Article content
There’s a price shocker coming at the pumps.

“It’s not often that we’re served up a WTF moment like this,” I wrote on April 20, when the May contract for crude-oil benchmark-grade West Texas Intermediate (WTI) plunged to minus -$37.63 in a straight line, thus violating the WOLF STREET beer-mug dictum that “Nothing Goes to Heck in a Straight Line.” It was the first time in history that a US crude oil futures contract plunged into the negative. The peculiar dynamics that came together and caused this are expected to continue and some of them are expected to get worse over the next month or two. So here is the postmortem of this infamous day, by the US Energy Information Agency (EIA).
On Monday, April 20, 2020, New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX) West Texas Intermediate (WTI) crude oil front-month futures prices fell below zero dollars per barrel (b)—at one point, trading at -$40.32/b (Figure 1)—and remained below zero for part of the following trading day. Monday marked the first time the price for the WTI futures contract fell below zero since trading began in 1983.
Negative prices in commodity markets are very rare, but when they occur they typically indicate high transactions costs and significant infrastructure constraints.
In this case, the WTI front-month futures contract was for May 2020 delivery, and the contract was set to expire on April 21, 2020. Market participants that hold WTI futures contracts to expiration must take physical delivery of WTI crude oil in Cushing, Oklahoma.
Typically, most market participants close any futures contracts ahead of expiration through cash settlement in order to avoid taking physical delivery, and only about 1% of contracts are physically settled. The extreme market events of April 20 and April 21 were driven by several factors, including the inability of contract holders to find other market participants to sell the futures contracts. In addition, in this case, the scarcity of available crude oil storage meant several market participants could not take physical delivery at expiration and resorted to selling their futures contracts at negative prices, in effect paying a counterparty to take hold of the contracts.
Crude oil and other commodities are traded on futures markets, which are financial exchanges that market participants use to manage risk in a variety of businesses, including but not limited to, upstream crude oil production, refining, shipping, and wealth management. Because they can be delivered physically, prices for WTI futures contracts, for the most part, converge with spot market prices after expiration.
The spot market reflects cash transactions for physical buying and selling of the underlying commodity. For more information on the interaction between physical commodity markets and financial markets, the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) provides explanations and updated material on its web page What Drives Crude Oil Prices?
The terms and conditions contained in the settlement procedures of the May 2020 WTI contract as stipulated by CME Group—which owns and operates the NYMEX on which the contract is traded—are key to understanding the recent price activity.
On expiration, the holder of a WTI contract has two options to meet the contract’s physical delivery requirement:
First, up until 2:00 p.m. on the business day following the expiration date, a contract holder can settle the position by entering into an Exchange for Physical (EFP) contract with a counterparty, which transfers the contract to a counterparty in exchange for cash or other futures contracts with later expirations.
Second, settlement can also occur if a contract holder takes physical delivery of the crude oil. As per the NYMEX contract’s specifications, delivery of the physical crude oil volumes must occur at a pipeline or storage facility in Cushing, Oklahoma, with pipeline access to Enterprise Product Partner’s crude oil terminal or Enbridge Inc.’s crude oil terminal. This delivery must also occur within a specific time, which is currently set no earlier than the first calendar day of the contract month and no later than the month’s last calendar day.
Under normal conditions, taking delivery of crude oil at Cushing is straightforward. Buyers can have the oil transferred into a storage facility or pipeline that they own or lease. Or, with the seller’s consent, they can transfer ownership of the crude oil somewhere else in the pipeline and storage system.
Normal physical settlement has been disrupted, however, by the recent decline in the availability of uncommitted crude oil storage capacity. Because of the impact of the 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) on economic activity and the consumption of petroleum products, U.S. consumption of crude oil and petroleum products has sharply declined. As of the week ending April 17, U.S. refinery runs fell to 12.8 million barrels per day (b/d), 4.1 million b/d (24%) lower than the same time last year.
As a result of this extreme demand shock, excess imported and domestically-produced crude oil volumes have been placed into storage. Crude oil storage facilities at Cushing have 76 million barrels of working storage capacity, of which 60 million barrels (76% after accounting for pipeline fill and stocks in transit) were filled as of April 17 (Figure 2). Although Cushing has physically unfilled storage available, some of this physically unfilled storage is likely to have already been leased or otherwise committed, limiting the uncommitted storage available for contract holders without pre-existing arrangements. In this case, these contract holders would likely have to pay much higher rates to storage operators that have uncommitted space available.


