WASHINGTON (AP) — Millions of people with private health insurance would be able to pick up over-the-counter methods like condoms, the “morning after” pill and birth control pills for free under a new rule the White House proposed on Monday.
Right now, health insurers must cover the cost of prescribed contraception, including prescription birth control or even condoms that doctors have issued a prescription for. But the new rule would expand that coverage, allowing millions of people on private health insurance to pick up free condoms, birth control pills, or “morning after” pills from local storefronts without a prescription.
The proposal comes days before Election Day, as Vice President Kamala Harris affixes her presidential campaign to a promise of expanding women’s health care access in the wake of the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision to undo nationwide abortion rights two years ago. Harris has sought to craft a distinct contrast from her Republican challenger, Donald Trump, who appointed some of the judges who issued that ruling.
“The proposed rule we announce today would expand access to birth control at no additional cost for millions of consumers,” Health and Human Services Secretary Xavier Becerra said in a statement. “Bottom line: women should have control over their personal health care decisions. And issuers and providers have an obligation to comply with the law.”
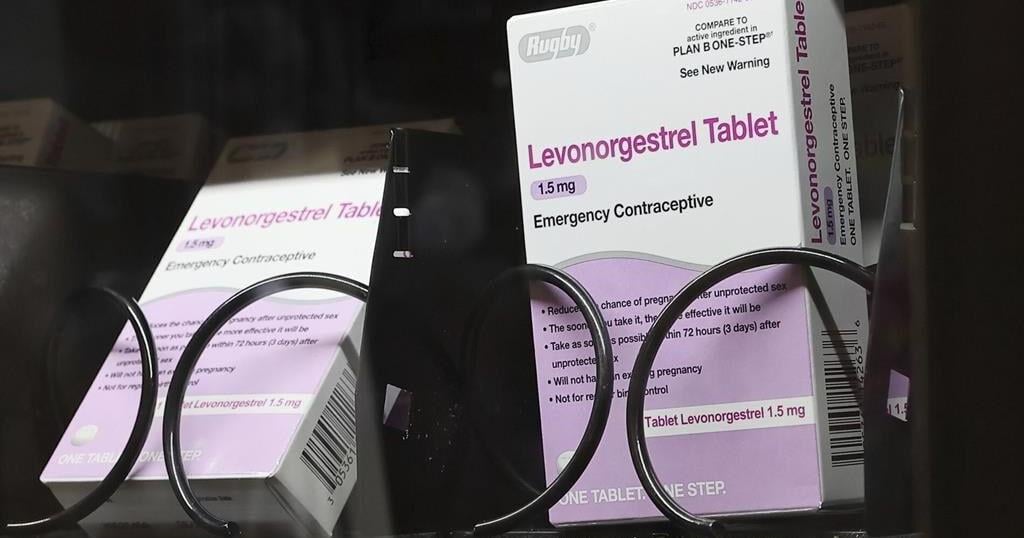
The emergency contraceptives that people on private insurance would be able to access without costs include levonorgestrel, a pill that needs to be taken immediately after sex to prevent pregnancy and is more commonly known by the brand name “Plan B.”
Without a doctor’s prescription, women may pay as much as $50 for a pack of the pills. And women who delay buying the medication in order to get a doctor’s prescription could jeopardize the pill’s effectiveness, since it is most likely to prevent a pregnancy within 72 hours after sex.
If implemented, the new rule would also require insurers to fully bear the cost of the once-a-day Opill, a new over-the-counter birth control pill that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved last year. A one-month supply of the pills costs $20.
Federal mandates for private health insurance to cover contraceptive care were first introduced with the Affordable Care Act, which required plans to pick up the cost of FDA-approved birth control that had been prescribed by a doctor as a preventative service.
The proposed rule would not impact those on Medicaid, the insurance program for the poorest Americans. States are largely left to design their own rules around Medicaid coverage for contraception, and few cover over-the-counter methods like Plan B or condoms.