la Salle) studied and described Paul’s giant jawbone and we had hoped that one day another would come to light. This new specimen is more complete, better preserved, and shows that we now have two of these giant bones — called a surangular — that have a unique shape and structure. I became very excited, to say the least.”
Justin and Ruby, together with Paul, Dr Lomax, and several family members, visited the site to hunt for more pieces of this rare discovery. Over time, the team found additional pieces of the same jaw which fit together perfectly, like a multimillion-year-old jigsaw.
Justin said: “When Ruby and I found the first two pieces we were very excited as we realised that this was something important and unusual. When I found the back part of the jaw, I was thrilled because that is one of the defining parts of Paul’s earlier discovery.”
The last piece of bone was recovered in October 2022.
The research team, led by Dr Lomax, revealed that the jaw bones belong to a new species of giant ichthyosaur that would have been about the size of a blue whale. Comparing the two examples of the same bone with the same unique features from the same geologic time zone supports their identifications.
The team have called the new genus and species Ichthyotitan severnensis, meaning “giant fish lizard of the Severn.”
The bones are around 202 million years old, dating to the end of the Triassic Period in a time known as the Rhaetian. During this time, the gigantic ichthyosaurs swam the seas while the dinosaurs walked on land. It was the titans’ final chapter, however — as the story told in the rocks above these fossils record a cataclysm known as the Late Triassic global mass extinction event. After this time, giant ichthyosaurs from the family known as Shastasauridae go extinct. Today, these bones represent the very last of their kind.
Ichthyotitan is not the world’s first giant ichthyosaur, but de la Salles’ and Reynolds’ discoveries are unique among those known to science. These two bones appear roughly 13 million years after their latest geologic relatives, including Shonisaurus sikanniensis from British Columbia, Canada, and Himalayasaurus tibetensis from Tibet, China.
Dr Lomax added: “I was highly impressed that Ruby and Justin correctly identified the discovery as another enormous jawbone from an ichthyosaur. They recognised that it matched the one we described in 2018. I asked them whether they would like to join my team to study and describe this fossil, including naming it. They jumped at the chance. For Ruby, especially, she is now a published scientist who not only found but also helped to name a type of gigantic prehistoric reptile. There are probably not many 15-year-olds who can say that! A Mary Anning in the making, perhaps.”
Ruby said: “It was so cool to discover part of this gigantic ichthyosaur. I am very proud to have played a part in a scientific discovery like this.”
Further examinations of the bones’ internal structures have been carried out by master’s student, Marcello Perillo, from the University of Bonn, Germany. His work confirmed the ichthyosaur origin of the bones and revealed that the animal was still growing at the time of death.
He said: “We could confirm the unique set of histological characters typical of giant ichthyosaur lower jaws: the anomalous periosteal growth of these bones hints at yet to be understood bone developmental strategies, now lost in the deep time, that likely allowed late Triassic ichthyosaurs to reach the known biological limits of vertebrates in terms of size. So much about these giants is still shrouded by mystery, but one fossil at a time we will be able to unravel their secret.”
Concluding the work, Paul de la Salle added: “To think that my discovery in 2016 would spark so much interest in these enormous creatures fills me with joy. When I found the first jawbone, I knew it was something special. To have a second that confirms our findings is incredible. I am overjoyed.”
The new research has been published today in the open access journal PLOS ONE.
Ruby, Justin and Paul’s discoveries will soon go on display at the Bristol Museum and Art Gallery.
Lomax said: “This research has been ongoing for almost eight years. It is quite remarkable to think that gigantic, blue whale-sized ichthyosaurs were swimming in the oceans around what was the UK during the Triassic Period. These jawbones provide tantalising evidence that perhaps one day a complete skull or skeleton of one of these giants might be found. You never know.”
-



 Tech18 hours ago
Tech18 hours agoiPhone 15 Pro Desperado Mafia model launched at over ₹6.5 lakh- All details about this luxury iPhone from Caviar – HT Tech
-



 Sports18 hours ago
Sports18 hours agoLululemon unveils Canada's official Olympic kit for the Paris games – National Post
-



 Politics24 hours ago
Politics24 hours agoTrump gave MAGA politicians permission to move left on abortion. Some are taking it. – Semafor
-



 Science21 hours ago
Science21 hours agoAstronomers discover Milky Way's heaviest known black hole – Xinhua
-
Business23 hours ago
Traders Place Bets On $250 Oil – OilPrice.com
-
News16 hours ago
Toronto airport gold heist: Police announce nine arrests – CP24
-



 Tech16 hours ago
Tech16 hours agoVenerable Video App Plex Emerges As FAST Favorite – Forbes
-
Business24 hours ago
After 5 years, Budget 2024 lays out promised small business carbon rebate – Global News