Although data for storage costs are limited, the increased demand for storage has likely placed significant upward pressure on crude oil storage costs. Trade press reports of high on-land storage costs, high rates for crude oil maritime shipping (which can be used as an alternative to on-shore storage), and high levels of contango (when near-term futures prices are lower than longer-dated ones) all reflect an increase in storage costs since early March 2020.
The inability of some market participants to take physical delivery meant that they had to settle the May 2020 WTI contract financially by selling the contract to another market participant. As a result, owners of the May 2020 WTI futures contract most likely had to sell at lower prices to exit their contracts and avoid physical settlement. In this extreme market environment, several participants had to sell at negative prices—that is, pay the other party to take hold of the contract before expiration.
Theoretically, a contract holder could choose or be forced to fail to take physical delivery of the crude oil cargo, although doing so is likely to be costly. The specific costs associated with a failure to accept physical delivery depend on the specific contractual arrangements entered into by the futures contract holder and the Futures Commission Merchant (FCM)—the entity responsible for executing the buying and selling of futures contracts on behalf of a client.
The possible costs could include a combination of direct monetary penalties, reputational consequences, the liquidation of the collateral deposited by the client in the margin account with the FCM, the revocation of trading privileges, and the costs of any legal settlements resulting from the breach of contractual obligations. As a result, holders of expired contracts obligated to take physical settlement rarely fail to take delivery.
Taken together, these factors suggest that the phenomenon of negative WTI prices could be confined to the financial market, with few physical market participants paying negative prices. The positive pricing of other crude oil benchmarks (with the Brent contract for June 2020 delivery closing at $19.33/b on April 21), positive prices for longer-dated WTI prices, and positive spot prices for other U.S. crude oils suggest that the recent price action was predominantly driven by the timing of the May 2020 contract expiration.
The availability of storage in Cushing will remain an issue in the coming weeks, however, and could still result in volatile price movements in the June WTI futures contract or other U.S. crude oil spot prices that face limited storage options. EIA will continue to monitor these market developments. By the Energy Information Agency
By how much will economic activity in the US plunge? “Three times deeper than the Great Recession?” Read... How Far Will the U.S. Economy Plunge During Lockdown?
Enjoy reading WOLF STREET and want to support it? Using ad blockers – I totally get why – but want to support the site? You can donate. I appreciate it immensely. Click on the beer and iced-tea mug to find out how:
Would you like to be notified via email when WOLF STREET publishes a new article? Sign up here.
Gas prices have not been this high since August 2022


There’s a price shocker coming at the pumps.
Advertisement 2
Article content
Gas in Ontario, including the GTA, will go up 14 cents a litre overnight for customers filling up on Thursday, says Dan McTeague, the president of Canadians for Affordable Energy.
Article content
“So going from $1.65.9 (per litre) going to $1.79.9,” said McTeague adding the increase will affect the entire province except for northwestern Ontario, which gets its prices from the prairies market.
“That’s the highest level since August, 2022, almost two years ago,” he added.
Recommended from Editorial
McTeague said the reason for the price hike is that stations are switching over to summer-blend gasoline.
“Around this time of year prices go up to reflect the new blend of gasoline, which is more expensive to make,” he explained. “Butane is used in the winter, for gasoline, whereas in the summer it’s alkyaltes. Alkyaltes are extremely expensive.”
Advertisement 3
Article content
“In the winter you want your ignition to start quickly in cold temperatures, you uses volatile butane. You take that out in the summer. That’s a big difference. This is going to be around for awhile and it could get higher,” McTeague said.
McTeague also blamed the rise in gas prices in Canada on the carbon tax increase, the rising price of oil, and the weak Canadian dollar.
“It just makes a bad situation worse,” he said. “It’s just another brick in the wall, another load on the camel’s bank. The cost of denying our resources, blocking pipelines, is one of the most significant reasons why the Canadian dollar is so weak.”
Article content

CALGARY — A wildfire in west-central Alberta that was sparked by a natural gas pipeline rupture is under control, but an investigation into what caused the pipeline to break could take months or even years.
As of Wednesday morning, there was very little fire activity left in Yellowhead County, where a 10-hectare fire burned on Tuesday about 40 kilometres northwest of Edson.
“But for it to be considered extinguished, we’re going to have to hot spot,” said Caroline Charbonneau, area information co-ordinator with Alberta Forestry and Parks.
“That means we’ll have to dig into the ground, look and feel for hot spots, and then douse it with water. And that could take several days.”
ADVERTISEMENT
The fire on Tuesday, which occurred as much of Alberta is dealing with extremely dry early spring conditions, was sparked when a natural gas pipeline owned by TC Energy Corp. ruptured.
There were no injuries, and the fire was never a threat to any surrounding communities. The affected pipeline segment was isolated and shut in and there is no more gas leaking from the pipeline.
The Canada Energy Regulator had inspectors on site Wednesday to monitor the company’s response and the Transportation Safety Board is investigating the incident.
According to CER, there have been 12 natural gas pipeline ruptures in Canada since 2008, and Tuesday’s incident near Edson was the first rupture on that particular pipeline within that time period.
The 36-inch diameter pipe that ruptured is part of TC Energy’s NGTL pipeline system, which transports natural gas from Alberta and northeast B.C. to domestic and export markets. The system spans 24,631 kilometres and connects with TC Energy’s Canadian Mainline system, Foothills system and other third-party pipelines.
The NGTL pipeline system is like a web made up of different lines that have been developed in stages.
In 2022, there was a rupture on a separate part of the system that resulted in an explosion and fire near Fox Creek, Alta. There were no injuries.
A TSB investigation into that incident took more than 14 months, and concluded that the pipeline ruptured due to reduced pipe wall strength caused by external corrosion.
While the primary risk of a crude oil pipeline leak is an oil spill that harms the local ecosystem, natural gas pipeline ruptures can and do result in fires or explosions, said Bill Caram, executive director of the Pipeline Safety Trust, a U.S.-based non-profit organization.
“The chances are extremely high that a molecule of natural gas that enters a pipeline will go through that pipeline without a failure. Pipelines are quite safe, and when you look at incident rates compared to other modes of transportation like rail or truck, they are much less likely to have a failure,” Caram said.
“But what you don’t get a sense of by looking at the risks of pipelines in that way is how catastrophic a failure can be when it does happen.”
According to the TSB, there were 19 recorded incidences of fires related to pipelines in Canada between 2012 and 2022.
The TSB’s most recent report on pipeline transportation safety in Canada states that in 2022 there were 100 companies transporting either oil or gas or both in the federally regulated pipeline system, which includes approximately 19,950 km of oil pipelines and approximately 48,700 km of natural gas pipelines.
That year, there were 67 pipeline transportation accidents and incidents on federally regulated pipeline systems, according to the report.
That number was well below the 10-year average of 112 occurrences, and was also the lowest number of occurrences since 2019, when 52 pipeline accidents or incidents were recorded by the TSB.
The TSB defines a pipeline “accident” as an incident that results in a person being injured or killed, a fire or explosion, or significant damage to the pipeline affecting its operation.
Less severe pipeline events that involve the uncontrolled release of a commodity or a precautionary or emergency shutdown are classified by the TSB as “incidents.”
There have been no fatal accidents directly resulting from the operation of a federally regulated pipeline system since the inception of the TSB in 1990.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published April 17, 2024.
Companies in this story: (TSX:TRP)
Amanda Stephenson, The Canadian Press
Police say one former and one current employee of Air Canada are among the nine suspects that are facing charges in connection with the gold heist at Pearson International Airport last year.
At a news conference Wednesday on the one-year anniversary of the heist, police confirmed that five suspects were arrested and four others are facing charges in connection with the largest gold theft in Canadian history.
Police said the suspects face a total of 19 charges and Canada-wide warrants have been issued for the arrest of three of the suspects who have not yet been apprehended. All of the suspects arrested in connection with the heist have been released on bail, police confirmed in a news release issued Wednesday.
Peel Regional Police Chief Nishan Duraiappah said the heist was “carefully planned” by a “well-organized group of criminals.”
“This story is a sensational one and one which probably, we jokingly say, belongs in a Netflix series,” he said.
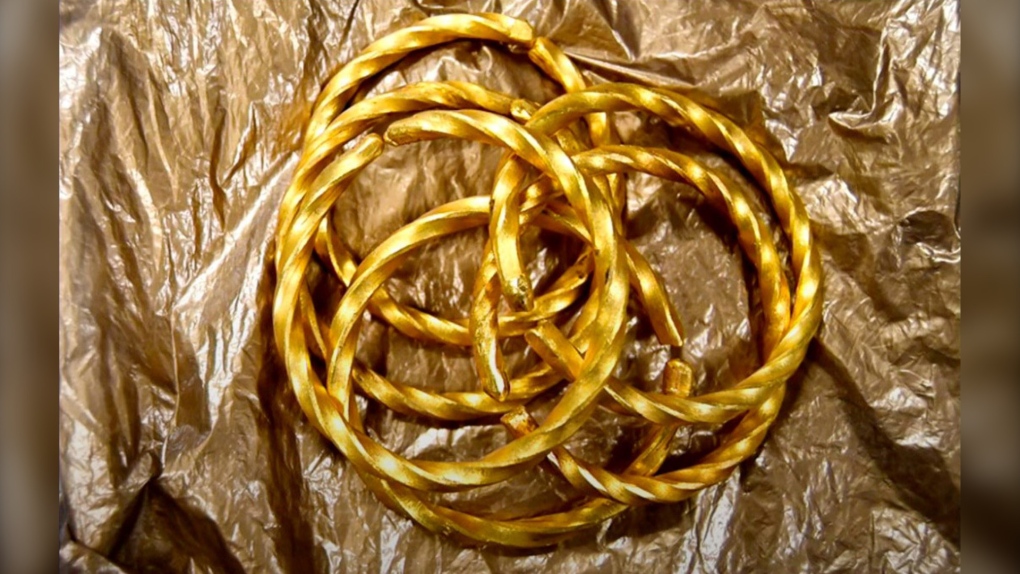
Police said 6,600 gold bars were stolen from Air Canada’s cargo facility on the evening of April 17, 2023 by a suspect who arrived at the warehouse in a five-tonne delivery truck.
The gold, along with about $2.5 million in foreign currency, had been shipped to Toronto from Zurich in the hull of an Air Canada plane and was offloaded to an Air Canada cargo facility shortly after the flight landed at Pearson Airport that afternoon.
Police allege that the suspect came into possession of the stolen gold and bank notes after presenting Air Canada personnel with a fraudulent airway bill.
“The airway bill was for a legitimate shipment of seafood that was picked up the day before,” Det.-Sgt. Mike Mavity, the major case manager for the joint investigation, dubbed Project 24K, told reporters on Wednesday.
“This duplicate airway bill was printed off from a printer within Air Canada cargo.”
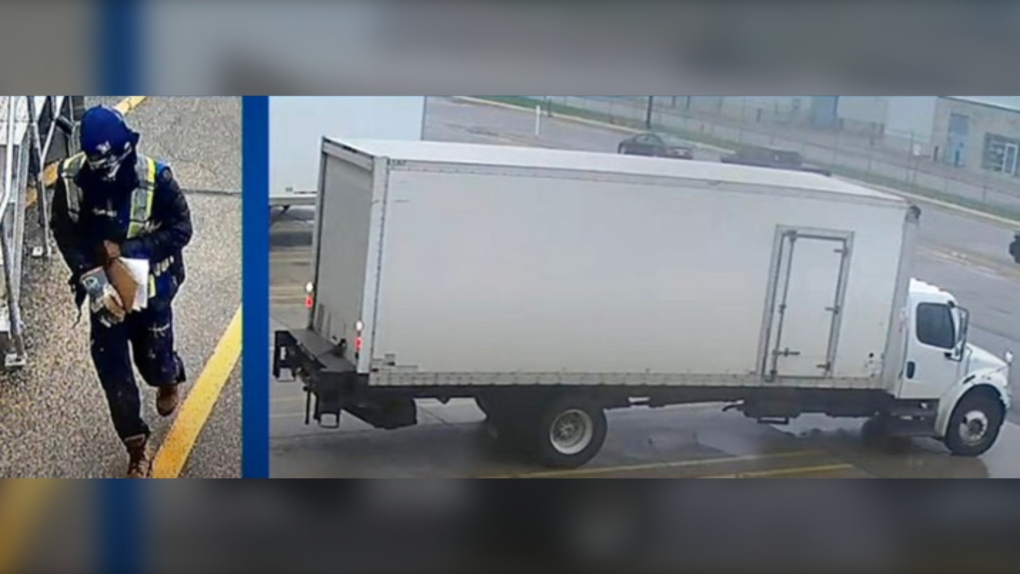


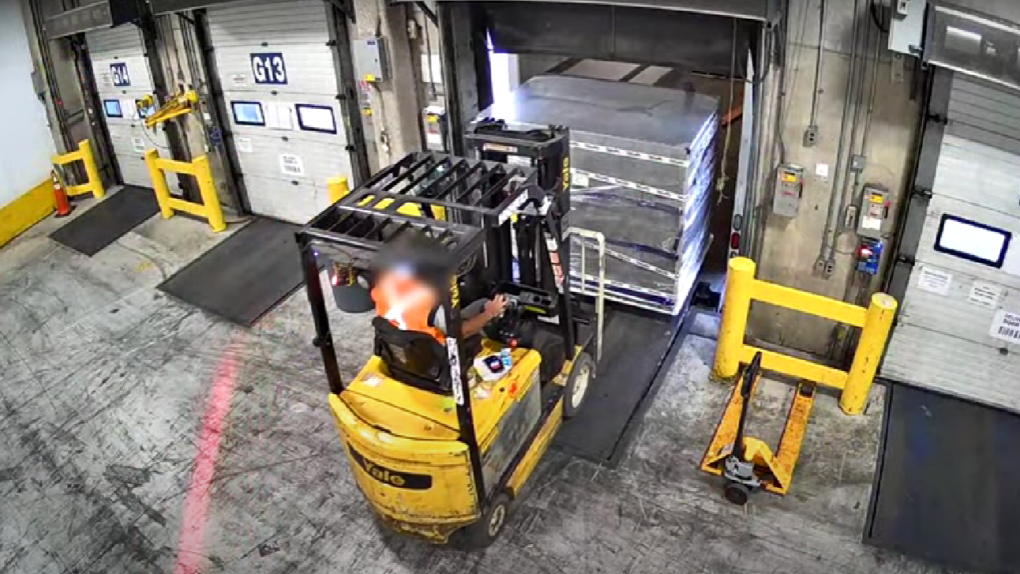
Brinks Canada, which was hired to provide security and logistics services for the transportation of the shipment, showed up at the facility a few hours later to pick up the items, police said.
According to investigators, when Air Canada employees tried to locate the container, they realized it was missing and quickly launched an internal investigation. Police were notified about the stolen goods shortly before 3 a.m. the following day, Mavity said.
An exhaustive investigation followed, police said, with officers reviewing video surveillance footage from 225 businesses and residences in an effort to track the path of the truck, which has since been recovered.
Mavity said that last summer, they identified 25-year-old Durante King-McLean as the driver of the truck but were unable to locate him.
In September 2023, Mavity said King-McLean was stopped in rental vehicle by Pennsylvania State Police near Chambersburg, Pennsylvania.
“After a brief foot chase, he was detained and troopers located 65 illegal firearms in the vehicle,” Mavity said Wednesday.
According to Mavity, investigators believe that the stolen gold was melted down and sold and the proceeds were used to purchase illegal guns for a firearms trafficking operation.
He said members of Project 24K have been liaising with the U.S. Alcohol, Tobacco, and Firearms Bureau (ATF) with respect to this aspect of the investigation.
Speaking at the news conference on Wednesday, a representative from the ATF said the law enforcement agency believes the 65 guns seized during the arrest of King-McLean were bound for Canada.
While King-McLean is currently in custody in the United States, he is now wanted on multiple charges in connection with the gold theft.
“We are alleging that some individuals who participated in this gold theft are also involved in aspects of this firearms trafficking,” Mavity added.


Two “debt lists” were found by investigators at separate locations during the investigation, police said.
“A common term in drug trafficking investigations, we believe these lists actually show where the money was distributed when the gold was sold by the suspects,” Mavity said.
He said the names on both lists are “consistent” and police are trying to identify all of those identified.


Police said one current Air Canada employee, identified as 54-year-old Brampton resident Parmpal Sidhu, has been charged with theft over $5,000 and conspiracy to commit an indictable offence. A Canada-wide warrant has been issued 31-year-old Simran Preet Panesar, who police said resigned from his position as a manager at Air Canada back in the summer.
“He has been known to us since early on in the investigation. He actually led a tour for Peel Regional Police before we knew his involvement,” Mavity said Wednesday.
He added that police have an idea where Panesar may be but did not elaborate on a possible location.
Mavity said he believes the suspects needed employees on the inside to carry out the heist.
“Because of their position within Air Canada, in my opinion, yeah they needed people inside Air Canada to facilitate this theft,” he said.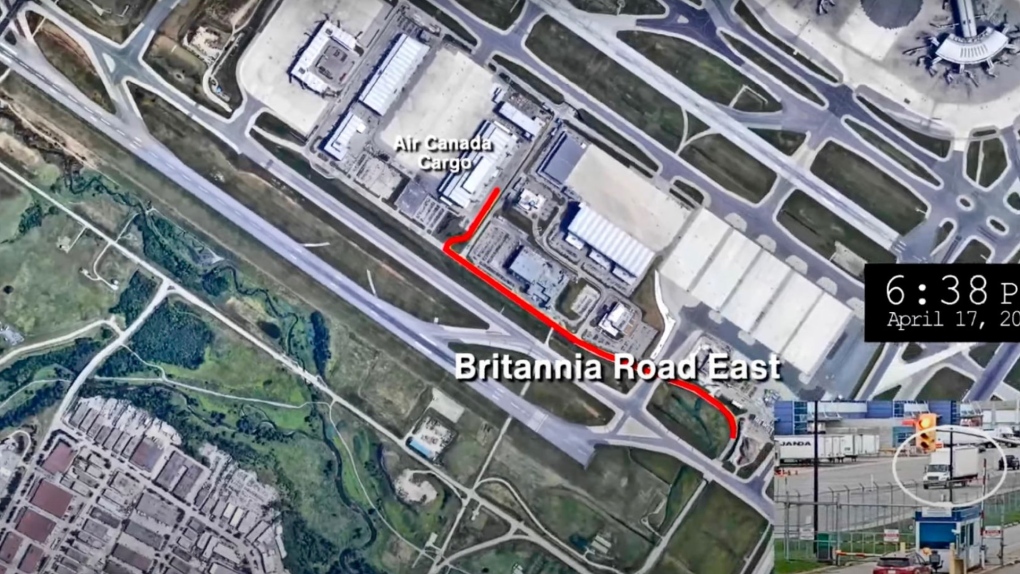





iPhone 15 Pro Desperado Mafia model launched at over ₹6.5 lakh- All details about this luxury iPhone from Caviar – HT Tech




Lululemon unveils Canada's official Olympic kit for the Paris games – National Post




Trump gave MAGA politicians permission to move left on abortion. Some are taking it. – Semafor




Anti-Trump Republican Larry Hogan navigates dangerous political terrain in pivotal Senate contest – Toronto Star




Astronomers discover Milky Way's heaviest known black hole – Xinhua




Venerable Video App Plex Emerges As FAST Favorite – Forbes
Traders Place Bets On $250 Oil – OilPrice.com
Toronto airport gold heist: Police announce nine arrests – CP24
Comments